Unraveling the Geography of Eritrea and Ethiopia: A Comprehensive Exploration
Related Articles: Unraveling the Geography of Eritrea and Ethiopia: A Comprehensive Exploration
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Geography of Eritrea and Ethiopia: A Comprehensive Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Geography of Eritrea and Ethiopia: A Comprehensive Exploration

The Horn of Africa, a geographically and culturally rich region, is home to two nations intricately linked by history, culture, and shared landscapes: Eritrea and Ethiopia. Understanding the geography of these countries, particularly their borders and geographical features, is essential for appreciating their complex relationship, understanding their development challenges, and appreciating their unique cultural identities.
A Shared History and a Contested Border:
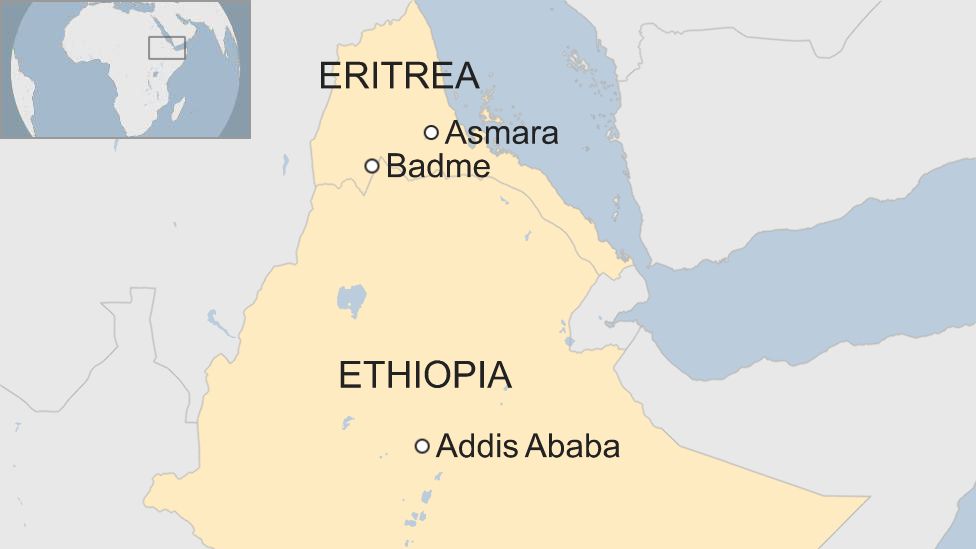
The border between Eritrea and Ethiopia, a source of significant tension in the past, is a complex and contested one. The current border was established in 1902 by the Italian colonial administration, which divided the region into Eritrea and Italian Somaliland. This division, however, disregarded the historical and cultural ties that bound the Eritrean and Ethiopian populations. Following Ethiopia’s annexation of Eritrea in 1962, the border became a symbol of Eritrean resistance and the struggle for independence.
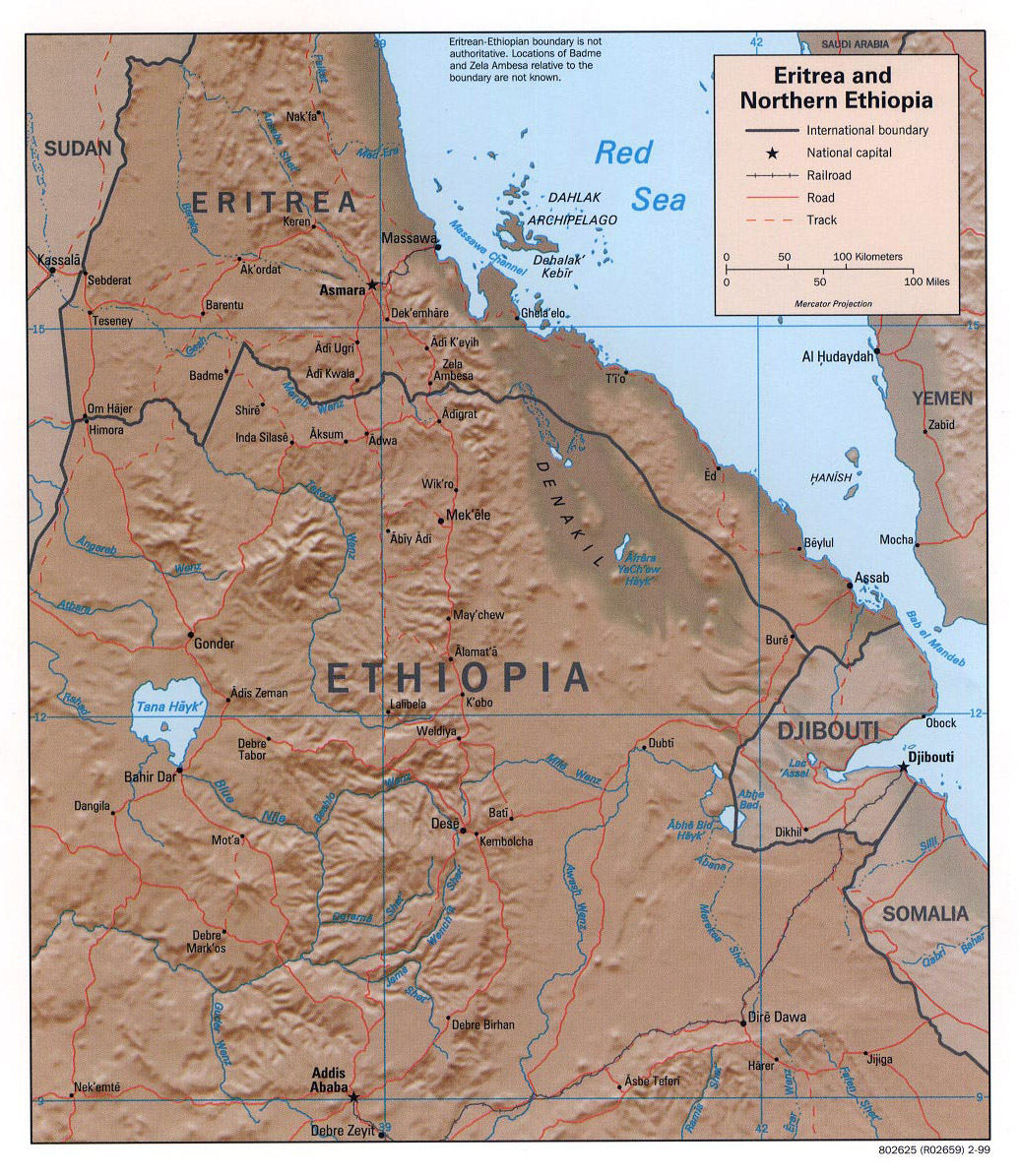
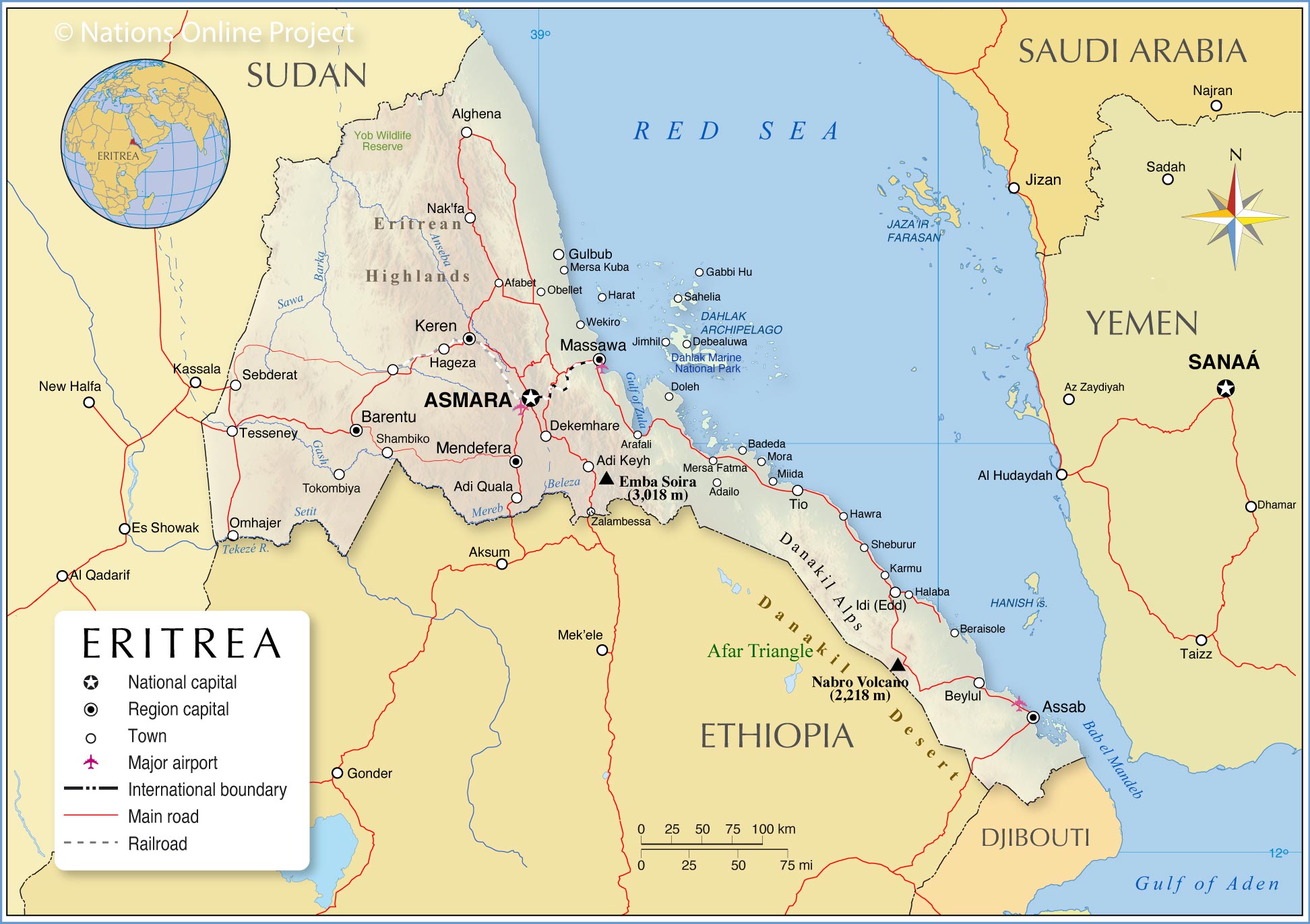
Eritrea: A Coastal Nation with Diverse Landscapes:
Eritrea, a nation on the Red Sea coast, boasts a diverse landscape that ranges from the rugged highlands of the Eritrean Plateau to the arid lowlands of the Danakil Depression. The country’s geography is marked by:
