Unlocking Arizona’s Water Lifeline: A Comprehensive Guide to Aquifer Maps
Related Articles: Unlocking Arizona’s Water Lifeline: A Comprehensive Guide to Aquifer Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unlocking Arizona’s Water Lifeline: A Comprehensive Guide to Aquifer Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unlocking Arizona’s Water Lifeline: A Comprehensive Guide to Aquifer Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unlocking Arizona’s Water Lifeline: A Comprehensive Guide to Aquifer Maps
- 3.1 What are Aquifer Maps and Why are They Important?
- 3.2 Types of Aquifer Maps and Their Applications
- 3.3 Arizona’s Aquifer System: A Complex Network
- 3.4 Understanding Aquifer Maps: A Closer Look at Arizona’s Water Resources
- 3.5 FAQs about Aquifer Maps in Arizona
- 3.6 Tips for Using Aquifer Maps Effectively
- 3.7 Conclusion: Aquifer Maps – A Key to Sustainable Water Management
- 4 Closure
Unlocking Arizona’s Water Lifeline: A Comprehensive Guide to Aquifer Maps

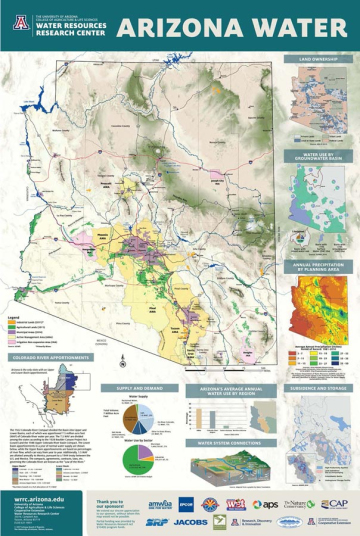
Arizona, a state renowned for its arid landscapes and vibrant desert ecosystems, faces a unique challenge: managing a precious and finite water resource. Understanding the distribution and characteristics of underground water sources, known as aquifers, is crucial for sustainable water management. This guide delves into the significance of aquifer maps in Arizona, providing a comprehensive overview of their purpose, applications, and essential information for informed decision-making.
What are Aquifer Maps and Why are They Important?
An aquifer map is a visual representation of underground water resources, depicting their location, depth, extent, and characteristics. These maps serve as essential tools for water resource management, providing crucial information for:
- Water Supply Planning: Aquifer maps help identify potential water sources, assess their availability, and predict future water demands. This information is vital for planning water infrastructure, developing water conservation strategies, and ensuring sustainable water supplies for communities and industries.
- Environmental Protection: Aquifer maps assist in understanding the interconnectedness of groundwater with surface water bodies, such as rivers and lakes. This knowledge helps in identifying areas vulnerable to contamination and developing strategies to protect groundwater quality.
- Land Use Planning: Aquifer maps inform decisions regarding land development and resource extraction. By understanding the location and characteristics of aquifers, planners can minimize potential impacts on groundwater resources and ensure sustainable land use practices.
- Disaster Preparedness: Aquifer maps play a crucial role in disaster preparedness by identifying areas susceptible to drought or flooding, facilitating effective emergency response and mitigation efforts.
Types of Aquifer Maps and Their Applications
Aquifer maps can be categorized based on their purpose and the information they depict. Common types include:
1. Hydrogeologic Maps: These maps focus on the geological and hydrological characteristics of aquifers, including the types of rock formations, the depth and thickness of aquifers, and the direction of groundwater flow. These maps are essential for understanding the fundamental properties of aquifers and their potential for water supply.
2. Water Table Maps: These maps show the elevation of the water table, the upper surface of the saturated zone in an aquifer. They provide valuable insights into the availability of groundwater and potential areas of depletion.
