Understanding the Current Map of Israel: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding the Current Map of Israel: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Current Map of Israel: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Current Map of Israel: A Comprehensive Guide
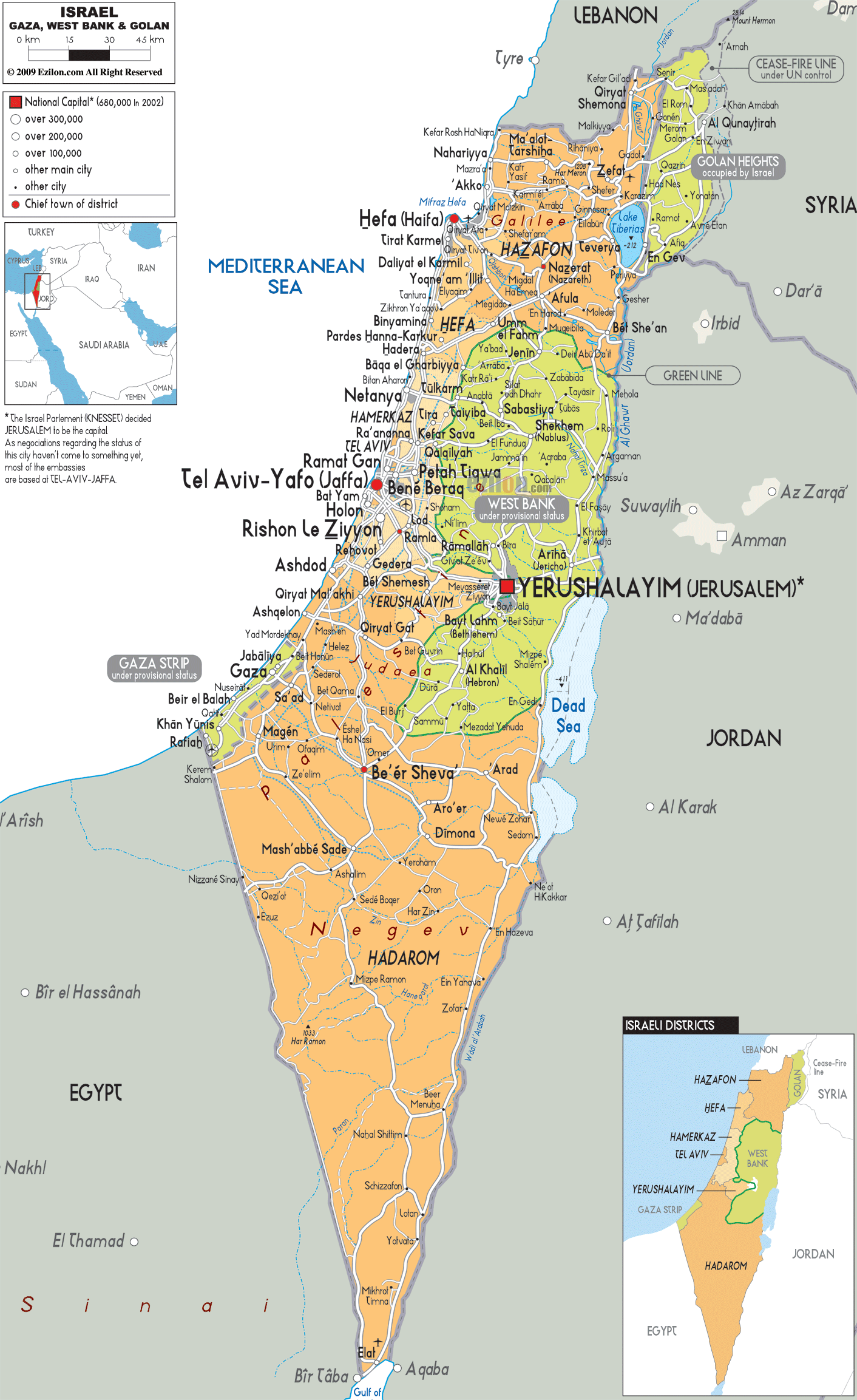
The map of Israel, a dynamic and contested landscape, has been the subject of intense scrutiny and debate for decades. Its current configuration, a result of historical events, political negotiations, and ongoing conflicts, presents a complex picture that requires careful analysis. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the current map of Israel, exploring its key features, historical context, and contemporary challenges.
