The Power of Visual Storytelling: Understanding the United States through Color-Coded Maps
Related Articles: The Power of Visual Storytelling: Understanding the United States through Color-Coded Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Power of Visual Storytelling: Understanding the United States through Color-Coded Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Power of Visual Storytelling: Understanding the United States through Color-Coded Maps

The United States, a vast and diverse nation, is often best understood through visual representation. Among these, color-coded maps stand out as powerful tools for communicating complex data and fostering deeper understanding. These maps, utilizing color variations to highlight specific geographical features or statistical trends, offer a compelling visual narrative that transcends words.
The Fundamentals of Color-Coded Maps
At their core, color-coded maps rely on the principle of visual encoding. By assigning distinct colors to different categories or data values, they transform numerical data into readily interpretable visual patterns. This allows viewers to quickly identify spatial relationships, trends, and anomalies that might otherwise remain obscured.
Types of Color-Coded Maps and Their Applications
The versatility of color-coded maps is evident in their diverse applications across various fields:
1. Geographic Maps:
- Physical Features: Depicting landforms like mountains, rivers, and deserts with distinct colors helps visualize the country’s topography.
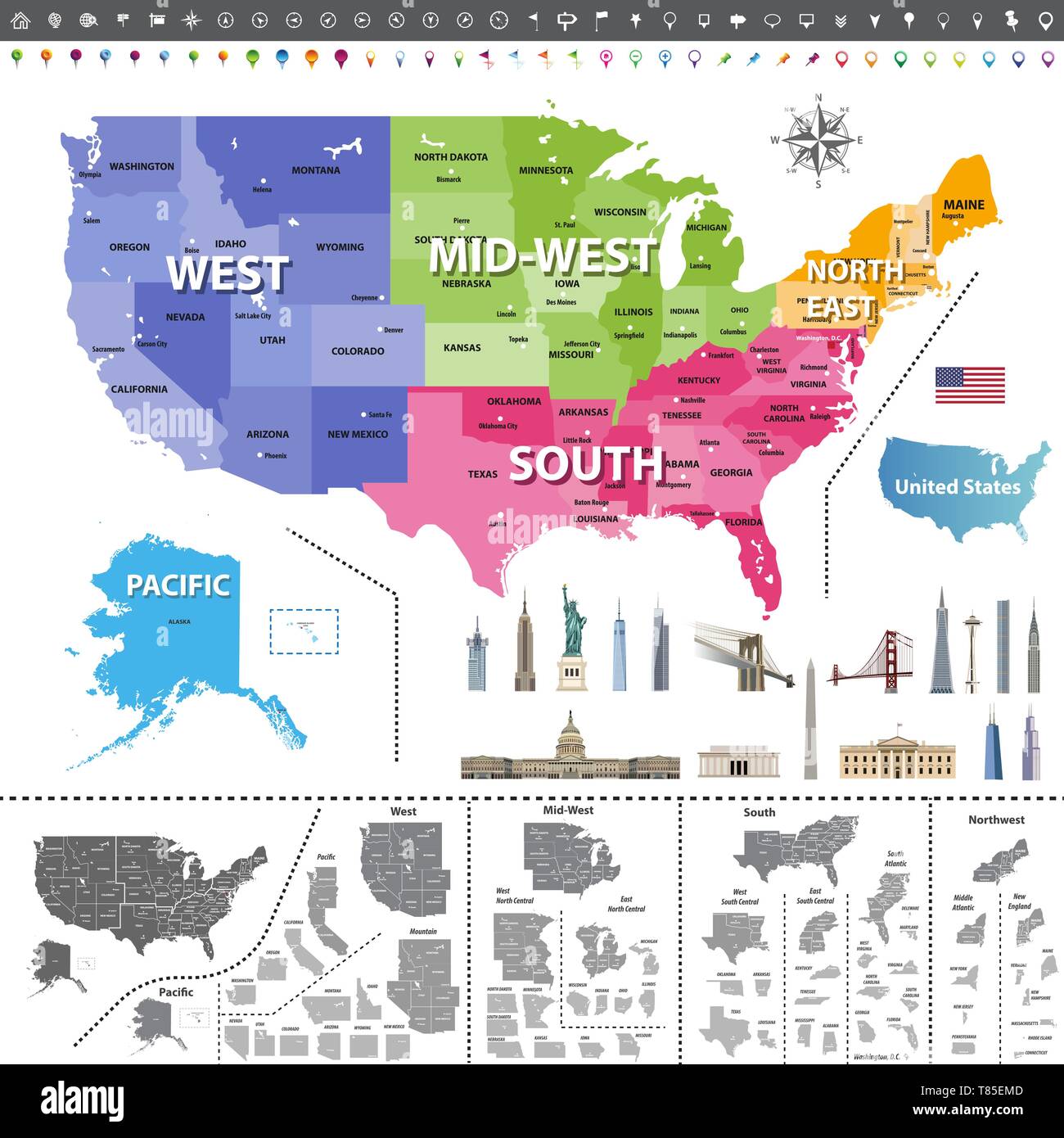
- Political Boundaries: State borders, county lines, and national parks are often highlighted using different colors, facilitating understanding of administrative divisions.
