The Amish Presence in Wisconsin: A Map of Tradition and Community
Related Articles: The Amish Presence in Wisconsin: A Map of Tradition and Community
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Amish Presence in Wisconsin: A Map of Tradition and Community. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Amish Presence in Wisconsin: A Map of Tradition and Community
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Amish Presence in Wisconsin: A Map of Tradition and Community
- 3.1 A Tapestry of Settlement: Mapping the Amish in Wisconsin
- 3.2 Understanding the Map: A Glimpse into Amish Culture
- 3.3 The Map as a Tool for Engagement: Navigating the Amish World
- 3.4 Frequently Asked Questions About the Amish in Wisconsin
- 3.5 Tips for Interacting with Amish Communities
- 3.6 Conclusion: A Legacy of Tradition and Resilience
- 4 Closure
The Amish Presence in Wisconsin: A Map of Tradition and Community
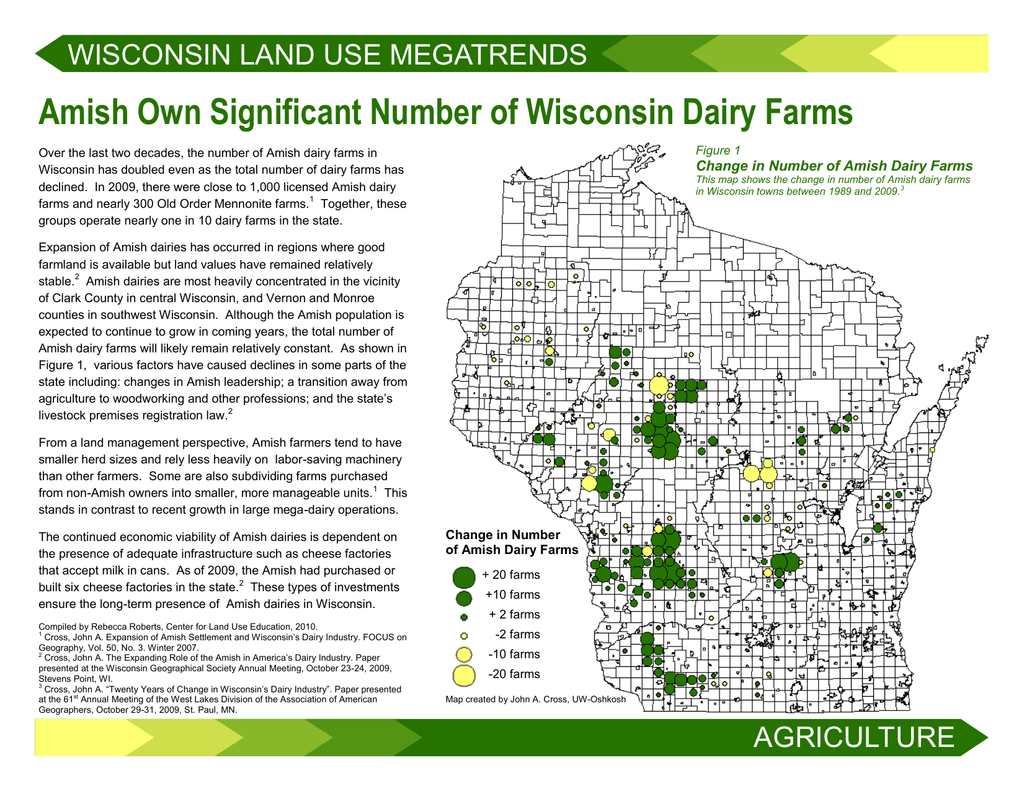
The Amish, a religious group known for their simple lifestyle and commitment to tradition, have a significant presence in Wisconsin. Understanding the geographical distribution of Amish communities in the state provides valuable insights into their cultural practices, economic contributions, and the challenges they face in modern society.
A Tapestry of Settlement: Mapping the Amish in Wisconsin
Wisconsin’s Amish population is concentrated in the southeastern and south-central regions of the state, with a notable presence in the following counties:
- Green County: Known as the "Amish Capital of Wisconsin," Green County boasts the largest concentration of Amish settlements. Its rolling hills and fertile farmlands provide ideal conditions for their traditional agricultural practices.
- Monroe County: Situated south of Green County, Monroe County is home to a significant Amish population, with settlements scattered across its countryside.
- Dane County: While primarily known for its vibrant city of Madison, Dane County also harbors several Amish communities, particularly in its rural outskirts.