The Physical Landscape:
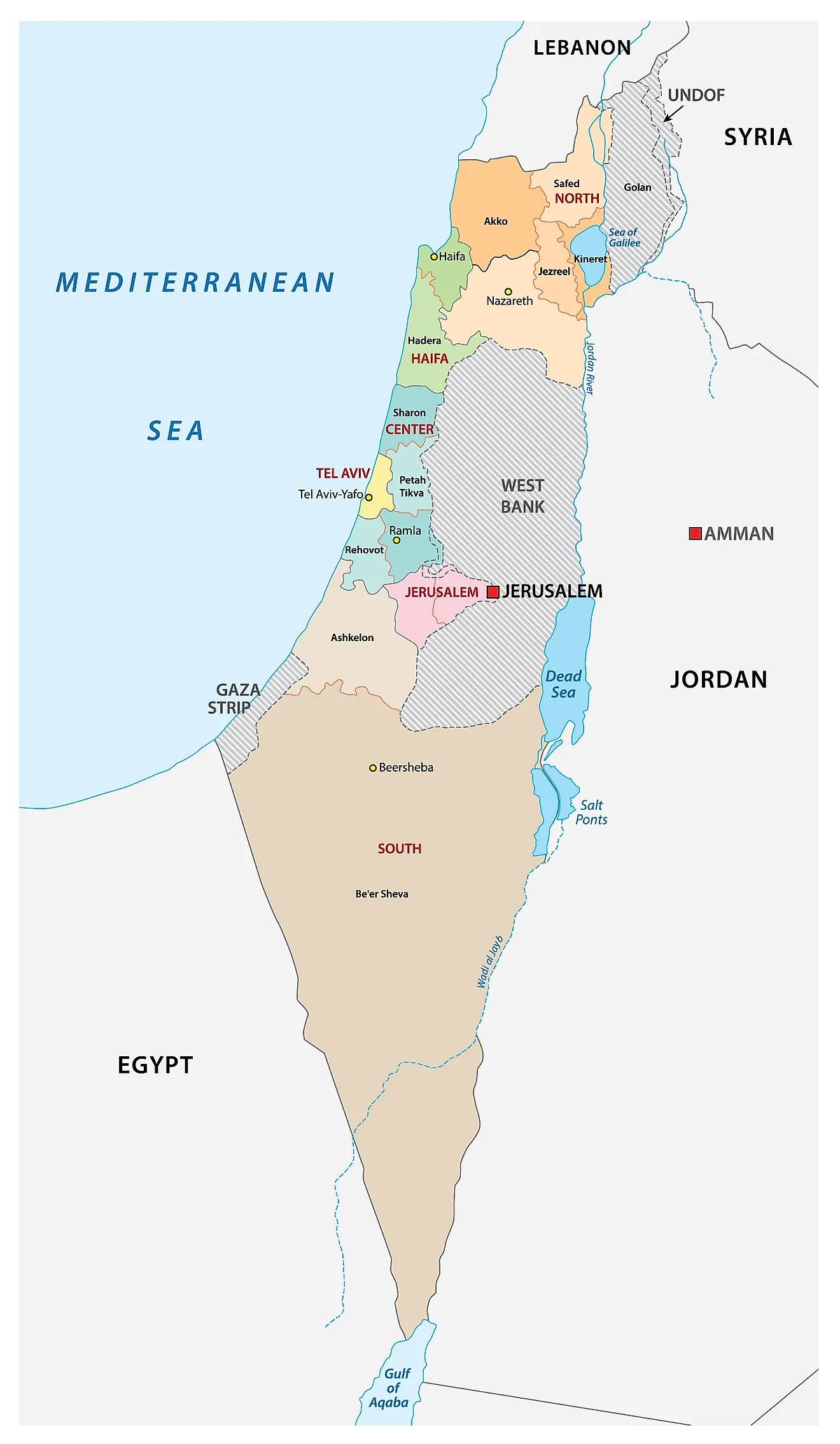
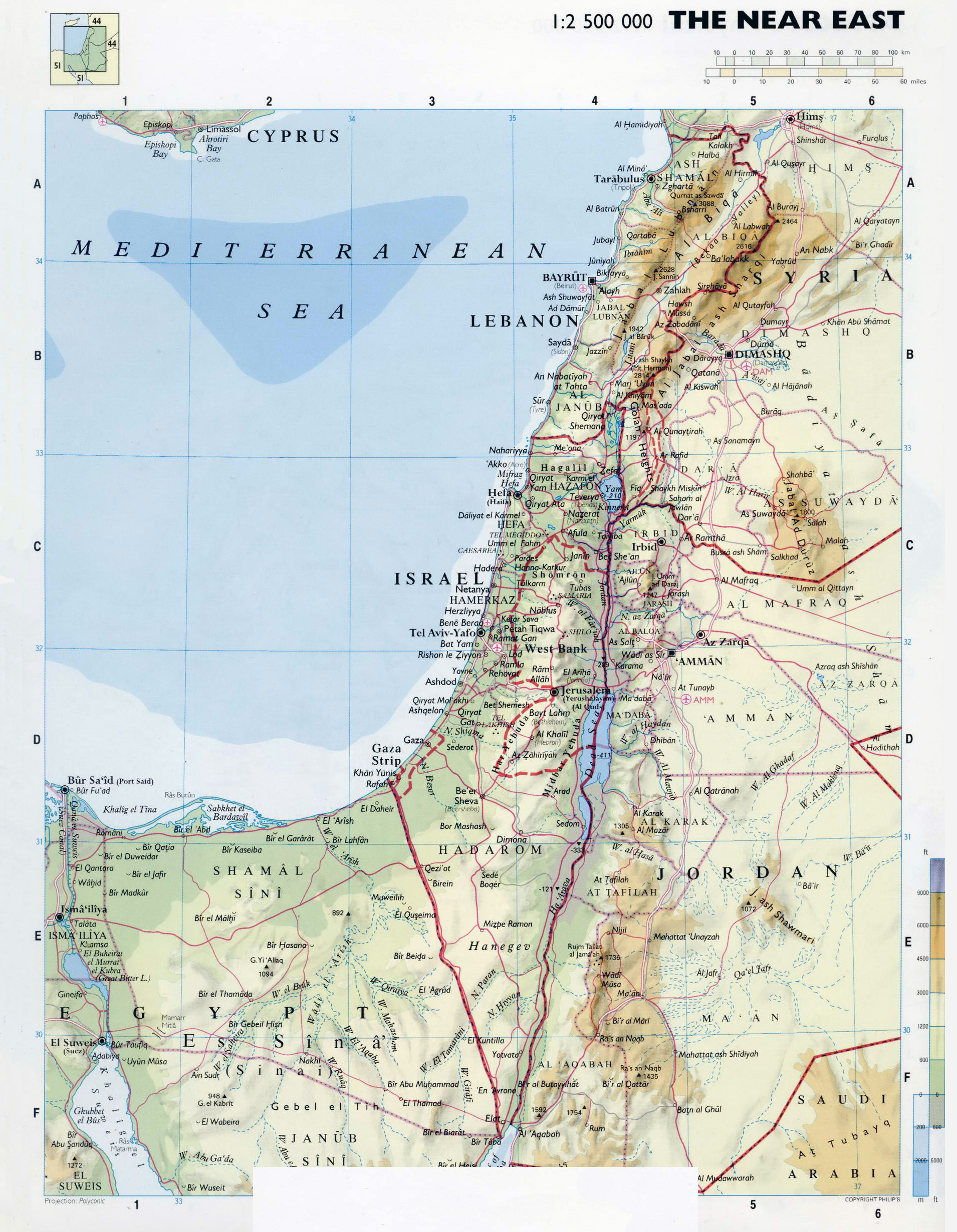
Israel, a relatively small country in the Middle East, is situated at the eastern edge of the Mediterranean Sea. Its physical geography encompasses a diverse range of landscapes, from the fertile coastal plain and the rolling hills of the Galilee to the arid Negev Desert in the south. The country is also home to the Dead Sea, the lowest point on Earth, and the Jordan River, a vital water source.
Historical Context:
The history of the land now known as Israel is deeply intertwined with the narratives of ancient empires, religious traditions, and modern nation-building. The region has been a crossroads of civilizations for millennia, home to significant events in Jewish, Christian, and Islamic history. Following World War II and the Holocaust, the Zionist movement gained momentum, advocating for a Jewish state in Palestine. The establishment of the State of Israel in 1948, following the British withdrawal from the region, was met with resistance from neighboring Arab states, leading to the first Arab-Israeli War.
