Unveiling the Diversity of Mexico: A Comprehensive Guide to its Geographic Regions
Related Articles: Unveiling the Diversity of Mexico: A Comprehensive Guide to its Geographic Regions
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Diversity of Mexico: A Comprehensive Guide to its Geographic Regions. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Diversity of Mexico: A Comprehensive Guide to its Geographic Regions
Mexico, a vibrant tapestry of cultures, landscapes, and traditions, is geographically diverse, with distinct regions boasting unique characteristics and attractions. Understanding the map of Mexico’s regions is crucial for any traveler or individual seeking to delve deeper into the country’s rich heritage and natural wonders.
The North: Where Desert Meets Mountains
The northern region of Mexico, often referred to as "El Norte," encompasses states like Baja California, Sonora, Chihuahua, and Coahuila. This vast expanse is characterized by its arid climate, rugged mountain ranges, and vast deserts. The region’s landscape is dominated by the Sierra Madre Occidental, a majestic mountain range that stretches from the U.S. border to the Pacific coast. The Sonoran Desert, known for its unique flora and fauna, lies in the west, while the Chihuahuan Desert, the largest in North America, stretches across the central and eastern parts of the region.
Key Features of the North:
- Arid Climate: The region experiences low rainfall and high temperatures, particularly in the desert areas.
- Mountainous Terrain: The Sierra Madre Occidental and other mountain ranges create diverse landscapes, from high peaks to deep canyons.
- Rich Indigenous Culture: The region is home to numerous indigenous communities, including the Tarahumara, Yaqui, and Seri, who have maintained their traditions and languages.
- Mining and Agriculture: Mining, particularly for silver and copper, has historically been a significant industry. Agriculture, focused on crops like wheat, corn, and beans, is also a vital part of the economy.
- Tourist Attractions: The region offers a diverse range of attractions, from the historic colonial cities of Chihuahua and Durango to the stunning landscapes of Copper Canyon, a network of canyons even larger than the Grand Canyon.
The Central Mexico Plateau: The Heart of the Nation
The Central Mexico Plateau, also known as the Mexican Altiplano, is the geographical and cultural heart of Mexico. It encompasses states like Mexico City, Guanajuato, Jalisco, and Michoacán, and is characterized by its high elevation, volcanic landscapes, and fertile valleys. The region is home to some of Mexico’s most iconic landmarks, including the Valley of Mexico, where the Aztec civilization thrived, and the majestic Popocatépetl and Iztaccíhuatl volcanoes.
Key Features of the Central Mexico Plateau:
- High Elevation: The region lies at a high altitude, resulting in a cooler climate than the coastal areas.
- Volcanic Landscape: The region is dotted with volcanoes, some of which are still active, creating dramatic landscapes and fertile soil.
- Rich History and Culture: The Central Mexico Plateau is the cradle of Mesoamerican civilizations, with numerous archaeological sites and historical cities.
- Industrial and Economic Hub: The region is a major industrial and economic center, home to Mexico City, the capital, and other important cities.
- Tourist Attractions: The region boasts a wealth of attractions, from the ancient pyramids of Teotihuacan and the colonial city of Guanajuato to the vibrant cultural scene of Mexico City.
The Gulf Coast: Where History Meets Tropical Charm
The Gulf Coast region, known as the "Costa del Golfo," stretches along the Gulf of Mexico from Tamaulipas to Veracruz. This region is characterized by its humid tropical climate, lush vegetation, and coastal plains. It is home to a diverse array of ecosystems, including mangrove swamps, rainforests, and coastal lagoons.
Key Features of the Gulf Coast:
- Tropical Climate: The region enjoys warm temperatures year-round, with high humidity and frequent rainfall.
- Coastal Plains and Lagoons: The Gulf Coast is characterized by flat, fertile plains and numerous lagoons, providing rich biodiversity and scenic beauty.
- Oil and Gas Production: The region is a major oil and gas producing area, with significant economic activity related to these industries.
- Rich History and Culture: The Gulf Coast played a crucial role in Mexico’s colonial history, with cities like Veracruz and Tampico serving as important ports.
- Tourist Attractions: The region offers a range of attractions, from the ancient Mayan ruins of El Tajín to the vibrant beaches and bustling cities of Veracruz and Cancún.