- The Eritrean Plateau: This plateau, rising to over 3,000 meters in altitude, is characterized by its rugged terrain, volcanic peaks, and fertile valleys. The plateau serves as the heartland of Eritrea, supporting a significant portion of its population and agricultural production.
- The Red Sea Coast: Eritrea’s coastline stretches for over 1,200 kilometers, offering access to the Red Sea and its rich marine life. This coastline is dotted with ports like Massawa and Assab, which have historically served as important trading centers.
- The Danakil Depression: This desolate and inhospitable region, located in the eastern part of Eritrea, is the lowest point on the African continent. It is characterized by its extreme temperatures, volcanic activity, and salt flats.
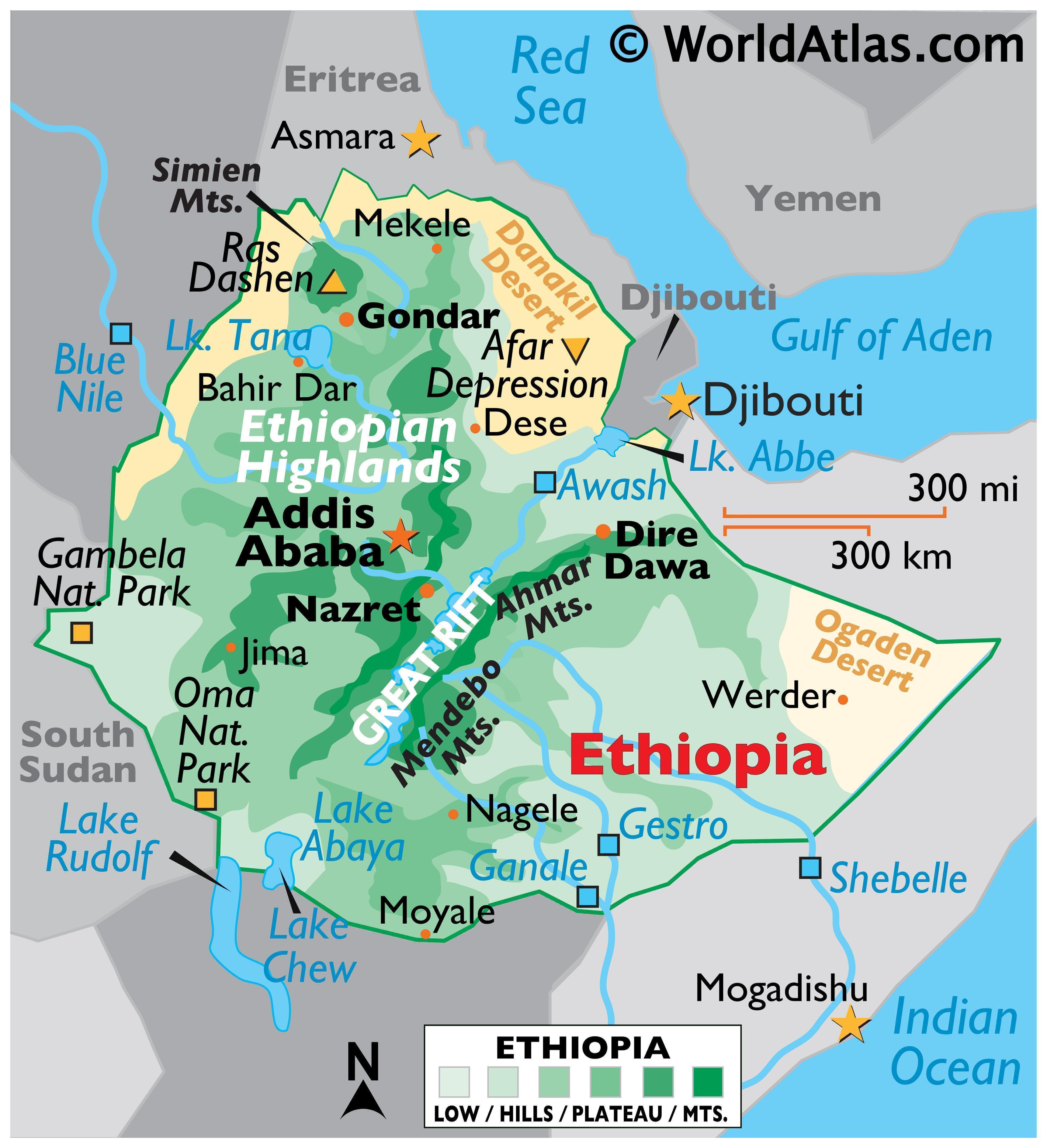
Ethiopia: A Land of High Plateaus and Rift Valleys:
Ethiopia, a landlocked country, is known for its dramatic landscapes and diverse ecosystems. Its geography is defined by:
- The Ethiopian Highlands: These highlands, a vast plateau rising to over 4,000 meters, are the heartland of Ethiopia. They are home to the country’s major cities, including Addis Ababa, and support a significant portion of its population and agricultural production.
- The Great Rift Valley: This geological wonder, stretching across East Africa, cuts through Ethiopia, creating a series of deep valleys and volcanic peaks. The Rift Valley is home to numerous lakes, including Lake Tana, the source of the Blue Nile.
- The Somali Region: Located in the southeastern part of Ethiopia, this region is characterized by its arid climate and low-lying plains. It is home to various nomadic communities and is a major producer of livestock.
The Importance of Understanding the Geography of Eritrea and Ethiopia:
Understanding the geography of Eritrea and Ethiopia is crucial for several reasons:
