Unlocking the Secrets of the Weather: A Comprehensive Guide to Temperature Forecast Maps
Related Articles: Unlocking the Secrets of the Weather: A Comprehensive Guide to Temperature Forecast Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unlocking the Secrets of the Weather: A Comprehensive Guide to Temperature Forecast Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unlocking the Secrets of the Weather: A Comprehensive Guide to Temperature Forecast Maps
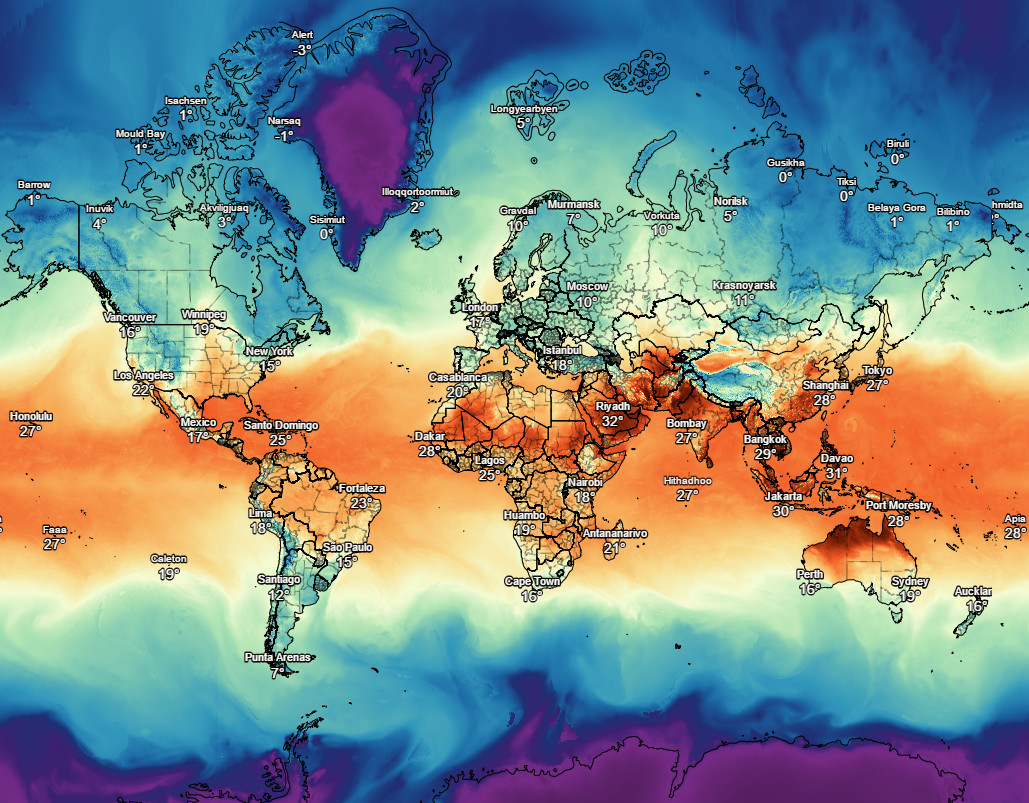
The world around us is constantly in flux, and the weather is one of the most dynamic and unpredictable elements of our environment. Yet, understanding the nuances of weather patterns is crucial for countless aspects of our lives, from planning outdoor activities to ensuring the safety of critical infrastructure. In this regard, temperature forecast maps emerge as invaluable tools, providing a visual representation of predicted temperature variations across a geographical area.
Understanding the Basics: What is a Temperature Forecast Map?
Temperature forecast maps are visual representations of predicted temperature variations across a specific geographical area. They are often used by meteorologists, weather enthusiasts, and the general public to gain insights into anticipated temperature changes. These maps typically depict the expected temperature range for a particular time period, using color gradients or symbols to illustrate the variation.
The Power of Visualization: How Temperature Forecast Maps Work
Temperature forecast maps rely on complex meteorological models that analyze various atmospheric data points, including:
- Air Pressure: High and low pressure systems influence weather patterns, including temperature changes.
- Wind Speed and Direction: Wind patterns play a crucial role in transporting heat and moisture across regions.
- Humidity: Moisture in the air affects temperature, influencing the rate of cooling or warming.
- Solar Radiation: The amount of solar radiation reaching a particular area significantly influences temperature.