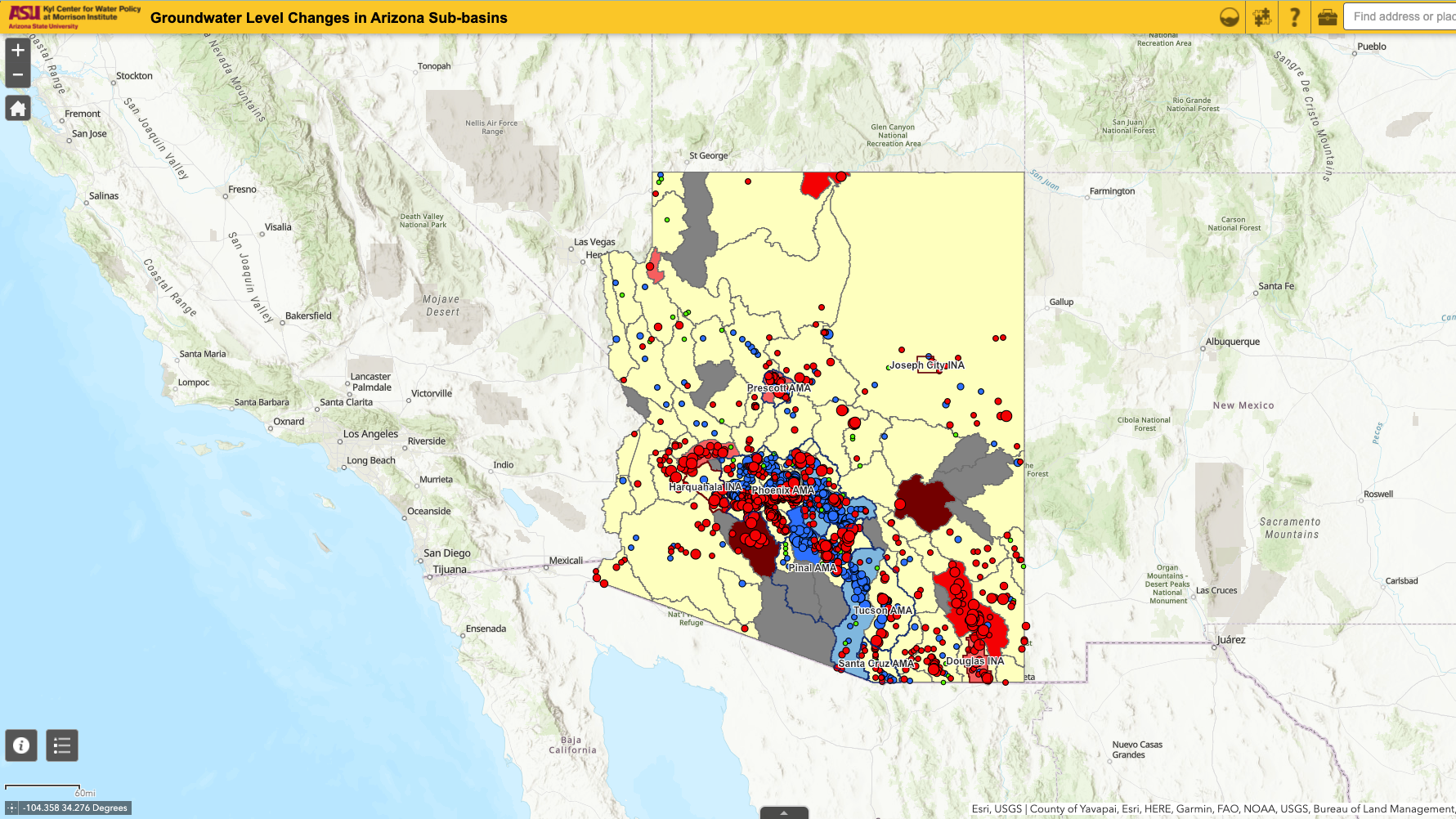
3. Groundwater Contour Maps: These maps depict the elevation of groundwater levels at specific points in time, providing information about the direction and rate of groundwater flow. They are crucial for understanding the movement of groundwater and potential impacts of pumping or recharge activities.
4. Groundwater Quality Maps: These maps illustrate the chemical and physical characteristics of groundwater, such as salinity, pH, and contaminant levels. This information is essential for assessing the suitability of groundwater for drinking, irrigation, and industrial uses.
5. Vulnerability Maps: These maps identify areas susceptible to groundwater contamination from various sources, such as agricultural runoff, industrial waste, and septic systems. They are crucial for developing strategies to protect groundwater quality and prevent contamination.
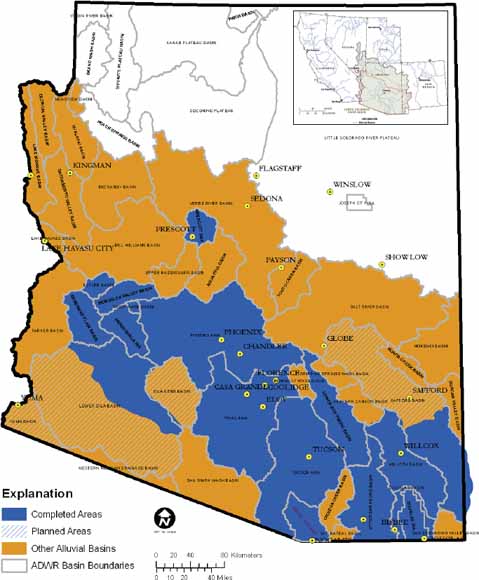
Arizona’s Aquifer System: A Complex Network
Arizona’s aquifer system is a complex network of underground water sources, encompassing various formations and geological units. Some key aquifers in Arizona include:
- The Coconino Aquifer: This aquifer, located in northern Arizona, is a major source of water for the Flagstaff area and surrounding communities. It is characterized by its relatively high water quality and significant storage capacity.