The Pacific Coast: A Tapestry of Landscapes and Cultures
The Pacific Coast region, known as the "Costa del Pacífico," stretches along the Pacific Ocean from Baja California to Chiapas. This vast region encompasses diverse landscapes, from the arid deserts of Baja California to the lush rainforests of Chiapas. It is home to a rich tapestry of cultures, including indigenous communities, colonial cities, and modern resorts.
Key Features of the Pacific Coast:
- Diverse Landscapes: The region features a wide range of landscapes, including beaches, deserts, mountains, and rainforests.
- Mild Climate: The Pacific Coast enjoys a mild climate, with warm temperatures and moderate rainfall.
- Agriculture and Fishing: Agriculture, particularly the cultivation of fruits and vegetables, and fishing are important industries in the region.
- Tourist Attractions: The Pacific Coast is a popular tourist destination, offering a wide range of attractions, from the beaches of Acapulco and Puerto Vallarta to the ancient Mayan ruins of Palenque and the colonial city of San Miguel de Allende.
The Yucatan Peninsula: A Land of Ancient Wonders
The Yucatan Peninsula, located in southeastern Mexico, is a region renowned for its ancient Mayan civilization and its unique natural environment. The peninsula is characterized by its flat, limestone terrain, cenotes (natural sinkholes filled with water), and tropical climate. It is home to numerous Mayan archaeological sites, including Chichén Itzá, Uxmal, and Tulum.
Key Features of the Yucatan Peninsula:
- Flat, Limestone Terrain: The peninsula is characterized by a flat, limestone terrain, dotted with cenotes, which are a unique feature of the region.
- Tropical Climate: The Yucatan Peninsula enjoys a hot, humid tropical climate.
- Mayan Heritage: The peninsula is home to numerous Mayan archaeological sites, showcasing the region’s rich history and culture.
- Tourist Attractions: The Yucatan Peninsula is a major tourist destination, attracting visitors from around the world to its archaeological sites, beaches, and cenotes.
Understanding the Importance of Regions
The regional divisions of Mexico offer a valuable framework for understanding the country’s diverse geography, history, culture, and economy. Each region possesses unique characteristics, from its landscape and climate to its cultural traditions and economic activities. Understanding these regional differences is crucial for appreciating the depth and complexity of Mexican society and for engaging with the country’s rich heritage.
FAQs by Regions of Mexico
Northern Region:
-
Q: What are the most popular tourist destinations in the North?
- A: Some of the most popular tourist destinations in the North include Copper Canyon, Chihuahua City, and the city of Durango.
-
Q: What are the major industries in the North?
- A: The North is known for its mining industry, particularly for silver and copper. Agriculture, focusing on wheat, corn, and beans, is also a significant industry.
-
Q: What are the major cultural influences in the North?
- A: The North is home to numerous indigenous communities, including the Tarahumara, Yaqui, and Seri, who have maintained their traditions and languages.
Central Mexico Plateau:
-
Q: What are the most popular tourist destinations on the Central Mexico Plateau?
- A: The Central Mexico Plateau is home to numerous popular tourist destinations, including Mexico City, Teotihuacan, Guanajuato, and the Popocatépetl and Iztaccíhuatl volcanoes.
-
Q: What are the major industries on the Central Mexico Plateau?
- A: The Central Mexico Plateau is a major industrial and economic hub, with industries ranging from manufacturing and tourism to finance and technology.
-
Q: What are the major cultural influences on the Central Mexico Plateau?
- A: The Central Mexico Plateau is the cradle of Mesoamerican civilizations, with a rich cultural heritage influenced by the Aztec, Toltec, and other ancient civilizations.
Gulf Coast:
-
Q: What are the most popular tourist destinations on the Gulf Coast?
- A: The Gulf Coast is known for its beaches, with popular destinations including Veracruz, Cancún, and Playa del Carmen. The ancient Mayan ruins of El Tajín are also a significant attraction.
-
Q: What are the major industries on the Gulf Coast?
- A: The Gulf Coast is a major oil and gas producing area, with significant economic activity related to these industries. Tourism is also a significant industry.
-
Q: What are the major cultural influences on the Gulf Coast?
- A: The Gulf Coast played a crucial role in Mexico’s colonial history, with a blend of indigenous, Spanish, and African cultural influences.
Pacific Coast:
-
Q: What are the most popular tourist destinations on the Pacific Coast?
- A: The Pacific Coast is home to numerous popular tourist destinations, including Acapulco, Puerto Vallarta, and the beaches of Baja California. The colonial city of San Miguel de Allende and the ancient Mayan ruins of Palenque are also major attractions.