- Terrain and Elevation: Topography influences temperature patterns, with higher altitudes typically experiencing lower temperatures.
These data points are fed into sophisticated computer models that simulate the behavior of the atmosphere, producing forecasts of temperature changes. The results are then visualized on a map, allowing users to understand the spatial distribution of predicted temperatures.
Beyond the Basics: Types of Temperature Forecast Maps
Temperature forecast maps come in various forms, each designed to serve specific purposes:
- Surface Temperature Maps: These maps illustrate the expected temperature at ground level, offering insights into the overall thermal conditions of a region.
- Upper Air Temperature Maps: These maps focus on temperatures at higher altitudes, providing information about conditions in the atmosphere, crucial for aviation and weather forecasting.
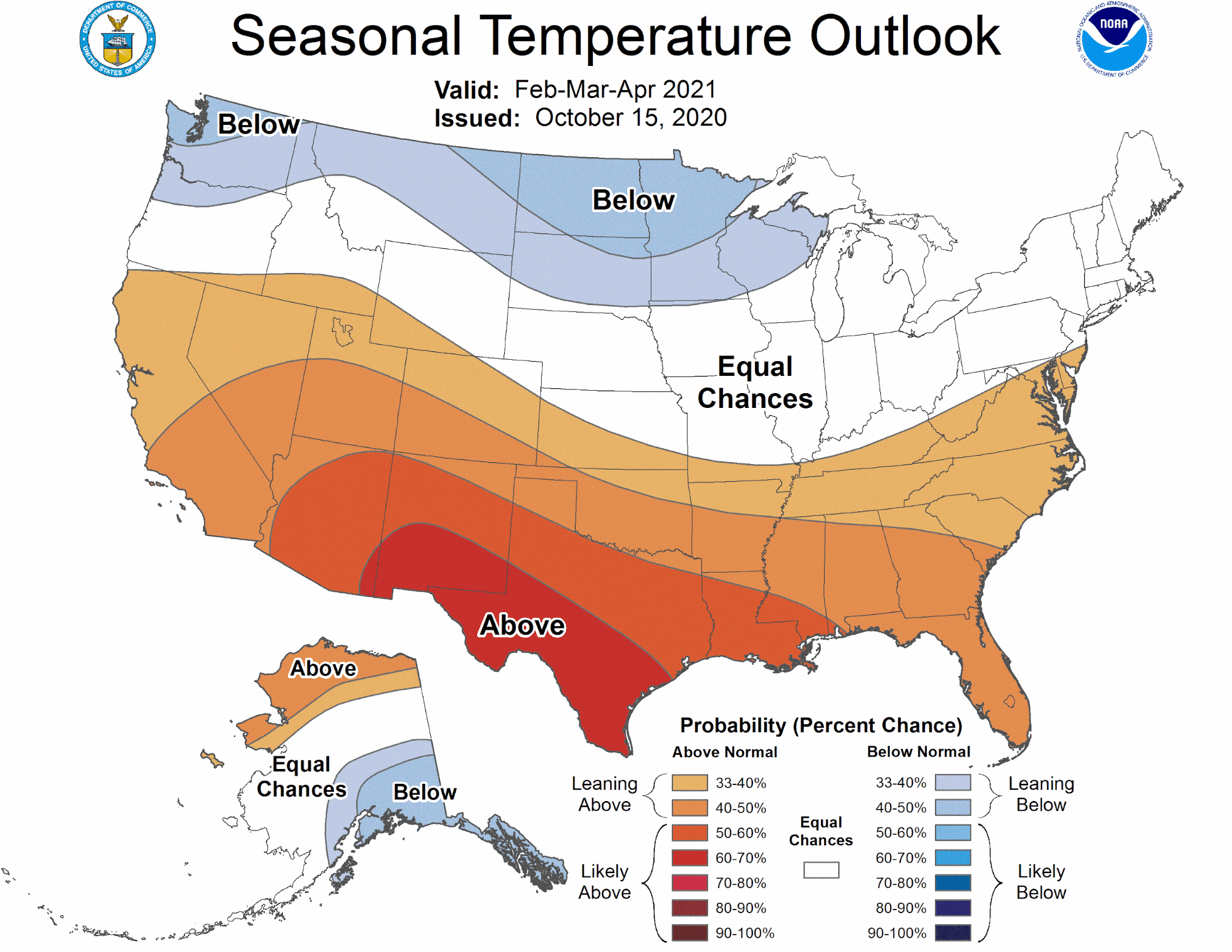
- Anomaly Maps: These maps highlight temperature deviations from long-term averages, providing insights into the severity of heat waves or cold spells.
