The Sioux Nation: A Historical and Geographical Perspective
Related Articles: The Sioux Nation: A Historical and Geographical Perspective
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Sioux Nation: A Historical and Geographical Perspective. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Sioux Nation: A Historical and Geographical Perspective
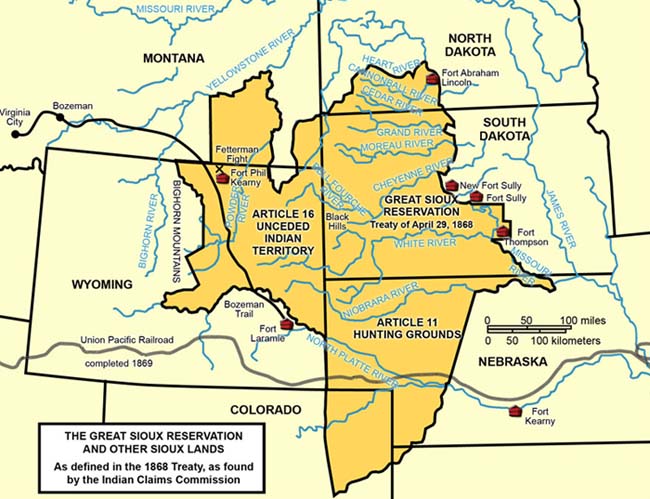
The term "Sioux Nation" encompasses a complex and diverse group of Indigenous peoples, historically known as the Lakota, Dakota, and Nakota. While often referred to collectively, it’s crucial to understand that these are distinct nations with their own languages, cultures, and histories.
Understanding the Sioux: A Historical Perspective
The Sioux people, historically known as the "Oceti Sakowin" (Seven Council Fires), were traditionally nomadic hunter-gatherers who inhabited the vast plains of North America, stretching from the Missouri River in the east to the Rocky Mountains in the west. This expansive territory encompassed areas that are now part of present-day North Dakota, South Dakota, Nebraska, Montana, Wyoming, and Minnesota.
The Sioux tribes were known for their skilled horsemanship, their reliance on the buffalo for sustenance and resources, and their intricate social and spiritual systems. They lived in harmony with the land, respecting its bounty and adhering to a deep understanding of its cycles.
The Impact of European Colonization
The arrival of European colonists in the 18th and 19th centuries dramatically altered the lives of the Sioux people. The introduction of diseases, the displacement from their ancestral lands, and the forced assimilation policies of the United States government led to significant hardship and cultural disruption.
The United States government, through treaties and executive orders, systematically sought to confine the Sioux to reservations, often in areas deemed unsuitable for agriculture. This forced relocation resulted in the loss of traditional hunting grounds, disrupting their way of life and leading to conflict.
The Sioux Nation Today
The Sioux people today continue to reside on reservations throughout the Great Plains. Despite the challenges they have faced, they have persevered and maintained their cultural identities. The Sioux Nation is comprised of nine federally recognized tribes, each with its own distinct governance and cultural practices.
A Geographical Overview of the Sioux Nation
Understanding the geography of the Sioux Nation is essential for appreciating their historical experiences and their present-day realities. The reservations, scattered across the Great Plains, reflect the historical patterns of forced relocation and treaty-making.
- Lakota: The Lakota people, traditionally the westernmost of the three groups, inhabit reservations in South Dakota, including the Pine Ridge, Rosebud, Cheyenne River, and Standing Rock reservations.
- Dakota: The Dakota people, historically residing in the central plains, have reservations in South Dakota, North Dakota, and Minnesota. The largest of these is the Sisseton-Wahpeton Reservation in South Dakota.
- Nakota: The Nakota people, traditionally the easternmost group, reside in reservations in Montana and North Dakota. The Fort Belknap Reservation in Montana is one of their main territories.
The Importance of Understanding the Sioux Nation
The Sioux Nation, with its rich history, diverse cultures, and enduring resilience, is a vital part of the American tapestry. Understanding their past, their present, and their ongoing struggles is crucial for fostering a more inclusive and just society.
By engaging with the Sioux Nation’s history, we can gain a deeper understanding of the complex relationship between Indigenous peoples and the United States government, the impact of colonization, and the ongoing fight for self-determination and cultural preservation.
FAQs about the Sioux Nation
- What is the difference between the Lakota, Dakota, and Nakota? While often referred to collectively as "Sioux," these are distinct nations with their own languages, cultures, and histories. The Lakota are known for their strong warrior traditions, the Dakota for their agricultural practices, and the Nakota for their adaptability and cultural blending.
- Where are the Sioux reservations located? Sioux reservations are scattered throughout the Great Plains, primarily in South Dakota, North Dakota, Montana, and Minnesota. Each reservation is governed by its own tribal council and has its own unique cultural traditions.
- What is the significance of the Wounded Knee Massacre? The Wounded Knee Massacre, which occurred in 1890, was a tragic event in which US Army soldiers killed hundreds of unarmed Lakota men, women, and children. It represents a dark chapter in the history of the Sioux Nation and the broader relationship between Indigenous peoples and the United States government.
- What are the current challenges facing the Sioux Nation? The Sioux Nation continues to face challenges related to poverty, lack of access to healthcare, education, and economic opportunities. They also face issues related to environmental degradation and the impacts of climate change on their traditional lands.