- Iowa County: This county, located west of Dane County, has a growing Amish presence, with settlements primarily concentrated in its agricultural areas.
- Sauk County: Known for its scenic beauty and rolling hills, Sauk County is home to a small but growing Amish community, particularly in its rural areas.
These are just a few of the counties with established Amish settlements. Smaller communities can also be found in other parts of the state, contributing to the overall tapestry of Amish life in Wisconsin.
Understanding the Map: A Glimpse into Amish Culture
The geographical distribution of Amish communities in Wisconsin reveals valuable insights into their cultural practices and values. The concentration of settlements in rural areas reflects their preference for a simple life, close to nature, and free from the distractions of modern society.
Their agricultural pursuits, evident in the choice of settlement locations, are central to their economic self-sufficiency and way of life. The communities often operate their own businesses, schools, and social structures, fostering a strong sense of self-reliance and community cohesion.
The map also highlights the historical migration patterns of the Amish in Wisconsin. Many settlements originated from Pennsylvania and Ohio, reflecting the ongoing movement of Amish communities seeking new lands and opportunities.
The Map as a Tool for Engagement: Navigating the Amish World
The map of Amish settlements in Wisconsin serves as a valuable tool for understanding their cultural practices, economic contributions, and the challenges they face. It enables researchers, policymakers, and the general public to:
- Gain a deeper understanding of their cultural practices: By identifying the locations of Amish communities, researchers can better understand their traditions, beliefs, and values.
- Analyze their economic contributions: The map helps to assess the economic impact of Amish communities on the state, particularly in terms of agriculture, small businesses, and local employment.
- Address the challenges they face: Understanding the geographical distribution of Amish communities allows for a more targeted approach to addressing issues such as access to healthcare, education, and social services.
Frequently Asked Questions About the Amish in Wisconsin
1. What is the estimated population of Amish in Wisconsin?
The exact number of Amish in Wisconsin varies, but estimates suggest a population of several thousand. The Amish do not participate in official censuses, making precise population data difficult to obtain.
2. What are the main occupations of Amish in Wisconsin?
Agriculture remains a central occupation for most Amish in Wisconsin. They are known for their farming skills and dedication to traditional methods. Other common occupations include woodworking, furniture making, and craft-based businesses.
3. Do Amish in Wisconsin use modern technology?
The Amish generally avoid modern technology, particularly those they perceive as disruptive to their traditional way of life. They commonly use horse-drawn buggies for transportation and rely on manual labor for most tasks. However, some communities may adopt certain technologies, such as electricity or telephones, for specific purposes.
4. How do Amish schools differ from public schools?
Amish schools are typically one-room schoolhouses, where students of various ages are taught together. The curriculum focuses on basic subjects, such as reading, writing, arithmetic, and biblical studies. They emphasize practical skills and traditional values, with limited exposure to secular subjects or modern technology.
5. How do Amish communities interact with the outside world?
While Amish communities are generally self-sufficient, they do interact with the outside world for essential goods and services. They may engage in trade, purchase supplies from local businesses, and seek medical care when necessary. However, they maintain a distinct cultural identity and strive to minimize interactions that could compromise their traditional way of life.
Tips for Interacting with Amish Communities
- Respect their privacy: Amish communities value their privacy and may be wary of outsiders. It is essential to be respectful of their boundaries and avoid intrusive behavior.
- Be mindful of their beliefs and practices: The Amish have a strong set of beliefs and practices that shape their daily lives. It is important to be respectful of their traditions and avoid behaviors that may be considered offensive.
- Communicate respectfully: When interacting with Amish individuals, use simple language and avoid slang or jargon. Show genuine interest in their culture and way of life without being intrusive.
- Support local businesses: The Amish often operate their own businesses, such as furniture shops, craft stores, and farm markets. Supporting these businesses helps to contribute to their economic well-being.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Tradition and Resilience
The Amish communities in Wisconsin, as reflected in the map of their settlements, represent a living testament to the enduring power of tradition and community. Their commitment to a simple lifestyle, their dedication to agricultural pursuits, and their strong social bonds have allowed them to maintain a unique cultural identity in a rapidly changing world.
The map serves as a valuable tool for understanding their cultural practices, economic contributions, and the challenges they face. By fostering respectful engagement and appreciation for their traditions, we can contribute to the continued preservation of this unique and resilient community.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Amish Presence in Wisconsin: A Map of Tradition and Community. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!