The Shifting Borders of Germany: A Historical Look at the 1940 Map
Related Articles: The Shifting Borders of Germany: A Historical Look at the 1940 Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Shifting Borders of Germany: A Historical Look at the 1940 Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Shifting Borders of Germany: A Historical Look at the 1940 Map

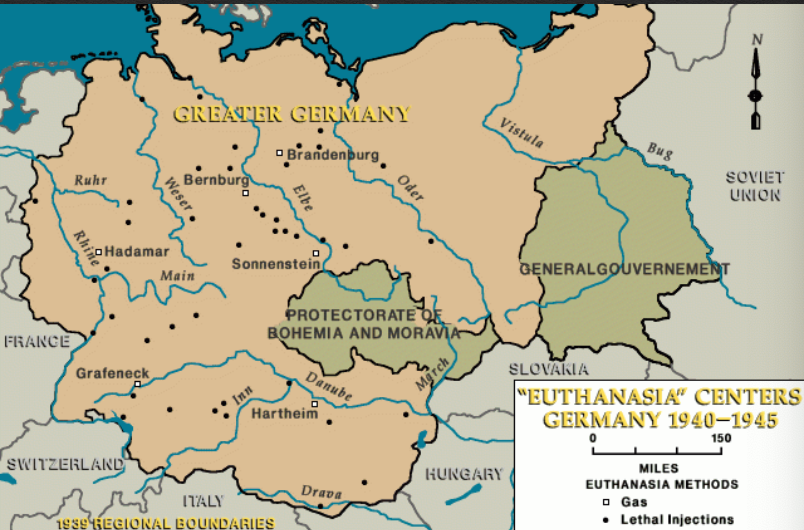
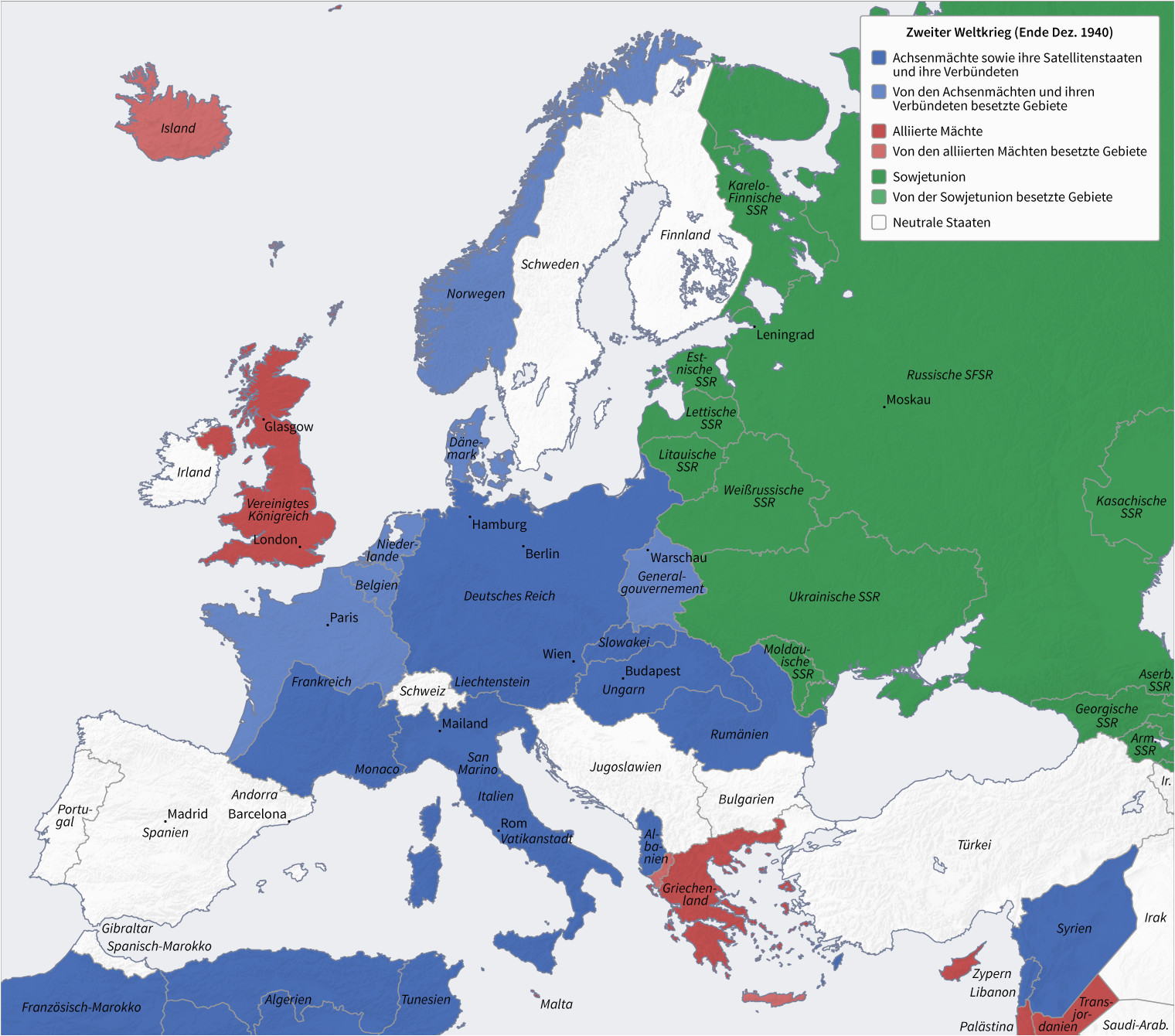
The map of Germany in 1940 presents a stark contrast to the modern-day political landscape of Europe. This period, marked by the height of Nazi Germany’s territorial expansion, reveals a complex web of territorial changes, annexations, and occupations that significantly impacted the geopolitical landscape of the continent.
