Unveiling the Secrets of Antarctica: A Topographic Journey
Related Articles: Unveiling the Secrets of Antarctica: A Topographic Journey
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Secrets of Antarctica: A Topographic Journey. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Secrets of Antarctica: A Topographic Journey

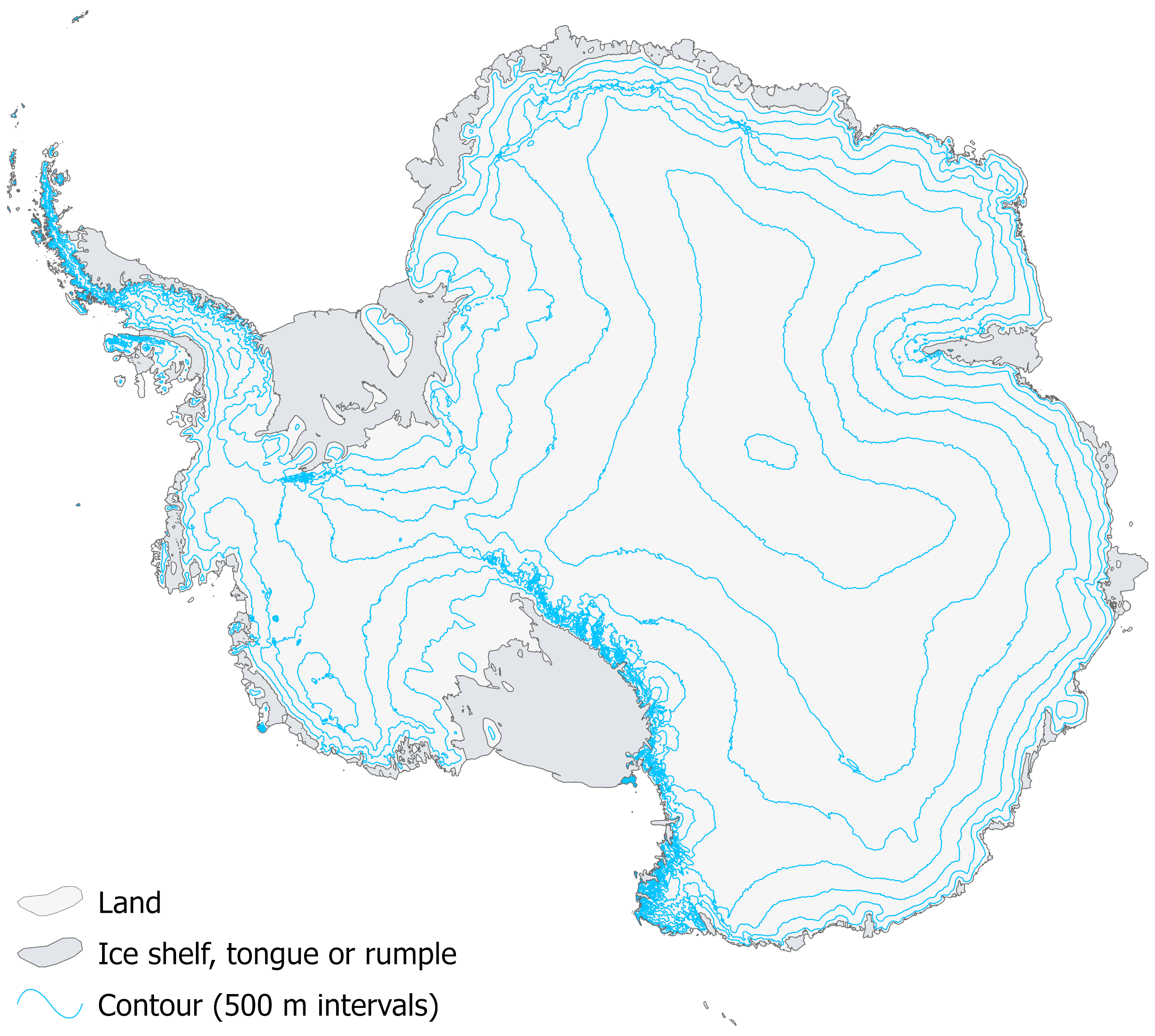
Antarctica, the Earth’s southernmost continent, is a land of stark beauty and extreme conditions. Its vast, icy landscape holds a wealth of scientific knowledge and captivating natural wonders. Understanding the topography of this frozen continent is crucial for navigating its challenges and unlocking its secrets. This exploration delves into the world of Antarctic topographic maps, revealing their significance and the insights they provide.