- Probability Maps: These maps show the likelihood of specific temperature ranges occurring, offering a more nuanced perspective on potential weather scenarios.
The Benefits of Using Temperature Forecast Maps
Temperature forecast maps offer a wide range of benefits, making them essential tools for individuals and organizations alike:
-
Improved Decision-Making: By understanding anticipated temperature changes, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions about various activities, including:
- Outdoor Activities: Planning outdoor events, sports, and recreational activities based on predicted temperatures.
- Agriculture: Optimizing crop management practices to minimize the impact of extreme temperatures.
- Construction: Adjusting construction schedules and materials to account for potential temperature fluctuations.
- Transportation: Planning transportation routes and schedules to mitigate the risks associated with extreme temperatures.
- Energy Management: Optimizing energy consumption patterns to minimize energy costs and reduce environmental impact.
-
Enhanced Safety and Preparedness: Temperature forecast maps play a crucial role in public safety and disaster preparedness by:
- Extreme Weather Alerts: Providing early warnings about heat waves, cold spells, and other extreme temperature events.
- Health Risks: Identifying regions at risk of heat-related illnesses, enabling proactive measures to protect vulnerable populations.
- Infrastructure Protection: Assessing the potential impact of extreme temperatures on critical infrastructure, such as power grids and transportation systems.
- Disaster Response: Guiding emergency response efforts during extreme weather events, ensuring efficient resource allocation.
-
Scientific Research and Climate Monitoring: Temperature forecast maps are vital tools for scientists and researchers studying climate change and its impacts. They provide:
- Climate Trend Analysis: Long-term temperature data from forecast maps contribute to understanding climate change trends and patterns.
- Climate Model Validation: Comparing forecast data with actual observations helps validate and refine climate models.
- Climate Impact Assessment: Assessing the potential impact of climate change on different sectors, such as agriculture, water resources, and human health.
Navigating the Map: Reading and Interpreting Temperature Forecast Maps
To effectively utilize temperature forecast maps, it is crucial to understand the key elements and symbols used to represent temperature data:
- Color Gradient: Most temperature forecast maps use a color gradient to illustrate temperature variations, with warmer temperatures typically represented by red and orange shades, and cooler temperatures by blue and purple shades.
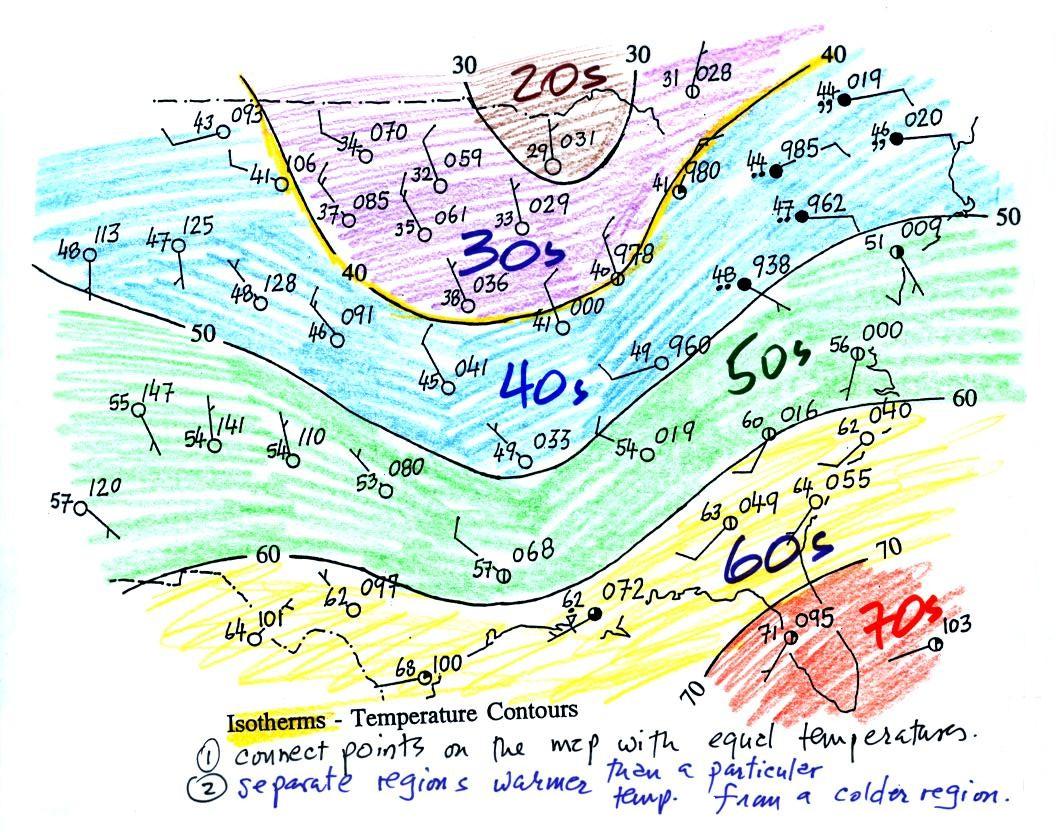
- Isotherms: Lines connecting points of equal temperature are called isotherms. These lines help visualize the spatial distribution of temperature changes.
-
Symbols: Different symbols may be used to represent specific features, such as:
- Fronts: Lines representing boundaries between different air masses, which can influence temperature changes.
- High and Low Pressure Systems: Symbols representing areas of high and low atmospheric pressure, indicating potential for different weather patterns.