The Pre-War Landscape:
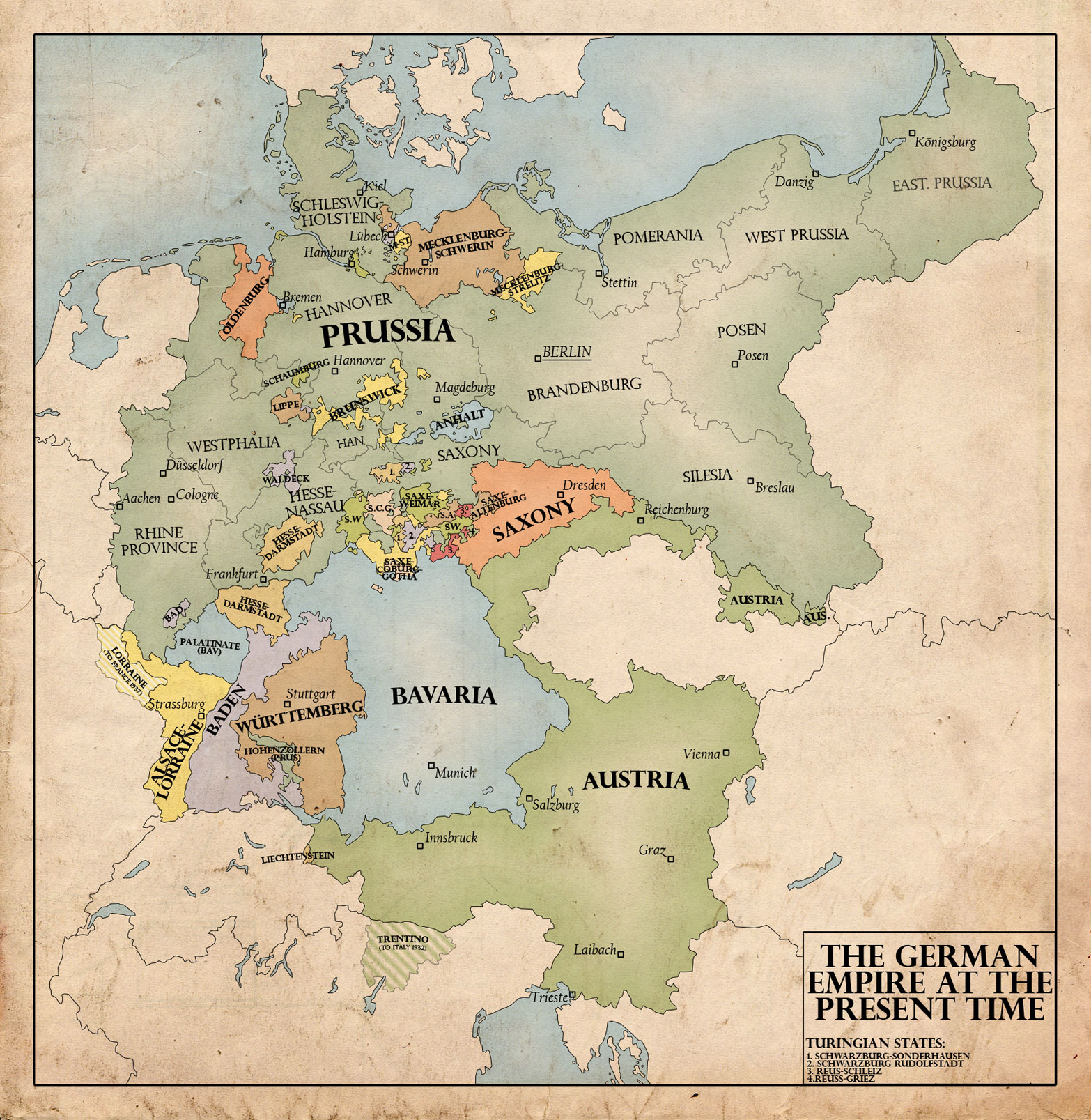
Before the outbreak of World War II, Germany’s borders were defined by the Treaty of Versailles, signed in 1919. This treaty, imposed by the victorious Allied powers, aimed to punish Germany for its role in the First World War. It resulted in the loss of significant territories, including Alsace-Lorraine to France, parts of Upper Silesia to Poland, and the Saarland, placed under the administration of the League of Nations.