The Importance of Topographic Maps in Antarctic Exploration
Topographic maps, which depict the physical features of a region, are indispensable tools for navigating and understanding Antarctica. They serve as visual guides, providing information on:
- Elevation: Antarctic topographic maps illustrate the continent’s dramatic elevation changes, ranging from the vast ice sheets to the towering mountain ranges. This data is vital for planning expeditions, understanding the flow of glaciers, and analyzing the impact of climate change on the continent’s ice mass.
- Landforms: These maps showcase the diverse landforms of Antarctica, including mountains, valleys, glaciers, ice shelves, and coastal features. This information is critical for identifying potential research sites, assessing the risk of crevasses and other hazards, and understanding the geological history of the continent.
- Geographic Coordinates: Topographic maps provide precise geographic coordinates, allowing researchers and explorers to pinpoint their location and navigate effectively. This is especially crucial in a region where satellite signals can be unreliable and visibility is often limited.
- Environmental Conditions: Topographic maps can incorporate data on environmental conditions, such as wind patterns, temperature variations, and precipitation, providing valuable insights for planning expeditions and conducting scientific research.
Exploring the Features of Antarctic Topographic Maps
Antarctic topographic maps are characterized by several key features:
- Contour Lines: These lines connect points of equal elevation, providing a visual representation of the terrain’s undulations. The closer the contour lines, the steeper the slope.
- Elevation Data: Topographic maps often include numerical elevation data, allowing for precise measurements of height and depth.
- Geographic Grid: A grid system based on latitude and longitude helps locate specific points on the map.
- Symbols and Legends: These elements represent various features, such as glaciers, mountains, lakes, and research stations, facilitating understanding and interpretation.
- Scale: The scale of the map determines the level of detail and the area covered. Large-scale maps provide detailed information for local exploration, while small-scale maps offer a broader overview of the continent.
The Evolution of Antarctic Topographic Mapping
The mapping of Antarctica has undergone a significant evolution, driven by advancements in technology and the increasing need for accurate data:
- Early Explorations: Early Antarctic expeditions relied on rudimentary methods, such as visual observations and compass readings, to create basic maps. These maps were often inaccurate and lacked detailed information.
- Aerial Photography: The advent of aerial photography in the early 20th century revolutionized Antarctic mapping. Aerial photographs provided a comprehensive view of the continent, allowing for more accurate and detailed mapping.
- Satellite Imagery: The launch of satellites in the 1960s ushered in a new era of Antarctic mapping. Satellite imagery offers high-resolution images of the continent, enabling the creation of highly accurate and detailed topographic maps.
- Digital Elevation Models (DEMs): The development of DEMs, which represent the terrain’s elevation in a digital format, has further enhanced Antarctic mapping. DEMs allow for the creation of three-dimensional models of the continent, providing a more comprehensive understanding of its topography.
The Benefits of Antarctic Topographic Maps
Antarctic topographic maps play a crucial role in various aspects of research and exploration:
- Scientific Research: Topographic maps provide essential information for scientists studying the continent’s geology, glaciology, climate, and biology. They help researchers identify potential research sites, analyze the flow of glaciers, and assess the impact of climate change on the continent’s ice mass.
