Unraveling the Tapestry of America: A Geographical Exploration
Related Articles: Unraveling the Tapestry of America: A Geographical Exploration
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Tapestry of America: A Geographical Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Tapestry of America: A Geographical Exploration

The United States of America, a vast and diverse nation, is a captivating tapestry woven with a rich geographical history. Understanding the intricate patterns of its landforms, climate, and natural resources is crucial for appreciating the nation’s unique identity and appreciating the challenges and opportunities it faces. This comprehensive exploration delves into the geographical tapestry of America, revealing its multifaceted nature and highlighting the vital role it plays in shaping the nation’s story.
A Land of Contrasts: The Diverse Geography of America
The United States, spanning over 3.8 million square miles, encompasses an astonishing range of geographical features, from towering mountain ranges to fertile plains, from vast deserts to lush forests, and from rugged coastlines to sparkling lakes. This geographical diversity has profoundly shaped the nation’s history, culture, and economy.
The Majestic Mountains:
- The Rocky Mountains: Stretching over 3,000 miles from Canada to Mexico, the Rocky Mountains are a defining feature of the Western United States. Their dramatic peaks, snow-capped summits, and rugged terrain have attracted adventurers, explorers, and settlers for centuries. They are a vital source of water for the region, and their mineral wealth has fueled economic growth.
- The Appalachian Mountains: Running along the eastern edge of the United States, the Appalachian Mountains are older and lower than the Rockies. They are characterized by rolling hills, fertile valleys, and coal deposits, which have played a significant role in the region’s industrial development.
The Expansive Plains:
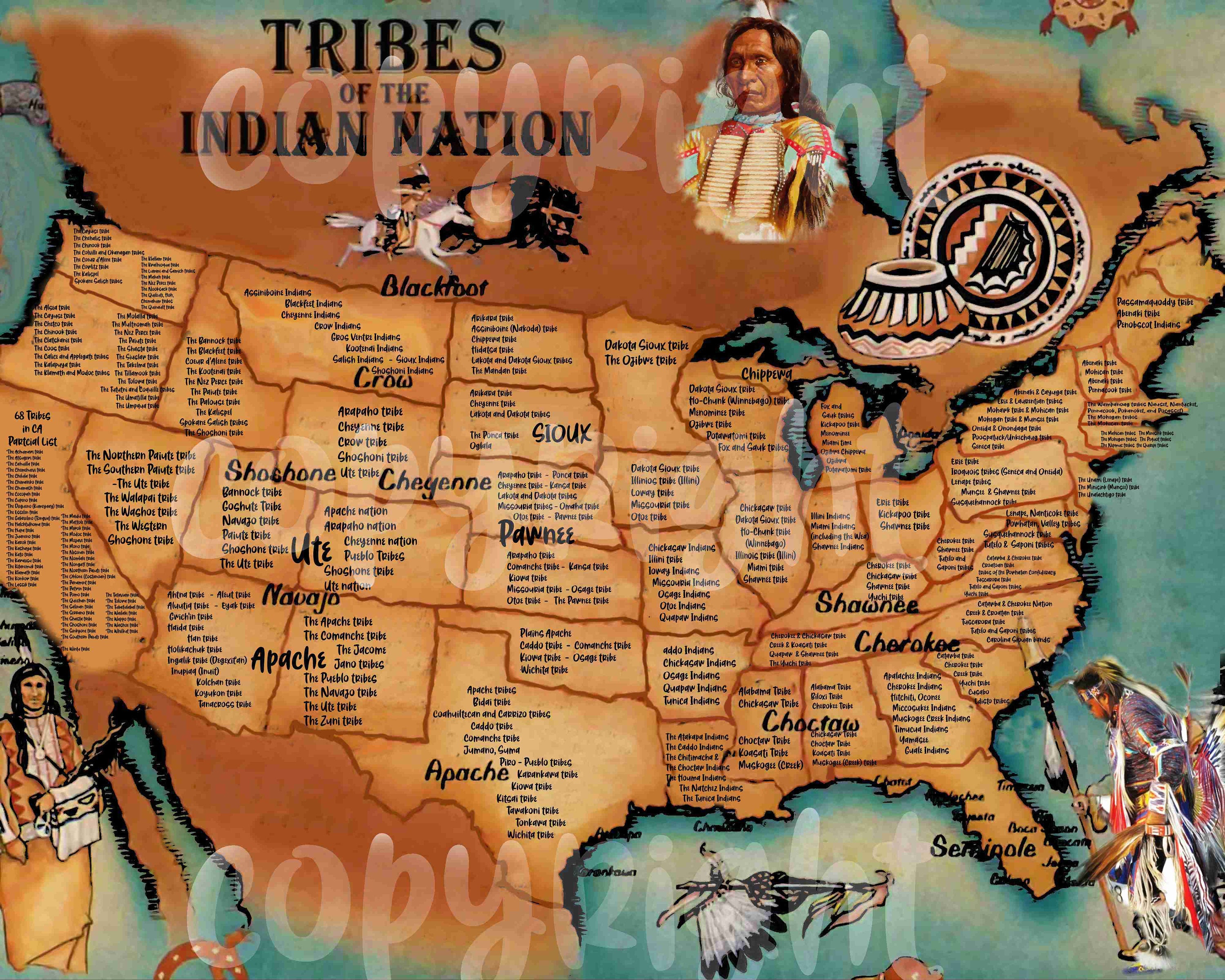
- The Great Plains: This vast expanse of grasslands stretches from the Rocky Mountains eastward to the Mississippi River. Historically, it was home to Native American tribes and bison herds. Today, it is a major agricultural region, producing wheat, corn, and cattle.
