The Reformation Map: A Visual Journey Through the Religious Transformation of Europe
Related Articles: The Reformation Map: A Visual Journey Through the Religious Transformation of Europe
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Reformation Map: A Visual Journey Through the Religious Transformation of Europe. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Reformation Map: A Visual Journey Through the Religious Transformation of Europe

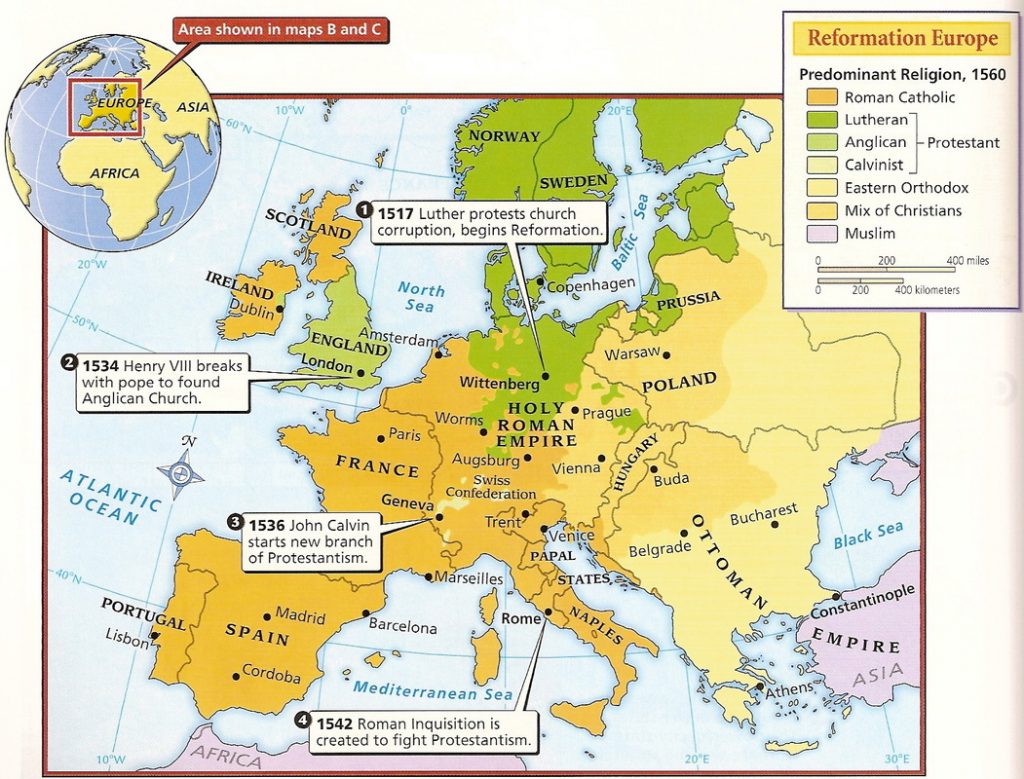
The Reformation, a pivotal period in European history, witnessed a dramatic shift in religious landscape. This seismic change, initiated by Martin Luther’s challenge to the Catholic Church’s authority, sparked a wave of religious reform and ultimately led to the emergence of Protestantism. To understand the complex and multifaceted nature of this historical event, it is essential to consider its geographical spread and the diverse responses it elicited across Europe.
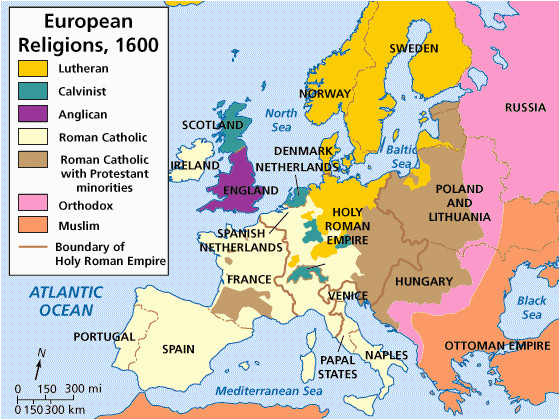
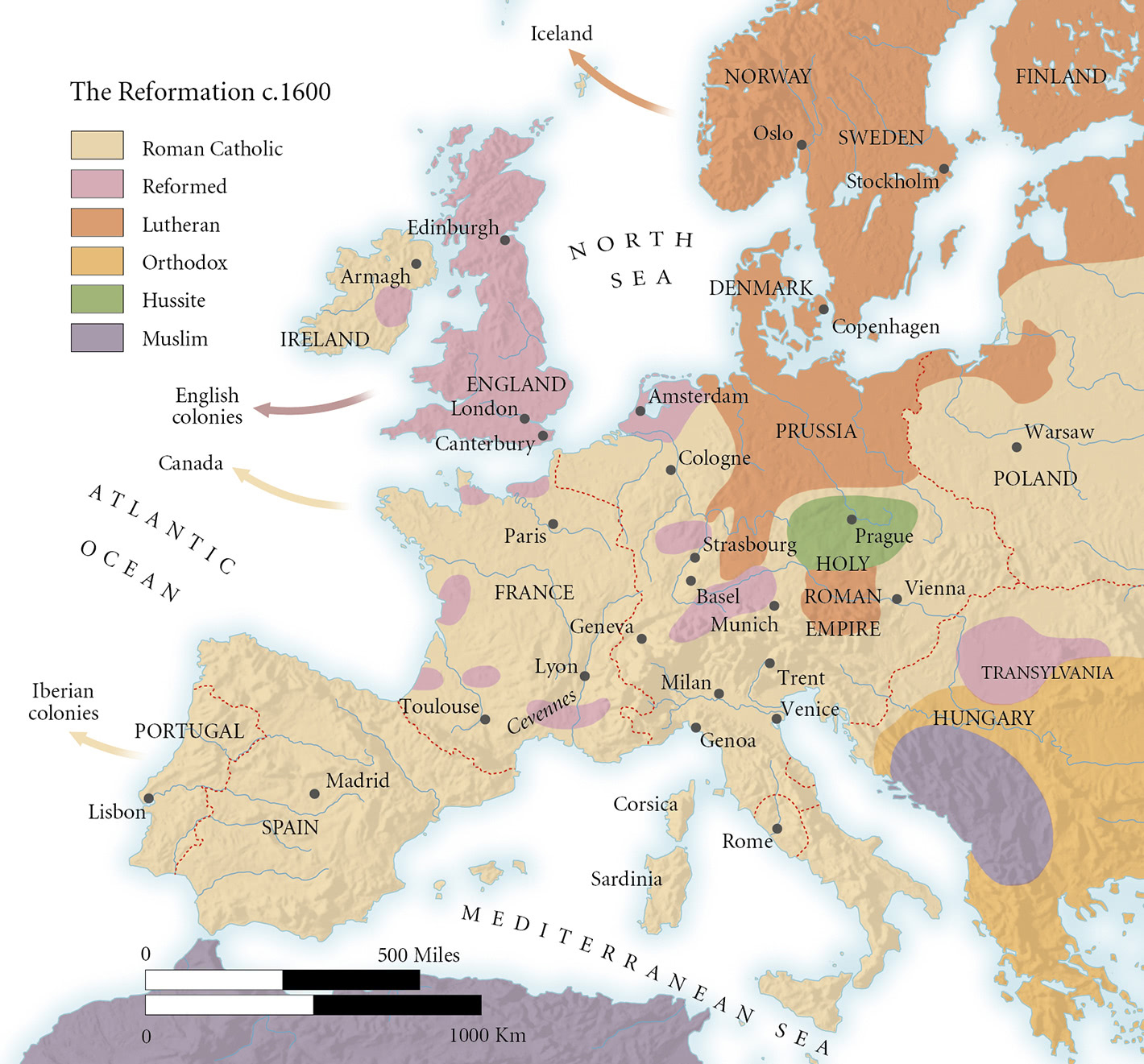
The Reformation Map, a visual representation of the Reformation’s geographical impact, provides a powerful tool for understanding this transformative period. It depicts the spread of Protestantism across Europe, highlighting the regions where it gained significant traction and those where it faced resistance or remained largely absent. This map not only reveals the geographical reach of the Reformation but also illuminates the intricate interplay of political, social, and religious factors that shaped its course.
Understanding the Reformation Map:
The Reformation Map typically presents a visual overview of Europe, with different regions colored according to the dominant religious affiliation. The following key elements are often included:
- Protestant Regions: These regions, typically colored in shades of red, orange, or yellow, indicate areas where Protestantism gained significant influence. This includes countries like England, Germany, Switzerland, Scotland, and parts of Scandinavia.
- Catholic Regions: These regions, typically colored in shades of blue or green, represent areas where Catholicism remained the dominant faith. This includes countries like France, Spain, Portugal, Italy, and parts of Eastern Europe.
- Mixed Regions: Some regions, often depicted in a combination of colors, indicate areas with a significant presence of both Catholicism and Protestantism. This reflects the complex religious landscape in countries like the Netherlands and Poland.
- Boundaries: The map often includes political boundaries of the time, allowing for an understanding of how political structures and alliances influenced the spread of the Reformation.
The Significance of the Reformation Map:
The Reformation Map serves as a valuable tool for historians, students, and anyone interested in understanding the Reformation’s profound impact on Europe. It offers several key insights:
- Geographical Reach: The map clearly demonstrates the Reformation’s widespread influence, extending beyond its origins in Germany to encompass significant parts of Europe. This highlights the movement’s ability to transcend geographical and cultural boundaries.