- The Santa Cruz Aquifer: This aquifer, extending from southern Arizona into Mexico, is a vital source of water for Tucson and surrounding areas. It is known for its high recharge rates and significant storage capacity.
- The Gila Aquifer: Located in southwestern Arizona, this aquifer is a significant source of water for Yuma and surrounding communities. It is characterized by its large size and relatively high water quality.
- The Phoenix Basin Aquifer System: This system comprises multiple aquifers, including the Agua Fria, Salt River, and Verde Aquifer, which provide water for the Phoenix metropolitan area. It is a complex system with varying water quality and recharge rates.
Understanding Aquifer Maps: A Closer Look at Arizona’s Water Resources
Aquifer maps play a vital role in managing Arizona’s water resources, offering crucial insights into:
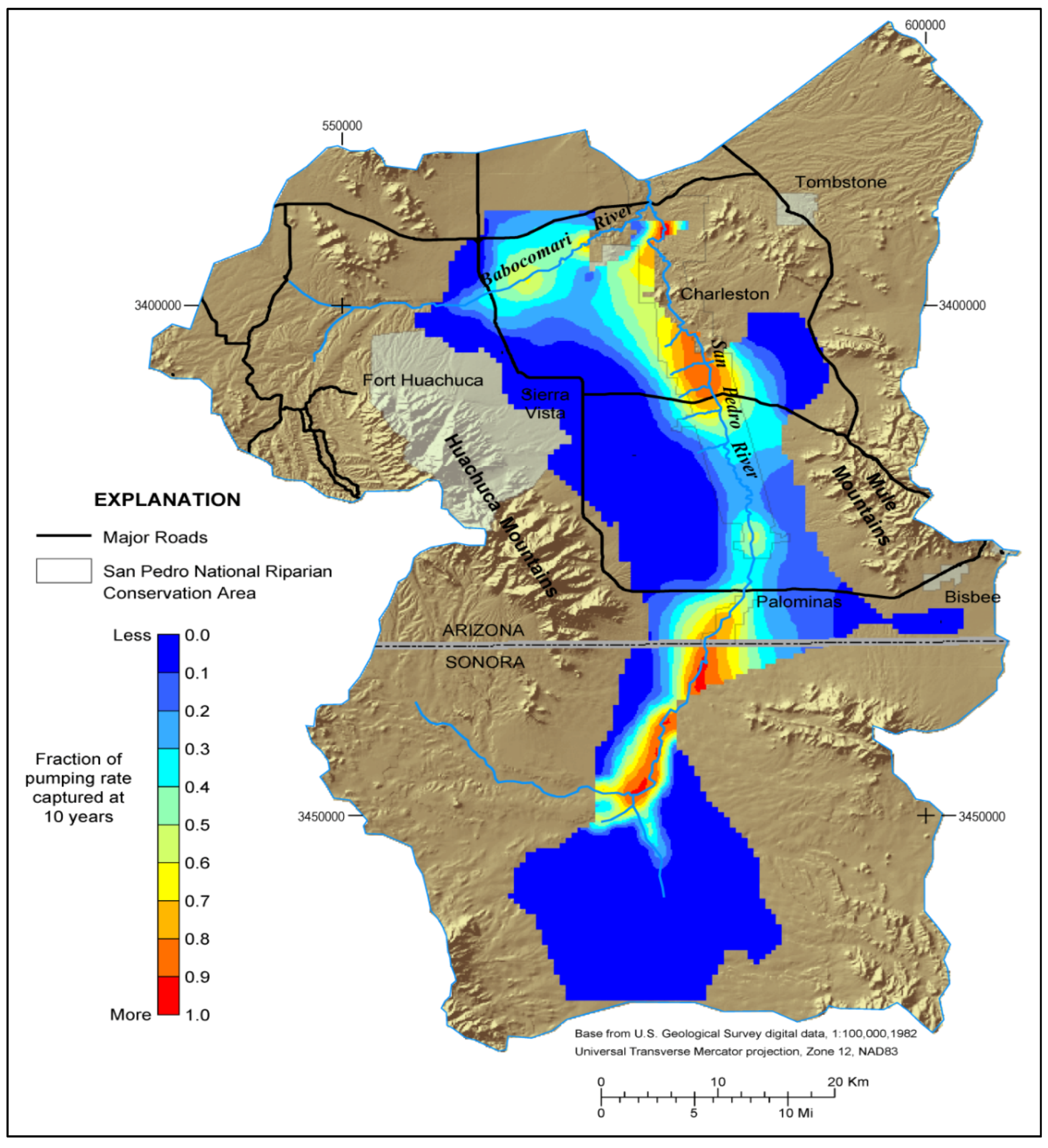
- Aquifer Recharge and Discharge: Aquifer maps help identify areas where groundwater is replenished (recharge) and areas where it is extracted (discharge). This understanding is crucial for balancing water use and maintaining aquifer sustainability.