- Climate Zones: Color-coded maps effectively illustrate variations in temperature, rainfall, and other climatic factors across the country.
2. Demographic Maps:
- Population Density: Colors can represent population density, revealing areas of high concentration and sparsity.
- Ethnic Composition: Mapping ethnic groups based on their geographic distribution provides valuable insights into cultural diversity.
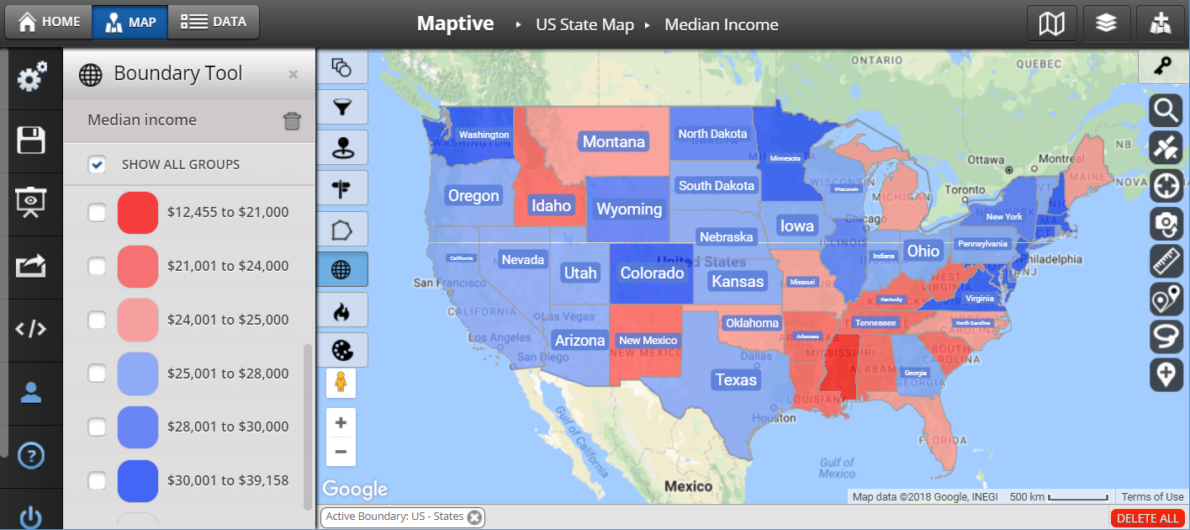
- Socioeconomic Indicators: Color-coding can represent income levels, poverty rates, or educational attainment, highlighting regional disparities.
3. Economic Maps:
- Agricultural Production: Different colors can indicate major agricultural products grown in specific regions, demonstrating agricultural specialization.
- Industrial Activity: Mapping industrial sectors by location reveals the geographic distribution of economic activity and potential resource concentration.
- Trade Flows: Color-coded maps can illustrate the movement of goods and services, highlighting important trade routes and economic interdependence.
4. Environmental Maps:
- Air Pollution: Color gradients can represent levels of air pollutants, identifying areas with high concentrations and potential health risks.
- Water Quality: Mapping water quality indicators like pH levels and nutrient concentrations allows for monitoring and management of water resources.
- Natural Disasters: Color-coding can depict areas prone to earthquakes, hurricanes, or wildfires, aiding in disaster preparedness and mitigation efforts.