The Nazi Expansion:
With the rise of the Nazi regime under Adolf Hitler, Germany’s ambitions for territorial expansion began to take shape. This expansion was fueled by a combination of factors, including:
- Revisionist Ideologies: The Nazi ideology espoused the notion of "Lebensraum," or living space, for the German people. This concept justified the expansion of German territory into neighboring countries, particularly in Eastern Europe.
- Economic Motives: Germany sought to acquire valuable resources and industrial infrastructure from conquered territories to fuel its war machine and bolster its economic power.
- Military Ambition: Hitler’s aggressive military strategy aimed to establish German dominance in Europe, leading to a series of territorial conquests.
The Map of Germany in 1940:
By 1940, Germany had achieved significant territorial gains, dramatically altering its map:
- Annexation of Austria: In March 1938, Germany annexed Austria through the Anschluss, a move that was met with little resistance.
- Occupation of Czechoslovakia: Following the Munich Agreement in 1938, Germany occupied the Sudetenland, a region of Czechoslovakia with a significant German population. In March 1939, the remainder of Czechoslovakia was annexed.
- Invasion of Poland: In September 1939, Germany invaded Poland, triggering the outbreak of World War II. This invasion led to the occupation of a large part of Poland, with the remaining territory being divided between the Soviet Union and Germany.
- Occupation of France: After the swift defeat of France in 1940, Germany occupied the northern and western parts of the country, including Paris. The southern part of France was established as a collaborationist regime under the Vichy government.
- Expansion into the Balkans: Germany’s influence extended into the Balkans, with the occupation of Yugoslavia and Greece.
The Significance of the 1940 Map:
The map of Germany in 1940 serves as a powerful reminder of the devastating consequences of unchecked aggression and territorial expansion. It highlights:
- The Cost of War: The territorial changes of this period were achieved through brutal warfare, resulting in immense loss of life and widespread destruction.
- The Impact on Europe: The expansion of Nazi Germany profoundly disrupted the political and social fabric of Europe, leading to the displacement of millions of people, the rise of oppressive regimes, and the perpetuation of violence and intolerance.
- The Importance of International Cooperation: The events of this period underscore the importance of international cooperation and diplomacy in preventing conflict and maintaining stability.
FAQs:
Q: What territories did Germany annex or occupy in 1940?
A: In 1940, Germany annexed Austria, occupied Czechoslovakia, invaded and occupied a large part of Poland, occupied northern and western France, and extended its influence into the Balkans by occupying Yugoslavia and Greece.
Q: What were the main reasons for Germany’s territorial expansion?
A: Germany’s expansion was driven by a combination of factors, including the Nazi ideology of "Lebensraum," economic motives, and military ambition.
Q: What was the impact of Germany’s expansion on the map of Europe?
A: Germany’s territorial gains significantly altered the political map of Europe, leading to the creation of new borders and the displacement of millions of people.
Q: What were the consequences of Germany’s expansion?
A: Germany’s expansion resulted in widespread war, death, and destruction, profoundly impacting the political and social landscape of Europe.
Tips for Understanding the 1940 Map:
- Use Historical Maps: Refer to historical maps of Europe from 1940 to visualize the territorial changes.
- Study Primary Sources: Read firsthand accounts and documents from the period to gain a deeper understanding of the events and their impact.
- Explore the Context: Consider the historical context of the period, including the rise of Nazi Germany, the Treaty of Versailles, and the political landscape of Europe.
- Learn About the Impact: Research the consequences of Germany’s expansion, including the displacement of people, the rise of oppressive regimes, and the impact on the political and social landscape of Europe.
Conclusion:
The map of Germany in 1940 serves as a sobering reminder of the destructive nature of aggression and the importance of international cooperation. It highlights the fragility of peace and the need for vigilance against ideologies that promote violence and intolerance. By understanding the historical context of this period, we can learn from the mistakes of the past and strive to build a more peaceful and just future.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Shifting Borders of Germany: A Historical Look at the 1940 Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!