The American Electoral Landscape: Understanding the State Voting Map
Related Articles: The American Electoral Landscape: Understanding the State Voting Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The American Electoral Landscape: Understanding the State Voting Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The American Electoral Landscape: Understanding the State Voting Map
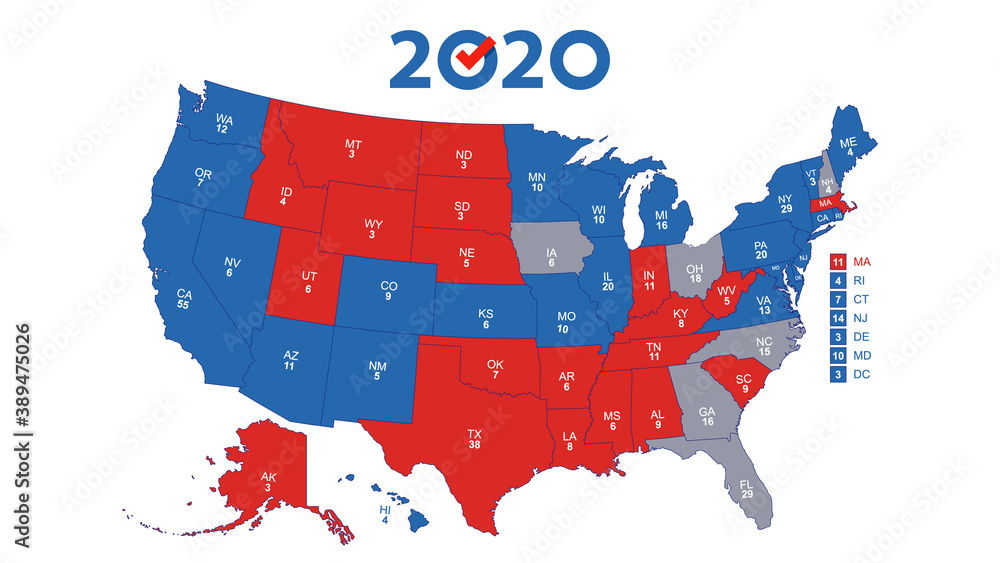
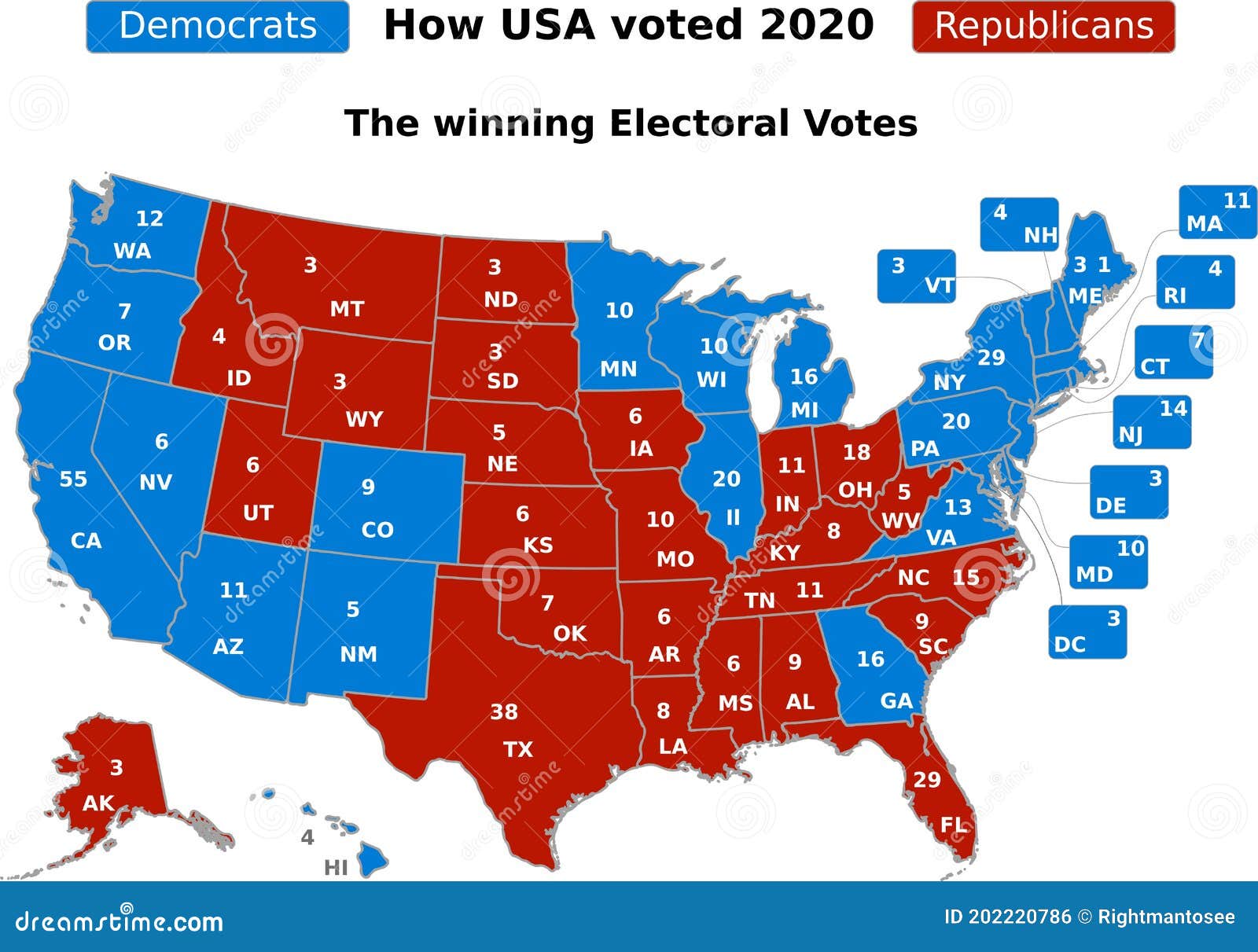
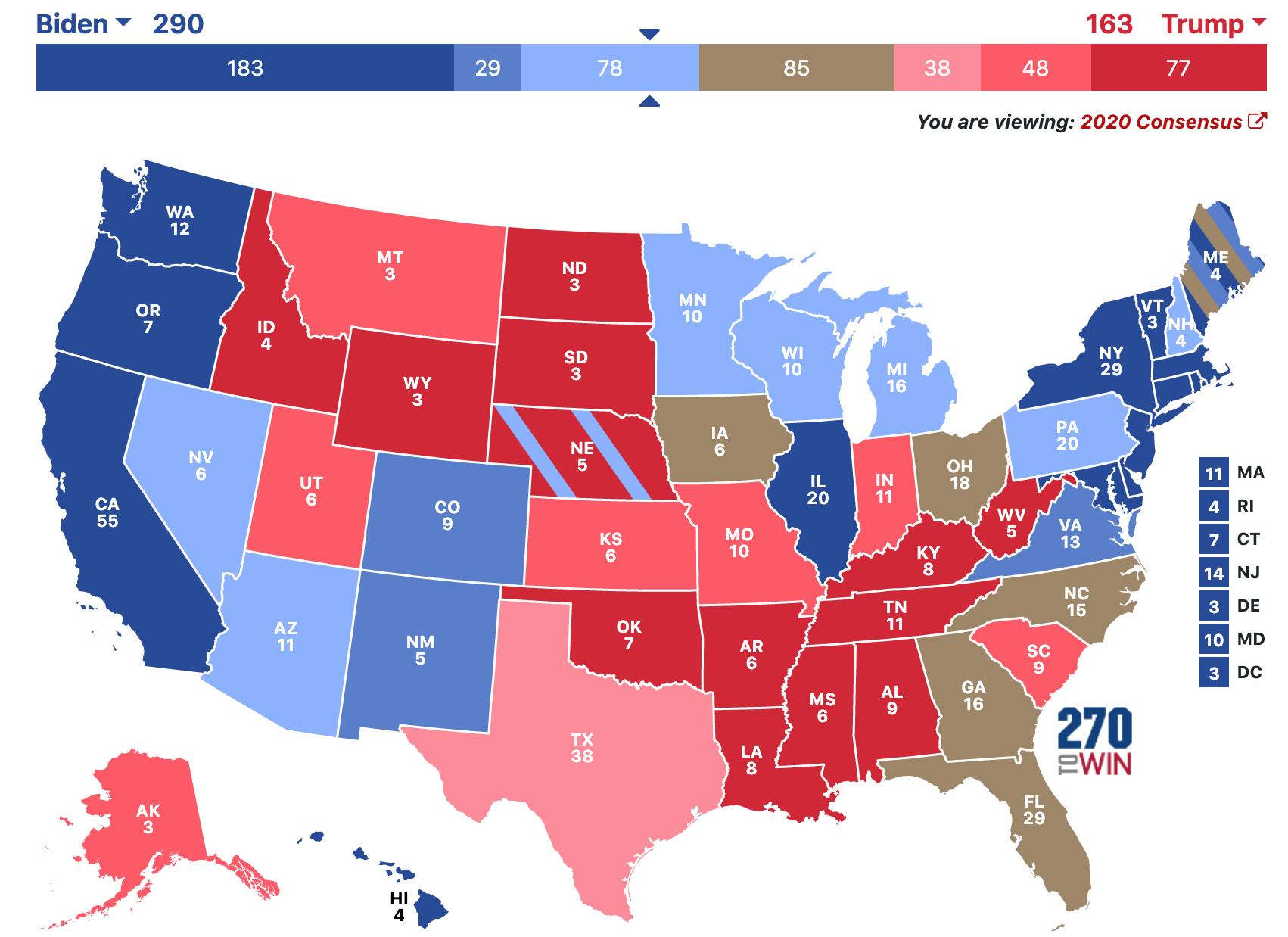
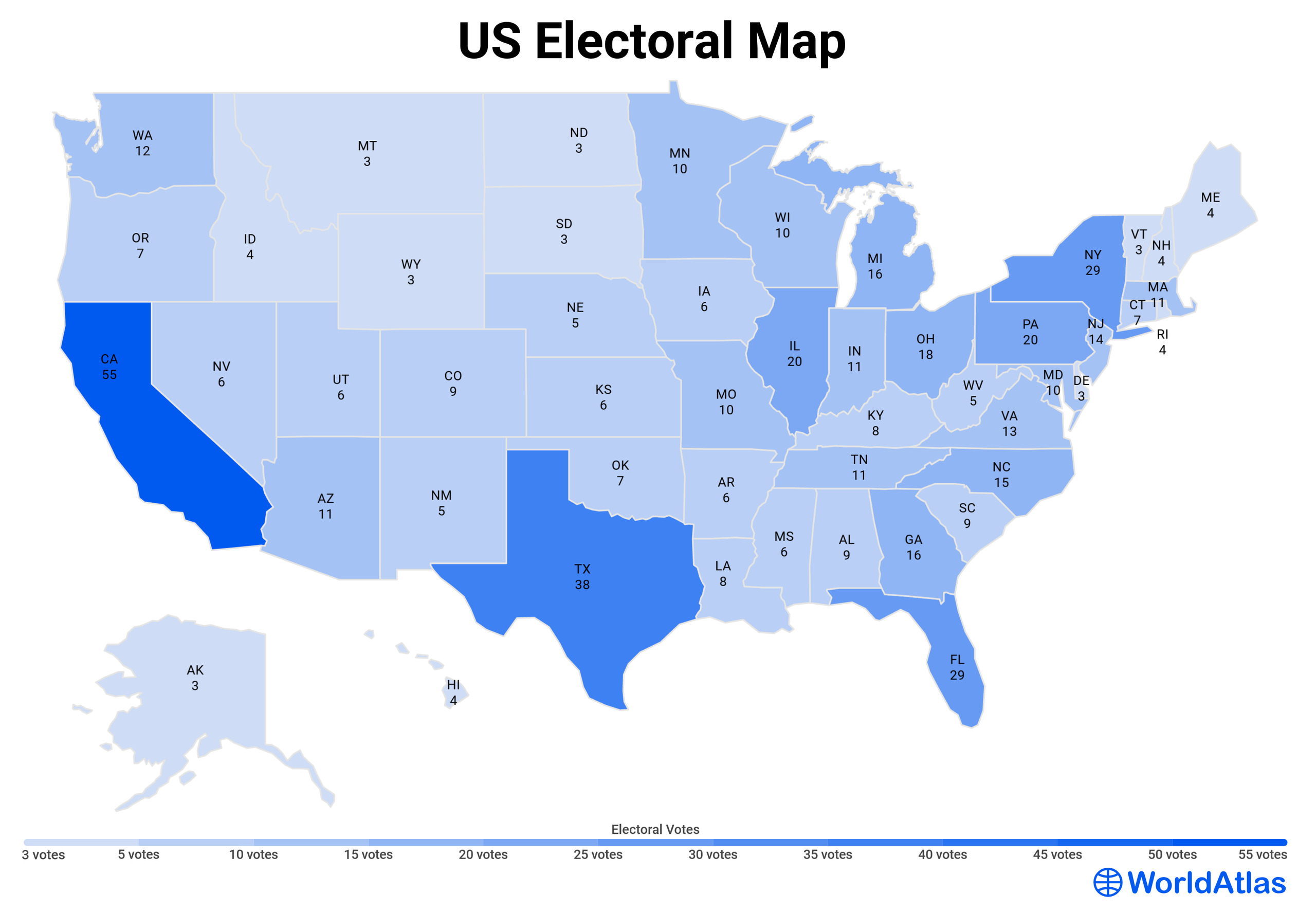
The United States presidential election is a complex process, and a key element in understanding its dynamics lies in the state voting map. This map, often visually represented with different colors to depict which