- Diversity of Responses: The map illustrates the diverse reactions to the Reformation across Europe. While some regions embraced Protestantism wholeheartedly, others remained staunchly Catholic, and still others experienced a complex mix of both faiths. This diversity reflects the intricate interplay of political, social, and religious factors that shaped the Reformation’s trajectory.
- Political Context: The map’s inclusion of political boundaries allows for an understanding of how political alliances, rivalries, and power dynamics influenced the spread of Protestantism. For example, the map highlights the role of powerful rulers like Henry VIII of England and Frederick the Wise of Saxony in promoting or suppressing Protestantism.
- Cultural Impact: The Reformation Map indirectly reflects the cultural and social changes brought about by the Reformation. The spread of Protestantism, with its emphasis on vernacular languages and biblical literacy, contributed to the development of national identities and the rise of literacy in many regions.
Beyond the Map: Exploring the Reformation’s Legacy:
While the Reformation Map provides a valuable visual representation of the Reformation’s geographical reach, it is important to remember that it represents only one aspect of this complex historical event. To truly understand the Reformation, we must consider its diverse theological, social, and political dimensions.
- Theological Debates: The Reformation was marked by intense theological debates about the nature of salvation, the role of the Church, and the interpretation of scripture. These debates led to the emergence of various Protestant denominations, including Lutheranism, Calvinism, and Anabaptism.
- Social and Political Change: The Reformation had a profound impact on European society and politics. It challenged the authority of the Catholic Church, leading to the rise of national churches and the emergence of new political structures. It also sparked religious wars and persecution, highlighting the deep divisions that the Reformation created within European society.
- Cultural and Intellectual Impact: The Reformation had a lasting impact on European culture and intellectual life. It encouraged biblical literacy, fostered the development of vernacular languages, and contributed to the rise of humanism and the Scientific Revolution.
FAQs about the Reformation Map:
1. What is the purpose of the Reformation Map?
The Reformation Map serves as a visual tool for understanding the geographical spread of the Reformation and its diverse responses across Europe. It highlights the regions where Protestantism gained traction, the areas where Catholicism remained dominant, and the mixed regions where both faiths coexisted.
2. What information is typically included on a Reformation Map?
A Reformation Map typically includes:
- Regions: Color-coded regions representing Protestant, Catholic, and mixed areas.
- Boundaries: Political boundaries of the time to understand the influence of political structures and alliances.
- Key Figures: Sometimes, key figures associated with the Reformation, such as Martin Luther, John Calvin, and Henry VIII, are marked on the map.
3. How does the Reformation Map reflect the political context of the Reformation?
The map’s inclusion of political boundaries allows for an understanding of how political alliances, rivalries, and power dynamics influenced the spread of Protestantism. It highlights the role of powerful rulers in promoting or suppressing the movement.
4. What are the limitations of the Reformation Map?
While the Reformation Map provides a valuable visual representation, it cannot fully capture the complex theological, social, and political dimensions of the Reformation. It is essential to consider these broader factors to gain a comprehensive understanding of this historical event.
5. Why is the Reformation Map important for understanding European history?
The Reformation Map is a crucial tool for understanding the profound impact of the Reformation on European history. It reveals the geographical reach of the movement, the diverse responses it elicited, and the lasting cultural, social, and political changes it brought about.
Tips for Using the Reformation Map:
- Compare and Contrast: Use the map to compare and contrast the spread of Protestantism in different regions of Europe. Consider the factors that contributed to its acceptance or rejection in specific areas.
- Analyze Political Influences: Examine the relationship between political boundaries and the spread of Protestantism. How did political alliances, rivalries, and power dynamics influence the Reformation’s trajectory?
- Connect to Broader Historical Events: Relate the Reformation Map to other historical events of the period, such as the Renaissance, the Scientific Revolution, and the Thirty Years’ War.
- Consider the Human Dimension: Remember that the Reformation was not just a geographical or theological phenomenon. It involved real people with diverse beliefs, motivations, and experiences. Explore the lives of individuals who were affected by the Reformation.
Conclusion:
The Reformation Map is a powerful visual tool that provides a valuable framework for understanding the geographical impact of the Reformation. It highlights the movement’s widespread influence, the diverse responses it elicited across Europe, and the lasting cultural, social, and political changes it brought about. However, it is crucial to remember that the map represents only one aspect of this complex historical event. To fully appreciate the Reformation, we must consider its theological, social, and political dimensions, and explore the lives of the individuals who shaped its course. By doing so, we can gain a deeper understanding of this pivotal period in European history and its lasting legacy.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Reformation Map: A Visual Journey Through the Religious Transformation of Europe. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!