- The Coastal Plains: These low-lying plains extend along the Atlantic and Gulf Coasts. They are characterized by fertile soils, sandy beaches, and abundant wetlands, making them ideal for agriculture, fishing, and tourism.
The Diverse Coastlines:
- The Atlantic Coast: The Atlantic Coast is a mix of rocky shores, sandy beaches, and sheltered bays. It is home to major cities like New York, Boston, and Philadelphia, and its harbors have played a vital role in the nation’s maritime history.
- The Pacific Coast: The Pacific Coast is characterized by rugged cliffs, sandy beaches, and towering redwood forests. It is home to major cities like San Francisco, Los Angeles, and Seattle, and its ports are crucial for international trade.
- The Gulf Coast: The Gulf Coast is a region of low-lying plains, sandy beaches, and wetlands. It is home to major cities like Houston, New Orleans, and Mobile, and its oil and gas resources have played a significant role in the nation’s economy.
The Inland Seas:
- The Great Lakes: The Great Lakes, formed by glacial activity, are the largest freshwater system in the world. They are a vital source of drinking water, transportation, and recreation for the surrounding region.
- The Mississippi River: The Mississippi River, the longest river in North America, flows through the heart of the United States. It has been a vital transportation route for centuries, and its fertile floodplain has supported agriculture for generations.
The Dynamic Climate:
The United States experiences a wide range of climates, influenced by latitude, altitude, and proximity to oceans.
- Tropical Climate: The southernmost parts of the United States, particularly Florida and parts of the Gulf Coast, experience a tropical climate with hot, humid summers and mild winters.
- Temperate Climate: Much of the eastern and western United States experiences a temperate climate with four distinct seasons.
- Arid Climate: The western United States, particularly the Great Basin and Southwest, experiences an arid climate with low rainfall and hot summers.
- Continental Climate: The central United States experiences a continental climate with hot, humid summers and cold, snowy winters.
Natural Resources: The Foundation of a Nation
The United States is blessed with abundant natural resources, which have played a crucial role in shaping its economic development.
- Fossil Fuels: The United States is a major producer of oil, natural gas, and coal. These resources have powered the nation’s industrial growth and transportation systems.
- Minerals: The United States is rich in minerals, including iron ore, copper, gold, and silver. These resources have fueled manufacturing and construction industries.
- Forests: The United States is home to vast forests, which provide timber, pulpwood, and other forest products. Forests also play a vital role in regulating the climate and providing habitat for wildlife.
- Water Resources: The United States has abundant water resources, including rivers, lakes, and groundwater. These resources are essential for agriculture, industry, and drinking water.
The Impact of Geography on American History
The geographical diversity of the United States has profoundly influenced its history, shaping its political, social, and economic development.
- Exploration and Settlement: The vastness and diversity of the land attracted explorers, settlers, and immigrants from around the world.
- Industrial Revolution: The availability of natural resources, particularly coal and iron ore, fueled the Industrial Revolution in the United States.
- Expansion and Development: The vastness of the land allowed for westward expansion and the development of new industries and agricultural practices.
- Regional Differences: The different geographical regions of the United States have developed distinct cultures, economies, and political identities.
The Challenges and Opportunities of a Diverse Land
The geographical diversity of the United States also presents challenges and opportunities.
- Natural Disasters: The United States is vulnerable to a wide range of natural disasters, including hurricanes, earthquakes, floods, and wildfires.
- Environmental Issues: The nation faces environmental challenges such as air and water pollution, climate change, and deforestation.