Benefits of Color-Coded Maps
- Enhanced Visual Communication: Color-coded maps transform complex data into easily digestible visual representations, making information accessible to a wider audience.
- Improved Spatial Awareness: By highlighting geographical relationships, these maps foster a deeper understanding of the spatial distribution of data, promoting informed decision-making.
- Effective Data Visualization: Color gradients and patterns effectively reveal trends, anomalies, and spatial correlations, fostering insights that might be missed in raw data.
- Enhanced Engagement: The visual appeal of color-coded maps can enhance audience engagement, promoting interest and understanding of complex data.
Understanding Color Choices
The effectiveness of a color-coded map hinges on the appropriate selection and application of colors. Certain color combinations are more effective than others in conveying specific information:
- Sequential Colors: Gradient variations of a single hue (e.g., blue to green) are ideal for representing continuous data like temperature or elevation.
- Diverging Colors: Two contrasting colors (e.g., red and blue) are effective for highlighting deviations from a central value or contrasting categories.
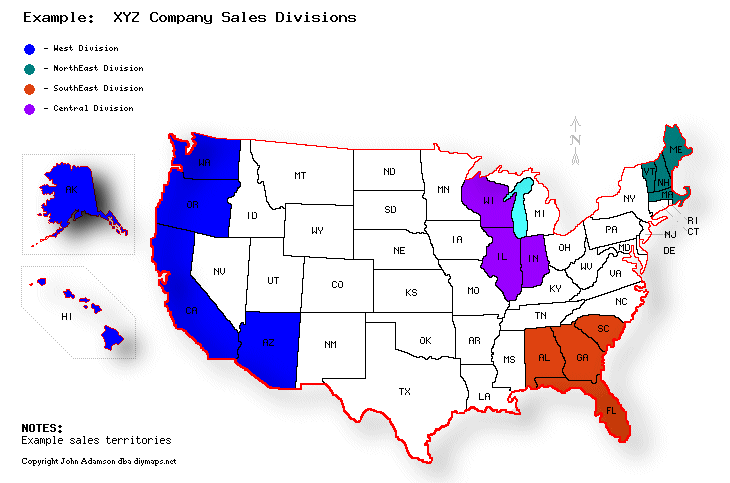
- Categorical Colors: Distinct, unrelated colors (e.g., red, blue, green) are used for representing distinct categories or groups.
Color Perception and Cultural Considerations
It’s crucial to consider color perception and cultural associations when selecting colors for maps. For instance, red is often associated with danger or heat, while green represents growth or prosperity. These associations can influence viewers’ interpretation of the data, necessitating careful color selection.
FAQs about Color-Coded Maps of the United States
1. What are the most common types of color-coded maps used to represent the United States?
Common types include maps depicting population density, economic activity, climate zones, political boundaries, and natural resources.
2. How can color-coded maps be used to highlight regional disparities in the United States?
By representing socioeconomic indicators like income levels, poverty rates, or educational attainment, color-coded maps can visually illustrate disparities between different regions.
3. What are the ethical considerations associated with using color-coded maps?
It’s crucial to avoid perpetuating stereotypes or biases through color selection. Color choices should be data-driven and reflect accurate representation.
4. How can color-coded maps contribute to informed decision-making?
By providing clear visual insights into spatial patterns and trends, color-coded maps can support informed decision-making in areas such as resource management, infrastructure development, and policy planning.
Tips for Creating Effective Color-Coded Maps
- Choose a clear and intuitive color scheme: Utilize color combinations that are readily interpretable and avoid confusing or clashing colors.
- Use legends and labels effectively: Provide clear explanations of color meanings and data values to ensure accurate interpretation.
- Maintain visual consistency: Use the same color scheme throughout the map to avoid confusion and promote visual coherence.
- Consider accessibility: Choose colors that are easily distinguishable by individuals with color vision deficiencies.
Conclusion
Color-coded maps of the United States offer a powerful and versatile tool for visualizing complex data, fostering deeper understanding, and promoting informed decision-making. By effectively utilizing color as a visual language, these maps can effectively communicate spatial relationships, trends, and anomalies, providing a compelling narrative that transcends words. Whether exploring physical features, demographic trends, or economic activity, color-coded maps remain essential tools for understanding the United States’ diverse landscape and its interconnected complexities.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Visual Storytelling: Understanding the United States through Color-Coded Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!