Unraveling the Tapestry of the American West Coast: A Geographical Journey
Related Articles: Unraveling the Tapestry of the American West Coast: A Geographical Journey
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Tapestry of the American West Coast: A Geographical Journey. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Tapestry of the American West Coast: A Geographical Journey

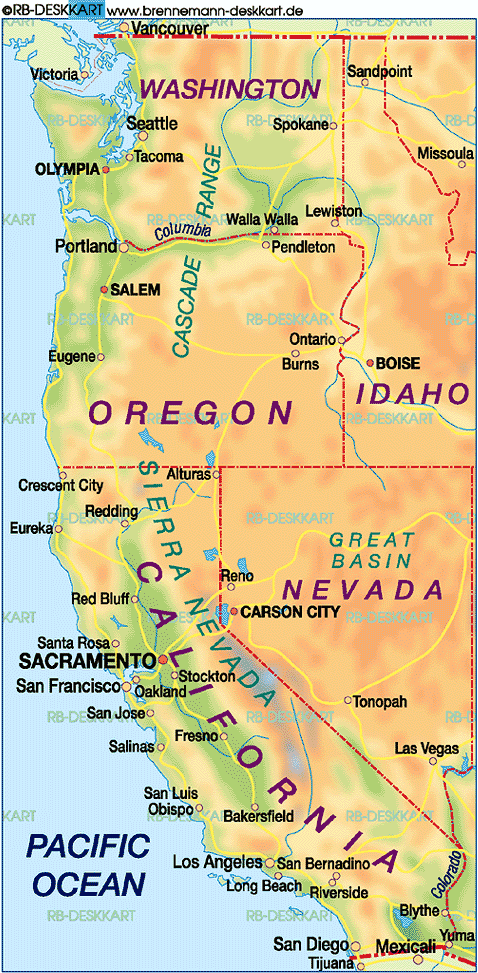
The West Coast of the United States, a region of unparalleled beauty and diverse landscapes, stretches from the rugged peaks of the Alaskan Panhandle south to the sun-drenched shores of Baja California. This vast expanse, encompassing the states of Washington, Oregon, California, and portions of Alaska, is a dynamic blend of coastal wonders, towering mountains, arid deserts, and vibrant cities. Understanding the geography of this region is crucial for comprehending its history, culture, and economic significance.
The West Coast’s Geographical Tapestry: A Detailed Exploration
1. The Pacific Coast: A Shoreline of Variety
The Pacific Ocean, a vast body of water, defines the West Coast’s identity. This coastline, stretching over 2,000 miles, is a tapestry of diverse landscapes:
-
The Pacific Northwest: This region, encompassing Washington and Oregon, is known for its lush forests, dramatic mountain ranges, and rugged coastlines. The Cascade Mountains, a volcanic chain, dominate the landscape, with Mount Rainier, the highest peak in the Cascade Range, towering over the region. The Pacific Northwest also boasts numerous fjords, inlets, and islands, showcasing the region’s unique geological history.
-
California’s Coast: California’s coastline is a mosaic of diverse landscapes, ranging from the towering redwoods of the Redwood National Park to the dramatic cliffs of Big Sur and the sandy beaches of Southern California. The San Andreas Fault, a major geological feature, runs along the coast, contributing to the region’s seismic activity.
-
Alaska’s Panhandle: The Alaskan Panhandle, a narrow strip of land bordering the Pacific Ocean, is a region of breathtaking beauty. Glaciers, fjords, and towering mountains create a dramatic landscape, showcasing the power of nature.
2. Mountains and Valleys: Shaping the West Coast’s Topography
Mountains and valleys are integral to the West Coast’s topography, shaping its climate, ecosystems, and human settlements:
-
The Cascade Range: This volcanic mountain range, stretching from British Columbia through Washington and Oregon, dominates the Pacific Northwest landscape. The Cascade Range’s volcanic activity has shaped the region’s geography, creating fertile valleys and stunning volcanic peaks like Mount Hood and Mount St. Helens.
-
The Sierra Nevada: This mountain range, located in eastern California, is renowned for its granite peaks, towering sequoia trees, and deep valleys. The Sierra Nevada is a source of fresh water for California, with the Sierra Nevada snowpack providing vital water resources to the state.
-
The Coast Ranges: These mountains, running parallel to the Pacific Coast, extend from the San Francisco Bay Area to the southern border of California. The Coast Ranges are characterized by rolling hills, redwood forests, and fertile valleys, contributing to the region’s agricultural productivity.
-
The Great Basin: This vast region, located in eastern Oregon, Nevada, Utah, and Idaho, is a high-desert plateau characterized by rugged mountains, dry valleys, and salt flats. The Great Basin is a unique ecological region, home to diverse plant and animal life adapted to arid conditions.
3. Rivers and Lakes: The West Coast’s Vital Waterways
Rivers and lakes are vital to the West Coast’s ecosystem and human settlements:
-
The Columbia River: This major river, flowing from British Columbia through Washington and Oregon, is a vital waterway for transportation, hydroelectric power, and salmon fishing. The Columbia River Gorge, a dramatic canyon carved by the river, is a renowned scenic area.