- Resource Management: The region’s geography influences its natural resources, including water, land, and minerals. Understanding the distribution and availability of these resources is essential for sustainable development and resource management.
- Climate Change: The region is highly vulnerable to climate change, particularly drought and desertification. Understanding the geography of the region is crucial for developing effective adaptation strategies to mitigate the impacts of climate change.
- Conflict and Security: The geography of the region has played a significant role in historical conflicts and ongoing security challenges. Understanding the terrain, borders, and access routes is essential for conflict resolution and peacebuilding efforts.
- Economic Development: The region’s geography influences its potential for economic development, particularly in agriculture, tourism, and infrastructure. Understanding the geographical constraints and opportunities is essential for promoting sustainable economic growth.
- Cultural Diversity: The geography of the region has shaped its cultural diversity, with different communities adapting to their unique environments. Understanding the geography is essential for appreciating the rich cultural heritage of Eritrea and Ethiopia.
FAQs:
Q: What are the major geographical features of Eritrea?
A: Eritrea’s major geographical features include the Eritrean Plateau, the Red Sea Coast, and the Danakil Depression.
Q: What are the major geographical features of Ethiopia?
A: Ethiopia’s major geographical features include the Ethiopian Highlands, the Great Rift Valley, and the Somali Region.
Q: What is the significance of the border between Eritrea and Ethiopia?