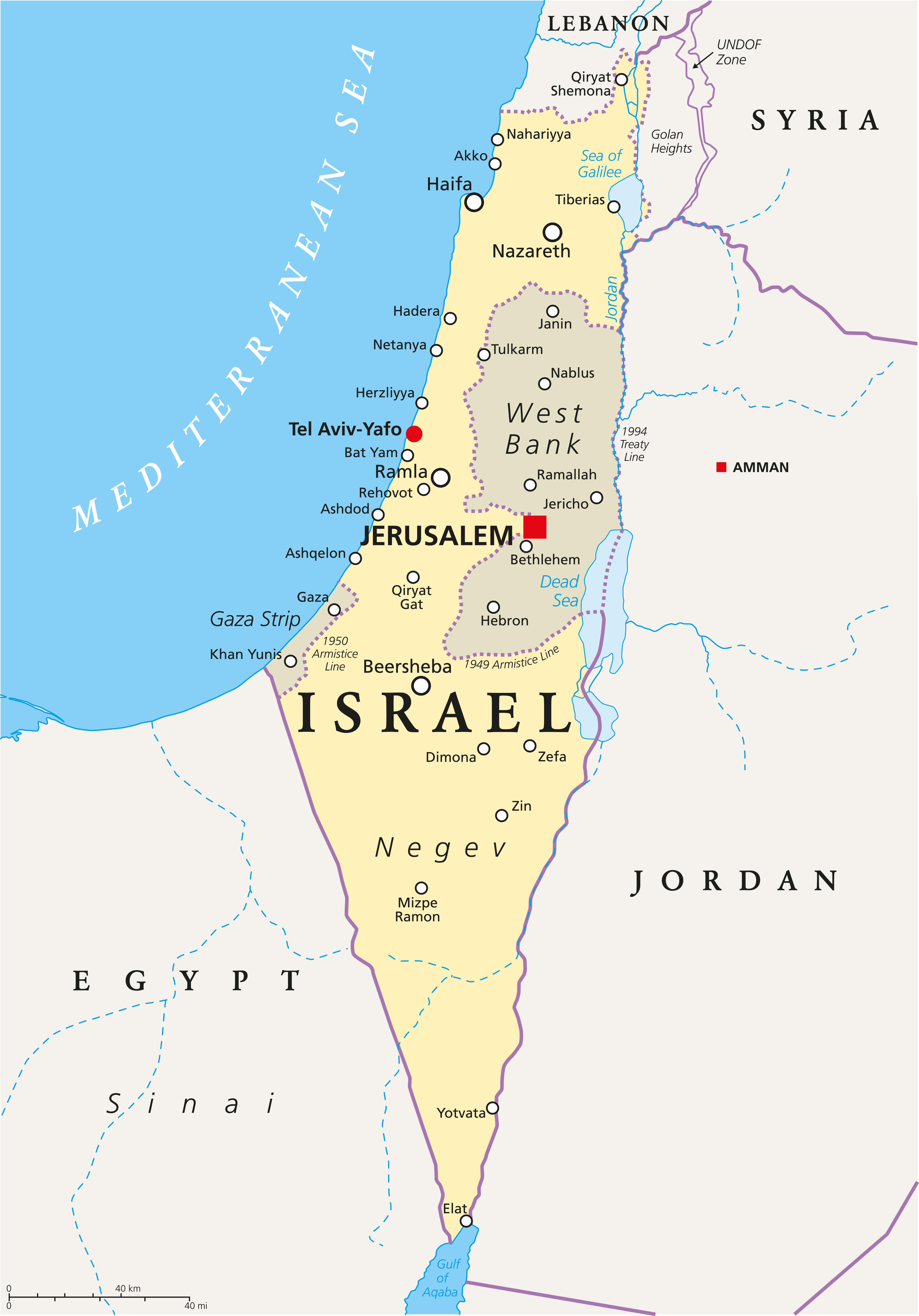
The Current Map:
The current map of Israel reflects the outcome of several wars and peace agreements. After the 1967 Six-Day War, Israel gained control of the West Bank, East Jerusalem, the Golan Heights, and the Sinai Peninsula. The Sinai Peninsula was returned to Egypt in 1982 following the Camp David Accords. However, the status of the West Bank, East Jerusalem, and the Golan Heights remains unresolved, leading to ongoing conflict and international disputes.