- Legend: A legend or key provides detailed information about the colors, symbols, and units used on the map.
FAQs about Temperature Forecast Maps
1. How accurate are temperature forecast maps?
The accuracy of temperature forecast maps depends on several factors, including the quality of input data, the sophistication of the meteorological models, and the time frame being predicted. Generally, short-term forecasts (1-3 days) are more accurate than long-term forecasts (7-14 days).
2. What are the limitations of temperature forecast maps?
Temperature forecast maps are based on complex models that cannot perfectly capture all atmospheric variables. As a result, there will always be a degree of uncertainty in the predictions. Additionally, localized weather events, such as thunderstorms or microbursts, can be difficult to predict accurately.
3. Where can I find reliable temperature forecast maps?
Reliable temperature forecast maps are available from various sources, including:
- National Meteorological Agencies: Government agencies responsible for weather forecasting, such as the National Weather Service in the United States.
- Private Weather Services: Companies specializing in weather forecasting, such as AccuWeather and The Weather Channel.
- Online Weather Websites: Numerous websites offer free access to temperature forecast maps, including Weather.com and Google Weather.
Tips for Using Temperature Forecast Maps Effectively
- Consider the Time Frame: Be mindful of the forecast period when interpreting the map. Short-term forecasts are generally more accurate than long-term forecasts.
- Check the Source: Choose reliable sources for your temperature forecast maps, such as national meteorological agencies or reputable private weather services.
- Look at the Legend: Pay attention to the legend or key to understand the colors, symbols, and units used on the map.
- Compare Forecasts: Compare forecasts from multiple sources to get a more comprehensive understanding of potential temperature changes.
- Stay Informed: Monitor weather updates and alerts to stay informed about any changes in the predicted temperature patterns.
Conclusion
Temperature forecast maps are invaluable tools for understanding and predicting temperature variations across geographical areas. By providing a visual representation of anticipated temperature changes, these maps empower individuals, businesses, and organizations to make informed decisions, enhance safety and preparedness, and contribute to scientific research and climate monitoring. As technology continues to advance, temperature forecast maps will likely become even more accurate and sophisticated, further enhancing our ability to navigate the complexities of our ever-changing climate.

![Global annual average temperature map [8640x4320] [OS] : MapPorn](https://external-preview.redd.it/iiwYEl1aPfhd6fsGm2qMuj1hGvIogmt9L74mNcKX8Pw.png?width=1200u0026height=628.272251309u0026auto=webpu0026s=1dd3411acb86ff1c8b22f1519bc3b4685254da6c)




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking the Secrets of the Weather: A Comprehensive Guide to Temperature Forecast Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!