A: The border between Eritrea and Ethiopia is a contested one, reflecting a history of conflict and tension. It is a symbol of the Eritrean struggle for independence and remains a sensitive issue in the relationship between the two countries.
Q: What are the challenges related to the geography of Eritrea and Ethiopia?
A: The challenges related to the geography of Eritrea and Ethiopia include resource scarcity, climate change vulnerability, conflict, and limited infrastructure development.
Tips:
- Use reliable sources: When researching the geography of Eritrea and Ethiopia, rely on credible sources such as academic journals, government reports, and reputable news organizations.
- Visualize the region: Utilize maps, satellite imagery, and other visual aids to understand the geographical features and their relationships.
- Consider the historical context: Understanding the historical context of the region, including colonial influences and past conflicts, is crucial for interpreting its current geography.
- Explore the cultural diversity: The geography of the region has shaped its diverse cultures. Explore the unique traditions, languages, and practices of different communities.
Conclusion:
The geography of Eritrea and Ethiopia is a complex and fascinating landscape that reflects the region’s rich history, diverse cultures, and ongoing challenges. Understanding the geographical features, borders, and environmental factors is essential for appreciating the region’s unique character and navigating its complex relationships. This knowledge is crucial for promoting sustainable development, resolving conflicts, and fostering a better future for the people of Eritrea and Ethiopia.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Geography of Eritrea and Ethiopia: A Comprehensive Exploration. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!