- Resource Management: Managing the nation’s natural resources sustainably is a critical challenge.
- Economic Development: The diverse geographical regions of the United States present opportunities for economic development in different sectors.
FAQs about the Geography of America
Q: What are the major landforms of the United States?
A: The major landforms of the United States include the Rocky Mountains, the Appalachian Mountains, the Great Plains, the Coastal Plains, the Great Lakes, and the Mississippi River.
Q: What are the different climate zones in the United States?
A: The United States experiences a wide range of climates, including tropical, temperate, arid, and continental.
Q: What are the major natural resources of the United States?
A: The major natural resources of the United States include fossil fuels, minerals, forests, and water resources.
Q: How has geography influenced American history?
A: Geography has profoundly influenced American history, shaping its exploration, settlement, industrial development, expansion, and regional differences.
Q: What are some of the challenges and opportunities presented by the geography of the United States?
A: The geographical diversity of the United States presents challenges such as natural disasters, environmental issues, and resource management. It also presents opportunities for economic development in different sectors.
Tips for Understanding the Geography of America
- Use maps and atlases: Maps and atlases are essential tools for visualizing the geographical features of the United States.
- Explore online resources: There are numerous online resources available, including websites, videos, and interactive maps, that provide information about the geography of the United States.
- Travel and experience the land: The best way to understand the geography of the United States is to travel and experience it firsthand.
Conclusion
The geographical tapestry of the United States is a complex and captivating story of diversity, resourcefulness, and resilience. From the majestic mountains to the vast plains, from the rugged coastlines to the sparkling lakes, the nation’s geography has shaped its history, culture, and economy. Understanding this geographical tapestry is essential for appreciating the unique identity of the United States and the challenges and opportunities it faces in the 21st century. By embracing the diverse landscape of America, we can better understand its past, present, and future.


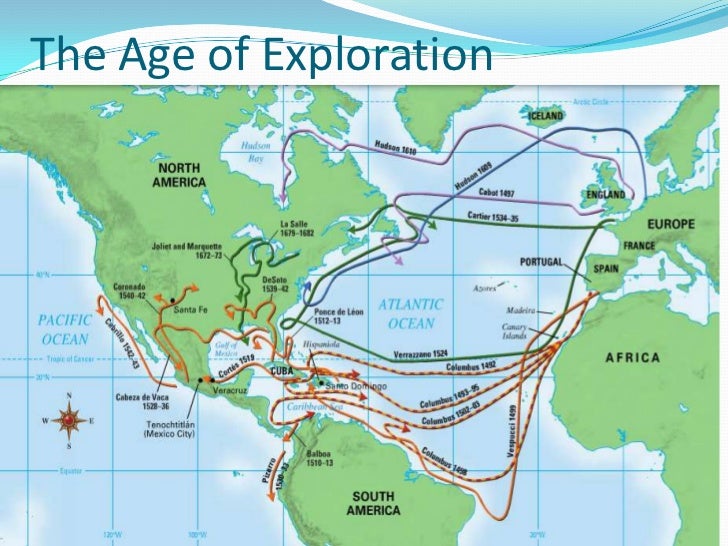
/Christopher-Columbus-58b9ca2c5f9b58af5ca6b758.jpg)

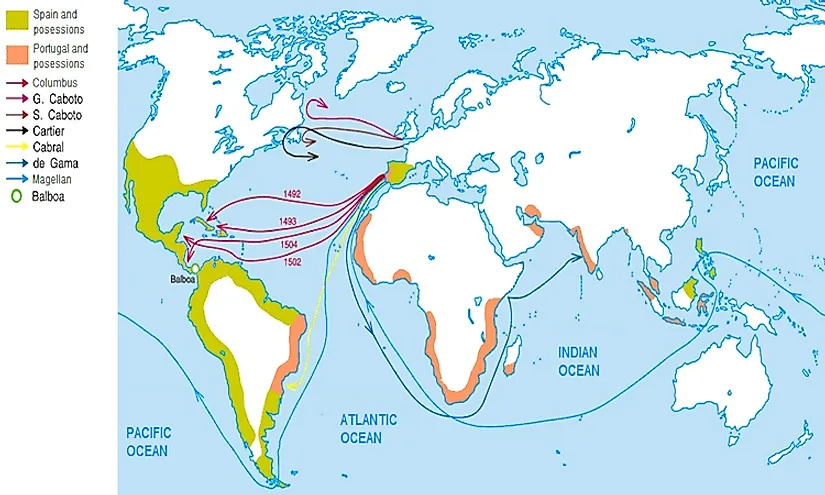

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Tapestry of America: A Geographical Exploration. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!