- How can I learn more about the Sioux Nation? There are numerous resources available to learn more about the Sioux Nation, including books, documentaries, museums, and websites dedicated to their history and culture. Visiting Sioux reservations and engaging with tribal members directly can provide valuable insights into their experiences and perspectives.
Tips for Understanding the Sioux Nation
- Approach the topic with respect and sensitivity: Remember that the Sioux Nation is a complex and diverse group of people with their own unique histories and perspectives.
- Engage with primary sources: Seek out firsthand accounts from Sioux elders, historians, and writers to gain a deeper understanding of their experiences.
- Support Indigenous-led organizations: There are many organizations dedicated to preserving Sioux culture, language, and traditions.
- Challenge Eurocentric narratives: Be critical of historical accounts that portray the Sioux Nation solely through the lens of colonialism.
- Embrace ongoing learning: The Sioux Nation’s history and culture are constantly evolving. Be open to learning new perspectives and challenging your own assumptions.
Conclusion
The Sioux Nation, with its rich history, enduring resilience, and diverse cultural traditions, is a vital part of the American story. Understanding their past, their present, and their ongoing struggles is essential for fostering a more inclusive and just society. By engaging with their history and culture, we can contribute to a more equitable future for all.






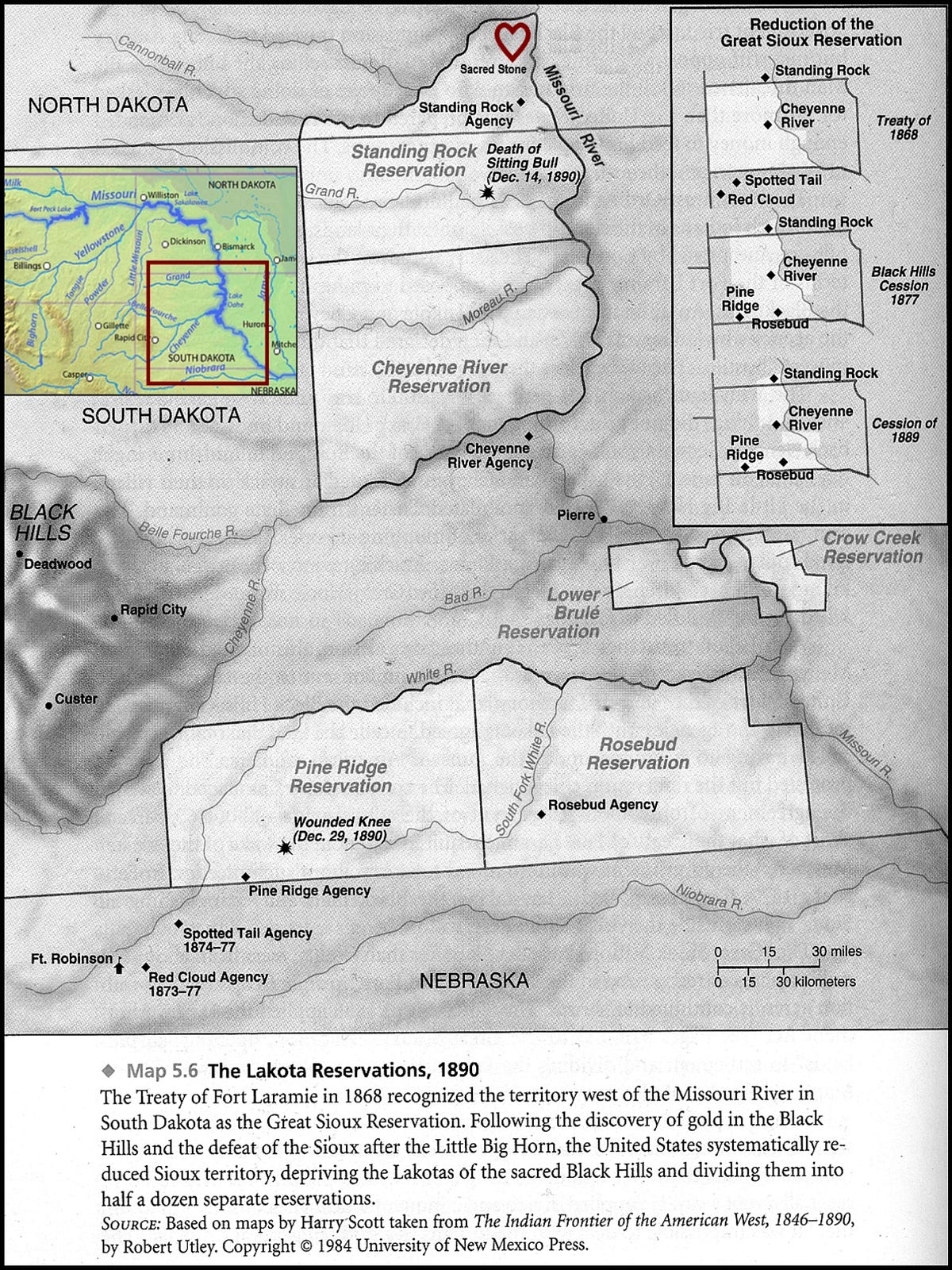
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Sioux Nation: A Historical and Geographical Perspective. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!