Unveiling the Cascadia Subduction Zone: A Guide to the Volcanoes Shaping the Pacific Northwest
Related Articles: Unveiling the Cascadia Subduction Zone: A Guide to the Volcanoes Shaping the Pacific Northwest
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Cascadia Subduction Zone: A Guide to the Volcanoes Shaping the Pacific Northwest. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Cascadia Subduction Zone: A Guide to the Volcanoes Shaping the Pacific Northwest

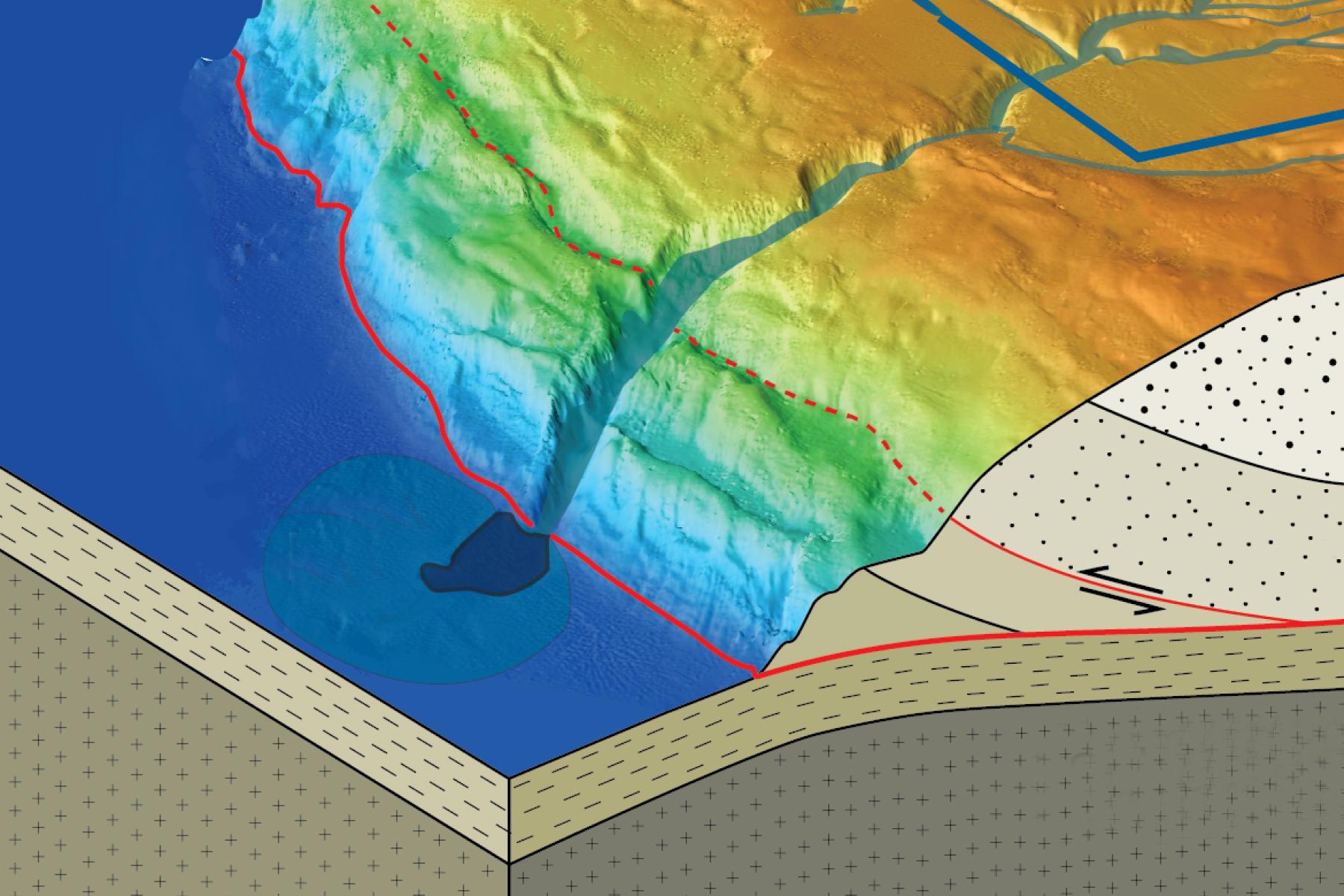
The Pacific Northwest of North America is a region of breathtaking beauty, characterized by towering forests, pristine lakes, and dramatic coastal landscapes. However, beneath this idyllic surface lies a powerful geological force: the Cascadia Subduction Zone. This zone, stretching from northern California to Vancouver Island, is responsible for shaping the region’s landscape, influencing its climate, and posing a significant natural hazard in the form of volcanic eruptions and earthquakes.