-
The Sacramento and San Joaquin Rivers: These rivers, flowing through California’s Central Valley, are essential for agriculture, transportation, and water supply. The Sacramento-San Joaquin Delta, a vast network of waterways, is a vital ecosystem and a source of drinking water for millions of Californians.
-
Lake Tahoe: Located on the border of California and Nevada, Lake Tahoe is a stunning alpine lake known for its crystal-clear waters, breathtaking scenery, and recreational opportunities.
4. Climate and Ecosystems: A Diverse Range
The West Coast’s diverse geography creates a range of climates and ecosystems:
-
The Pacific Northwest: Known for its temperate rainforest climate, the Pacific Northwest experiences mild, wet winters and cool, dry summers. The region’s lush forests, teeming with diverse plant and animal life, are a testament to its unique climate.
-
California: California’s climate is diverse, ranging from the Mediterranean climate of the coast to the arid climate of the deserts. The state’s coastline experiences mild, wet winters and warm, dry summers, while the interior is characterized by hot, dry summers and cold winters.
-
Alaska’s Panhandle: The Alaskan Panhandle experiences a subarctic climate, characterized by long, cold winters and short, cool summers. The region’s glaciers, fjords, and mountains create a unique ecosystem, home to diverse plant and animal life adapted to the harsh climate.
5. Human Settlements: A Tapestry of Cities and Towns
The West Coast is home to a diverse array of cities and towns, each with its own unique character and history:
-
Seattle: Located on the Puget Sound, Seattle is a major port city known for its vibrant arts and culture scene, its booming tech industry, and its proximity to the natural beauty of the Pacific Northwest.
-
Portland: Located on the Willamette River, Portland is a city known for its thriving culinary scene, its commitment to sustainability, and its vibrant arts and culture scene.
-
San Francisco: Situated on the San Francisco Peninsula, San Francisco is a global city known for its iconic Golden Gate Bridge, its diverse neighborhoods, and its role as a center for technology, finance, and culture.
-
Los Angeles: Located in Southern California, Los Angeles is a sprawling metropolis known for its Hollywood film industry, its diverse ethnic communities, and its beaches.
-
San Diego: Located on the Pacific coast of Southern California, San Diego is a city known for its beautiful beaches, its mild climate, and its thriving military presence.
The Importance of Understanding the West Coast’s Geography
Understanding the West Coast’s geography is crucial for comprehending its history, culture, and economic significance.
-
Historical Context: The region’s geography has shaped its history, influencing settlement patterns, transportation routes, and economic development. The Pacific Ocean has played a vital role in the region’s history, serving as a trade route and a source of resources.
-
Cultural Significance: The West Coast’s diverse landscapes have inspired artists, writers, and musicians, contributing to the region’s rich cultural heritage. The region’s natural beauty has attracted tourists and artists, shaping its cultural identity.
-
Economic Importance: The West Coast’s geography has played a vital role in its economic development. The region’s ports, waterways, and fertile valleys have made it a center for trade, agriculture, and industry.
FAQs about the West Coast’s Geography
-
What are the major mountain ranges on the West Coast? The major mountain ranges on the West Coast include the Cascade Range, the Sierra Nevada, and the Coast Ranges.
-
What are the major rivers on the West Coast? The major rivers on the West Coast include the Columbia River, the Sacramento River, and the San Joaquin River.
-
What are the major cities on the West Coast? The major cities on the West Coast include Seattle, Portland, San Francisco, Los Angeles, and San Diego.
-
What are the major climate zones on the West Coast? The major climate zones on the West Coast include the temperate rainforest climate of the Pacific Northwest, the Mediterranean climate of the California coast, and the arid climate of the Great Basin.
-
What are the major ecosystems on the West Coast? The major ecosystems on the West Coast include forests, deserts, grasslands, and wetlands.
Tips for Exploring the West Coast’s Geography
-
Visit National Parks: The West Coast is home to numerous national parks, offering a glimpse into the region’s diverse landscapes and ecosystems.
-
Go Hiking: The West Coast’s mountains and valleys provide ample opportunities for hiking, allowing visitors to experience the region’s natural beauty up close.
-
Take a Road Trip: A road trip along the Pacific Coast Highway offers stunning views of the coastline, mountains, and deserts.
-
Explore Coastal Cities: The West Coast’s coastal cities offer a unique blend of urban life and natural beauty.
-
Learn about the Region’s History: Visit historical sites and museums to learn about the West Coast’s rich history and cultural heritage.
Conclusion
The West Coast of the United States is a region of unparalleled beauty and diverse landscapes. From the rugged peaks of the Alaskan Panhandle to the sun-drenched shores of Baja California, this vast expanse is a dynamic blend of coastal wonders, towering mountains, arid deserts, and vibrant cities. Understanding the geography of this region is crucial for comprehending its history, culture, and economic significance. The West Coast’s geography is a testament to the power of nature, shaping its unique ecosystems, influencing its human settlements, and inspiring its cultural identity.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Tapestry of the American West Coast: A Geographical Journey. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!