party won each state, is more than just a visual representation of the election results. It reflects the intricate interplay of political ideologies, demographic trends, and historical factors that shape the American political landscape.
Deciphering the Map: Understanding the Electoral College
The state voting map is intricately linked to the Electoral College, a unique system that determines the winner of the presidential election. Unlike a direct popular vote, the Electoral College allocates electors to each state based on its congressional representation, with each state receiving a number of electors equal to its total number of senators and representatives in Congress. This system, established by the Constitution, ensures that smaller states retain a significant voice in the presidential election.
The state voting map, therefore, becomes crucial in understanding the dynamics of the Electoral College. A candidate needs to secure a majority of electoral votes (at least 270 out of 538) to win the presidency. This means that winning individual states, rather than the popular vote nationwide, is the primary focus of presidential campaigns.
Beyond the Colors: Understanding the State Voting Map’s Significance
The state voting map offers valuable insights into the political landscape beyond just the election results. It reveals:
-
Regional Political Trends: The map highlights the geographic distribution of political ideologies, revealing regional trends and pockets of strong support for particular parties. For instance, the consistent blue (Democratic) hue of the Northeast and West Coast reflects a liberal leaning in those regions, while the predominantly red (Republican) South points to a conservative base.
-
Demographic Shifts: The state voting map can reflect shifts in demographics over time. For example, the rise of Hispanic populations in certain states, such as Florida and Arizona, has contributed to their increased competitiveness in recent elections.
-
Electoral Strategies: The map informs campaign strategies by highlighting target states with a high concentration of electoral votes. Campaigns often prioritize resources and focus on winning key swing states, which are states with a close historical voting record and a potential for changing allegiances.