-
Q: What are the major industries on the Pacific Coast?
- A: The Pacific Coast is known for its agriculture, particularly the cultivation of fruits and vegetables, and fishing. Tourism is also a significant industry.
-
Q: What are the major cultural influences on the Pacific Coast?
- A: The Pacific Coast is a diverse region, with a blend of indigenous, Spanish, and modern influences.
Yucatan Peninsula:
-
Q: What are the most popular tourist destinations on the Yucatan Peninsula?
- A: The Yucatan Peninsula is a major tourist destination, known for its Mayan archaeological sites, including Chichén Itzá, Uxmal, and Tulum. The region’s cenotes and beaches are also popular attractions.
-
Q: What are the major industries on the Yucatan Peninsula?
- A: Tourism is the most important industry on the Yucatan Peninsula, followed by agriculture and fishing.
-
Q: What are the major cultural influences on the Yucatan Peninsula?
- A: The Yucatan Peninsula is deeply rooted in Mayan culture, with a rich history and traditions that continue to influence the region today.
Tips by Regions of Mexico
Northern Region:
- Tip 1: Pack for a dry climate, with light clothing and a hat for sun protection.
- Tip 2: Explore the unique culture of the Tarahumara people in the Sierra Madre Occidental.
- Tip 3: Take a scenic train ride through Copper Canyon, experiencing the grandeur of the landscape.
Central Mexico Plateau:
- Tip 1: Dress in layers, as temperatures can vary between day and night.
- Tip 2: Visit the historic colonial cities of Guanajuato and San Miguel de Allende.
- Tip 3: Immerse yourself in the vibrant cultural scene of Mexico City.
Gulf Coast:
- Tip 1: Be prepared for hot and humid weather, with light clothing and sunscreen.
- Tip 2: Explore the ancient Mayan ruins of El Tajín and the vibrant city of Veracruz.
- Tip 3: Relax on the beaches of Cancún and Playa del Carmen, enjoying the turquoise waters.
Pacific Coast:
- Tip 1: Pack for a mild climate, with comfortable clothing for both warm days and cool evenings.
- Tip 2: Visit the historic city of San Miguel de Allende, known for its architecture and art scene.
- Tip 3: Explore the ancient Mayan ruins of Palenque, hidden in the lush rainforest of Chiapas.
Yucatan Peninsula:
- Tip 1: Pack for a hot and humid climate, with light clothing and insect repellent.
- Tip 2: Explore the Mayan archaeological sites of Chichén Itzá, Uxmal, and Tulum.
- Tip 3: Swim in the refreshing waters of the cenotes, natural sinkholes filled with water.
Conclusion by Regions of Mexico
The map of Mexico’s regions is a valuable tool for understanding the country’s rich diversity and complexity. Each region possesses unique characteristics, from its landscape and climate to its cultural traditions and economic activities. By exploring these regions, travelers and individuals can gain a deeper appreciation for the depth and richness of Mexican culture and heritage. Whether it’s the arid landscapes of the North, the historic cities of the Central Mexico Plateau, the tropical beaches of the Gulf Coast, the diverse landscapes of the Pacific Coast, or the ancient wonders of the Yucatan Peninsula, Mexico offers a wealth of experiences for those who seek to discover its true essence.
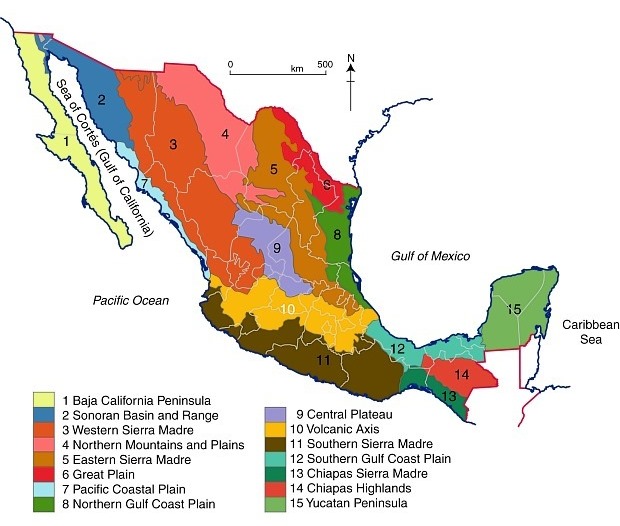






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Diversity of Mexico: A Comprehensive Guide to its Geographic Regions. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!