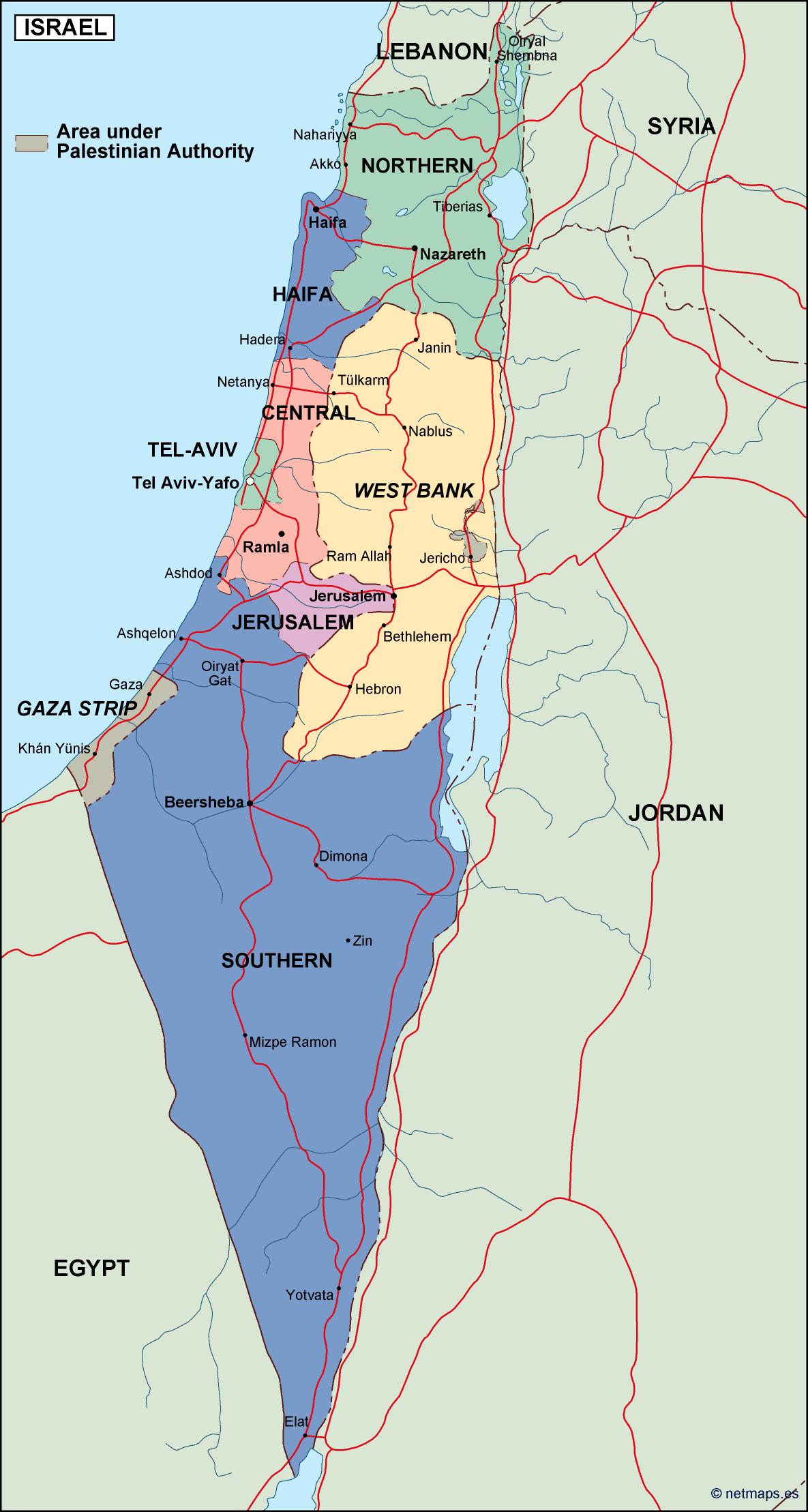
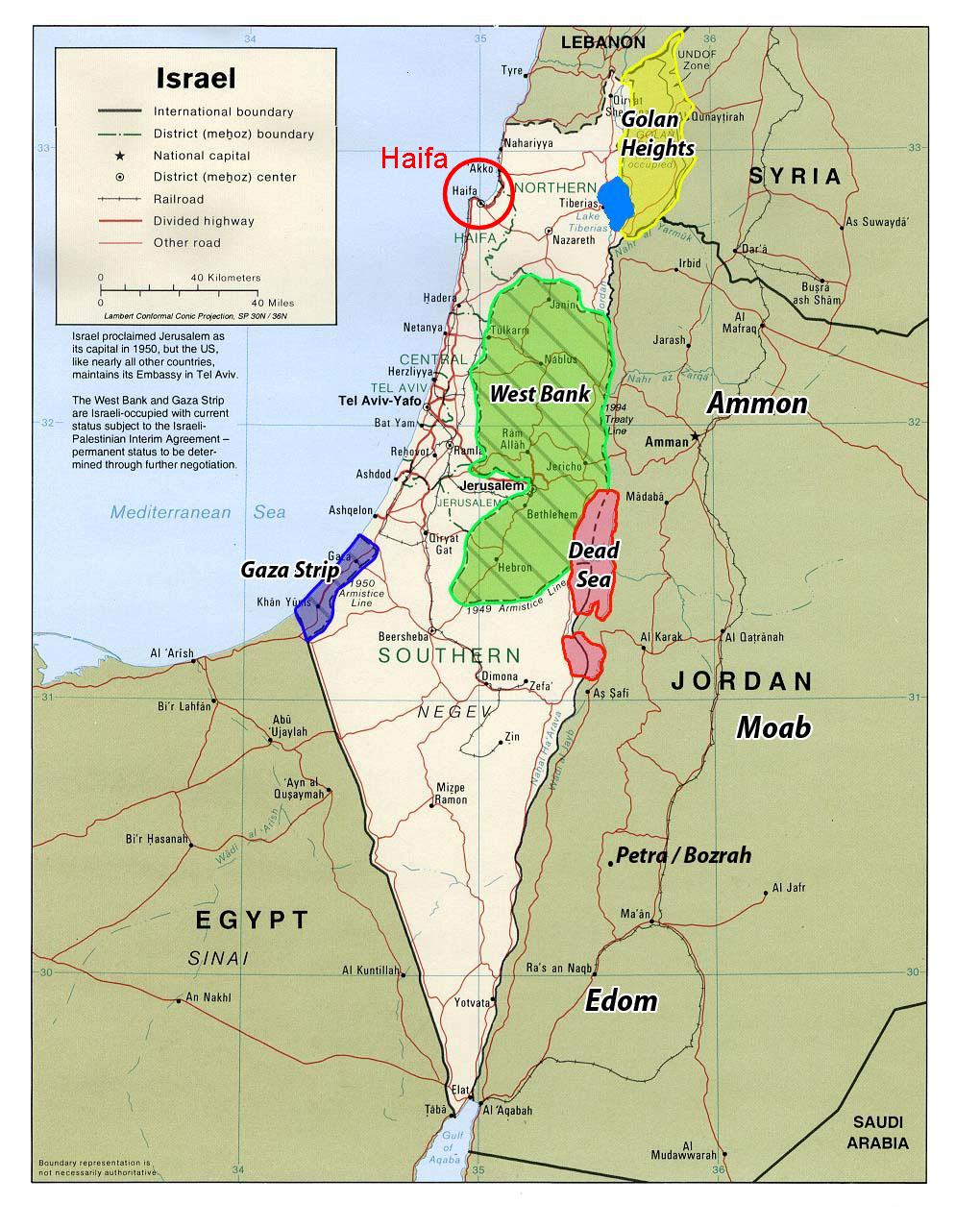
Key Features of the Current Map:
- Green Line: This line represents the pre-1967 borders of Israel, commonly referred to as the "1967 borders." It is often cited in international discussions regarding a potential two-state solution.
- West Bank: This territory, captured by Israel in 1967, is home to a significant Palestinian population. Its status is a major point of contention in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
- East Jerusalem: This section of Jerusalem, annexed by Israel in 1967, is claimed by Palestinians as the capital of a future state. It is a holy city for Jews, Christians, and Muslims, further complicating its political status.