- Groundwater Flow Patterns: Aquifer maps depict the direction and rate of groundwater flow, providing essential information for managing groundwater extraction and preventing overdraft.
- Water Quality Assessment: Aquifer maps help identify areas with potential contamination risks, enabling proactive measures to protect groundwater quality and ensure its suitability for various uses.
- Water Availability and Sustainability: Aquifer maps provide information about the volume of groundwater available for use and potential impacts of extraction on aquifer levels. This information is essential for developing sustainable water management strategies.
FAQs about Aquifer Maps in Arizona
1. Where can I find aquifer maps for Arizona?
Aquifer maps for Arizona are available from various sources, including:
- Arizona Department of Water Resources (ADWR): The ADWR website provides access to a range of groundwater maps, including hydrogeologic maps, water table maps, and groundwater contour maps.
- U.S. Geological Survey (USGS): The USGS provides national groundwater maps, including information on aquifers in Arizona.
- University of Arizona Water Resources Research Center: The University of Arizona Water Resources Research Center conducts research and provides resources on Arizona’s groundwater resources, including aquifer maps.
- Local Water Agencies: Local water agencies, such as cities and counties, often have their own aquifer maps specific to their areas.
2. How are aquifer maps created?
Aquifer maps are created through a combination of field data collection and analysis. This process typically involves:
- Geological Surveys: Geologists conduct surveys to identify the types of rock formations and their characteristics.
- Well Logs and Water Level Measurements: Data from wells, including well logs and water level measurements, provide information about aquifer depth, thickness, and water levels.
- Groundwater Sampling and Analysis: Groundwater samples are collected and analyzed to determine water quality parameters, such as salinity, pH, and contaminant levels.
- Geophysical Surveys: Geophysical techniques, such as seismic surveys and electrical resistivity surveys, are used to identify aquifer boundaries and other geological features.
- Computer Modeling: Computer models are used to simulate groundwater flow and predict the impact of various factors on aquifer levels and water quality.
3. What are some limitations of aquifer maps?
While aquifer maps provide valuable information, it’s important to recognize their limitations:
- Limited Spatial Resolution: Aquifer maps typically represent data at a specific scale, which may not capture detailed variations in aquifer characteristics or water quality.
- Time-Dependent Data: Groundwater conditions can change over time due to factors such as rainfall, pumping, and recharge. Aquifer maps represent conditions at a specific point in time and may not reflect current conditions.
- Uncertainty in Data: Data used to create aquifer maps can have inherent uncertainties, which can affect the accuracy of the maps.
- Simplified Representations: Aquifer maps are simplified representations of complex underground systems and may not capture all relevant factors affecting groundwater resources.
Tips for Using Aquifer Maps Effectively
- Consult Multiple Sources: Compare information from different sources, including government agencies, universities, and local water agencies, to ensure a comprehensive understanding of aquifer characteristics.
- Consider Time Frames: Recognize that groundwater conditions can change over time and select maps that reflect the relevant time period for your needs.
- Understand Map Scales: Pay attention to the map scale to determine the level of detail and accuracy of the information presented.
- Consult with Experts: If you have specific questions or need assistance interpreting aquifer maps, consult with hydrogeologists or other water resource experts.
Conclusion: Aquifer Maps – A Key to Sustainable Water Management
Aquifer maps are invaluable tools for understanding, managing, and protecting Arizona’s precious groundwater resources. By providing insights into the location, extent, and characteristics of aquifers, these maps facilitate informed decision-making for water supply planning, environmental protection, land use development, and disaster preparedness. As Arizona faces the challenges of a growing population and a changing climate, understanding and effectively utilizing aquifer maps becomes increasingly crucial for ensuring a sustainable future for the state’s water resources.

.png)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking Arizona’s Water Lifeline: A Comprehensive Guide to Aquifer Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!