- Expedition Planning: These maps are invaluable for planning expeditions, ensuring safe navigation, and identifying potential hazards. They help expedition leaders determine the best routes, assess the risks of crevasses and other hazards, and plan for logistical challenges.
- Environmental Monitoring: Topographic maps contribute to monitoring the changing environment of Antarctica, providing valuable data on glacial retreat, sea ice formation, and the impact of climate change on the continent’s ecosystem.
- Conservation Efforts: Topographic maps help identify areas of ecological significance and support conservation efforts by providing data on sensitive habitats, rare species, and potential threats to the Antarctic environment.
FAQs about Antarctic Topographic Maps
1. How can I access Antarctic topographic maps?
Antarctic topographic maps are available from various sources, including:
- National Mapping Agencies: Organizations like the United States Geological Survey (USGS), the British Antarctic Survey (BAS), and the Australian Antarctic Division (AAD) provide topographic maps of Antarctica.
- Scientific Institutions: Research institutions involved in Antarctic research often make their topographic maps available to the public.
- Online Databases: Several online databases, such as the Antarctic Digital Database (ADD) and the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC), offer access to digital topographic maps of Antarctica.
2. What are the different types of Antarctic topographic maps?
Antarctic topographic maps come in various types, depending on their purpose and scale:
- General-purpose maps: These maps provide a broad overview of the continent’s topography, including major landforms, elevation changes, and research stations.
- Regional maps: These maps focus on specific areas of Antarctica, providing more detailed information on local topography and features.
- Glacial maps: These maps focus on glaciers, ice sheets, and ice shelves, providing data on their flow, thickness, and changes over time.
- Geological maps: These maps depict the geological formations and structures of Antarctica, providing insights into the continent’s history and mineral resources.
3. What are the challenges in mapping Antarctica?
Mapping Antarctica presents several challenges:
- Extreme weather conditions: The harsh weather conditions, including extreme cold, strong winds, and limited daylight, make mapping difficult and dangerous.
- Remote and inaccessible terrain: The vast and remote nature of Antarctica makes access challenging, requiring specialized equipment and logistical planning.
- Ice movement: The constant movement of glaciers and ice shelves can distort measurements and create inaccuracies in maps.
- Technological limitations: Mapping technologies are constantly evolving, and limitations in data collection and processing can affect the accuracy and detail of maps.
4. How are topographic maps used in climate change research?
Topographic maps play a crucial role in climate change research by providing data on:
- Glacial retreat: Maps can track the retreat of glaciers and ice shelves, providing evidence of climate change’s impact on the continent’s ice mass.
- Sea level rise: Changes in the ice sheet’s volume and flow can contribute to sea level rise, and topographic maps provide data on these changes.
- Ocean currents: Topographic maps can help understand the influence of ocean currents on the Antarctic ice sheet and its contribution to climate change.
Tips for Using Antarctic Topographic Maps
- Understand the scale and projection: Pay attention to the map’s scale and projection, which can affect the accuracy of distances and areas.
- Use a legend and symbols: Familiarize yourself with the map’s legend and symbols to understand the different features represented.
- Consider the date of the map: Keep in mind that topographic maps can become outdated due to changes in the landscape, especially in a dynamic environment like Antarctica.
- Use multiple sources of information: Combine topographic maps with other sources of information, such as satellite imagery and scientific reports, for a more comprehensive understanding.
Conclusion
Antarctic topographic maps are essential tools for navigating and understanding the unique and challenging environment of this frozen continent. They provide a wealth of information on the continent’s topography, landforms, environmental conditions, and geological history. From planning expeditions to conducting scientific research, these maps play a vital role in unlocking the secrets of Antarctica and contributing to our understanding of the Earth’s climate system. As technology continues to advance, Antarctic topographic mapping will continue to evolve, providing increasingly accurate and detailed data to support research, exploration, and conservation efforts in this extraordinary region.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Secrets of Antarctica: A Topographic Journey. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!