- Golan Heights: This strategic plateau, captured from Syria in 1967, is a source of tension between Israel and Syria. Israel’s annexation of the Golan Heights is not recognized by the international community.
- Gaza Strip: This densely populated coastal territory, controlled by Hamas since 2007, is separated from the West Bank by Israeli territory. The Gaza Strip is subject to Israeli blockades, leading to humanitarian concerns.
The Israeli-Palestinian Conflict:
The current map of Israel is inextricably linked to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, one of the most enduring and complex conflicts in the world. The conflict revolves around competing claims to the same land, with both Israelis and Palestinians asserting their historical and cultural ties to the region. The conflict has been marked by violence, terrorism, and political deadlock, with no clear path towards a lasting peace agreement.
International Perspectives:
The international community holds diverse views on the current map of Israel and the ongoing conflict. Some countries support a two-state solution, advocating for the creation of an independent Palestinian state alongside Israel. Others support a one-state solution, proposing a unified state with equal rights for both Israelis and Palestinians. The status of Jerusalem, the West Bank, and the Golan Heights remains a contentious issue, with differing opinions on their future.
Challenges and Prospects:
The current map of Israel presents numerous challenges, including:
- Security Concerns: The ongoing conflict and the presence of armed groups pose significant security risks for both Israelis and Palestinians.
- Economic Disparities: The economic gap between Israelis and Palestinians is significant, contributing to social tensions and inequality.
- Political Impasse: The lack of progress in peace negotiations has created a sense of frustration and despair on both sides of the conflict.
- International Pressure: The international community’s involvement in the conflict, often with differing agendas, can complicate efforts to find a lasting solution.
Despite the challenges, there are also glimmers of hope. Some Israelis and Palestinians are actively working towards peace and reconciliation, advocating for dialogue, understanding, and compromise. The international community continues to play a role in facilitating negotiations and providing humanitarian assistance.
FAQs about the Current Map of Israel:
1. What are the current borders of Israel?
The current borders of Israel are contested and subject to ongoing debate. The internationally recognized borders of Israel are the pre-1967 borders, known as the "Green Line." However, Israel controls the West Bank, East Jerusalem, and the Golan Heights, which are not recognized as part of Israel by the international community.
2. What is the status of the West Bank?
The West Bank is a disputed territory, occupied by Israel since 1967. It is home to a significant Palestinian population, and its future remains uncertain. Some advocate for a two-state solution, with the West Bank becoming part of an independent Palestinian state, while others support a one-state solution, with the West Bank becoming part of a unified Israel.
3. What is the status of East Jerusalem?
East Jerusalem is claimed by both Israel and Palestine. Israel annexed East Jerusalem in 1967, but this annexation is not recognized by the international community. Palestinians consider East Jerusalem to be the capital of a future state. The status of East Jerusalem is one of the most sensitive issues in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
4. What is the situation in the Gaza Strip?
The Gaza Strip is a densely populated coastal territory controlled by Hamas, a Palestinian Islamist group. It is separated from the West Bank by Israeli territory and subject to Israeli blockades, leading to humanitarian concerns. The situation in Gaza is volatile and prone to conflict.
5. What is the role of the international community in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict?
The international community plays a significant role in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. It provides humanitarian assistance, facilitates negotiations, and imposes sanctions on both sides. However, differing perspectives on the conflict and the lack of consensus on a solution have hampered progress.
Tips for Understanding the Current Map of Israel:
- Consult multiple sources: Seek information from diverse perspectives, including academic journals, news articles, and reports from international organizations.
- Consider historical context: Understanding the historical events that have shaped the current map is crucial for comprehending the complexities of the conflict.
- Engage with different viewpoints: Seek out perspectives from both Israelis and Palestinians to gain a nuanced understanding of the conflict.
- Stay informed about ongoing developments: The situation in Israel and Palestine is constantly evolving, so it is important to stay informed about current events.
Conclusion:
The current map of Israel is a product of history, politics, and conflict. It reflects the complex and often contentious relationship between Israelis and Palestinians, with no easy answers or solutions. Understanding the historical context, the key features of the map, and the ongoing challenges is crucial for engaging in informed discussions about the future of the region. While the path towards peace remains uncertain, understanding the current map of Israel is essential for navigating the complexities of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict and advocating for a just and lasting resolution.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Current Map of Israel: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!