Understanding the Cascadia Subduction Zone
The Cascadia Subduction Zone is a prime example of a convergent plate boundary, where the Juan de Fuca Plate, a smaller oceanic plate, is being forced beneath the North American Plate. This process, known as subduction, is a slow and continuous movement, but it generates immense pressure and heat, leading to the formation of volcanoes and the potential for devastating earthquakes.
The Cascade Volcanic Arc: A Chain of Fire
As the Juan de Fuca Plate dives beneath the North American Plate, it melts, creating magma that rises to the surface, forming a chain of volcanoes known as the Cascade Volcanic Arc. This arc extends from northern California to southwestern British Columbia, encompassing some of the most iconic peaks in the Pacific Northwest, including Mount Rainier, Mount Hood, and Mount Shasta.
Exploring the Cascade Volcanoes Map
A Cascade Volcanoes map is an essential tool for understanding the distribution and characteristics of these volcanic giants. It provides a visual representation of the location, type, and potential hazards associated with each volcano. The map typically includes:
- Volcano Locations: The precise coordinates of each volcano are clearly marked, allowing for easy identification and analysis.
- Volcano Types: Different types of volcanoes are categorized and depicted, such as stratovolcanoes, shield volcanoes, and lava domes.
- Elevation and Prominence: The height and prominence of each volcano are often indicated, providing a sense of scale and relative size.
- Last Eruption Dates: The dates of the most recent eruptions are typically included, highlighting the active nature of these volcanoes.
- Potential Hazards: The map may also indicate potential hazards associated with each volcano, such as lava flows, pyroclastic flows, and ashfall.
Beyond the Map: Unveiling the Significance
The Cascade Volcanoes map is not merely a static visual representation. It serves as a crucial tool for scientists, researchers, and emergency planners, aiding in the following ways:
- Volcanic Monitoring: The map provides a framework for monitoring volcanic activity, allowing scientists to track changes in volcanic behavior and issue timely warnings.
- Hazard Assessment: By analyzing the map, researchers can assess the potential risks associated with each volcano, including the likelihood of eruptions and the potential impact on surrounding communities.
- Emergency Planning: The map plays a vital role in emergency preparedness, providing valuable information for developing evacuation plans, establishing warning systems, and allocating resources.
- Educational Tool: The map serves as a valuable educational resource, fostering public awareness about the risks and impacts of volcanic activity.
FAQs about the Cascade Volcanoes Map
Q: What are the most active volcanoes in the Cascade Range?
A: Mount St. Helens, Mount Rainier, and Mount Hood are considered the most active volcanoes in the Cascade Range. However, all volcanoes in the range pose a potential threat and are actively monitored.
Q: What are the major hazards associated with Cascade volcanoes?
A: The primary hazards associated with Cascade volcanoes include:
- Lava Flows: Molten rock flowing from a volcanic vent can cause significant damage to infrastructure and vegetation.
- Pyroclastic Flows: Rapidly moving mixtures of hot gas, ash, and rock fragments can be extremely destructive and deadly.
- Ashfall: Volcanic ash can disrupt transportation, contaminate water supplies, and cause respiratory problems.
- Lahars: Mudflows triggered by volcanic eruptions can cause significant flooding and damage.
Q: How can I stay informed about volcanic activity in the Cascades?
A: The United States Geological Survey (USGS) provides real-time updates and information on volcanic activity in the Cascade Range. You can visit their website or follow their social media channels for the latest updates.
Q: Are there any resources available for learning more about Cascade volcanoes?
A: Numerous resources are available for learning more about Cascade volcanoes, including:
- USGS Volcano Hazards Program: Provides comprehensive information on volcanic activity and hazards.
- National Park Service: Offers educational resources and visitor information for national parks with Cascade volcanoes.
- Cascade Volcano Observatory: A USGS research center dedicated to studying and monitoring volcanoes in the Cascade Range.
Tips for Using the Cascade Volcanoes Map
- Familiarize yourself with the map’s symbols and legends.
- Locate your home or community on the map.
- Identify the closest volcanoes to your location.
- Research the potential hazards associated with each volcano.
- Develop a plan for what to do in case of a volcanic eruption.
- Stay informed about volcanic activity through reliable sources.
Conclusion
The Cascade Volcanoes map is a powerful tool for understanding the geological forces shaping the Pacific Northwest. It provides a visual representation of the region’s volcanic landscape, highlighting the potential hazards and the importance of monitoring and preparedness. By utilizing this map and staying informed about volcanic activity, we can better understand and mitigate the risks associated with these powerful natural forces.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Cascadia Subduction Zone: A Guide to the Volcanoes Shaping the Pacific Northwest. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!