-
Political Polarization: The stark contrast between red and blue states on the map can also be interpreted as a visual representation of the increasing political polarization in the United States. While some states have consistently voted for the same party for decades, others have become battlegrounds, reflecting the growing divide in American political beliefs.
Analyzing the Map: Factors Influencing State Voting Patterns
Understanding the factors influencing state voting patterns is key to deciphering the state voting map. These factors can be broadly categorized as:
-
Economic Factors: Economic conditions, such as unemployment rates, income levels, and economic growth, can significantly influence voting behavior. States with strong economies often tend to favor incumbent parties, while those facing economic hardship may be more likely to vote for change.
-
Social Issues: Social issues like abortion rights, gun control, and same-sex marriage are increasingly influencing voting decisions. States with strong religious affiliations often tend to vote for parties that align with their social values.
-
Demographic Trends: Changes in demographics, such as population growth, racial and ethnic diversity, and age distribution, can impact voting patterns. States with growing minority populations may be more likely to favor candidates who address their concerns.
-
Historical Factors: Historical voting patterns and political affiliations can have a significant impact on current voting behavior. States with a long history of supporting a particular party may continue to do so, even if economic or social conditions change.
-
Media Influence: The media plays a crucial role in shaping public opinion and influencing voting decisions. Media coverage, particularly in swing states, can impact voters’ perceptions of candidates and their policies.
The State Voting Map: A Dynamic Landscape
The state voting map is not a static entity. It evolves with each election, reflecting changes in demographics, economic conditions, and political ideologies. The map provides a snapshot of the American political landscape at a given moment, offering insights into the complexities of the electoral process and the dynamics of American politics.
FAQs on the State Voting Map
1. What is the difference between the popular vote and the Electoral College?
The popular vote refers to the total number of votes cast for each candidate nationwide. The Electoral College, on the other hand, is a system that allocates electors to each state based on its congressional representation. The candidate who wins a majority of electoral votes (at least 270 out of 538) wins the presidency, regardless of who wins the popular vote.
2. Why is the state voting map important in understanding the presidential election?
The state voting map highlights the importance of individual states in the electoral process. Since the winner is determined by the Electoral College, campaigns focus on winning states rather than the national popular vote. The map reveals which states are considered swing states, where the outcome is uncertain, and which states are reliably red or blue.
3. How can I find a state voting map for a particular election year?
State voting maps are readily available online. Many news organizations and political websites provide detailed maps for each election year. You can also find maps from organizations like the United States Election Assistance Commission.
4. Does the state voting map always accurately reflect the political leanings of a state?
While the state voting map offers a general overview of political trends, it’s important to note that it doesn’t always accurately reflect the political leanings of every individual within a state. States often have diverse populations with varying political views.
5. How can I learn more about the history of the state voting map?
You can find information on the history of the state voting map by researching past presidential elections and the evolution of the Electoral College system. Academic journals, historical archives, and political science texts offer valuable insights into the historical context of the state voting map.
Tips for Understanding the State Voting Map
-
Pay attention to the electoral votes: The number of electoral votes allocated to each state is crucial in understanding the map’s significance.
-
Consider historical trends: Examining past election results can provide insights into the voting patterns of individual states.
-
Look for demographic data: Demographic information, such as population growth, racial and ethnic diversity, and income levels, can help explain voting trends.
-
Analyze media coverage: Media coverage of the election, particularly in swing states, can offer insights into the factors influencing voting decisions.
-
Engage with diverse perspectives: Seek out information from different sources, including political parties, think tanks, and academic institutions, to gain a well-rounded understanding of the state voting map.
Conclusion
The state voting map is an essential tool for understanding the American electoral landscape. It reveals the distribution of political ideologies, demographic trends, and historical factors that shape the dynamics of presidential elections. By analyzing the map and understanding the factors influencing state voting patterns, we gain a deeper understanding of the complexities of the electoral process and the evolving political landscape of the United States. As the map continues to evolve with each election, it remains a valuable resource for understanding the American political landscape and the choices that shape the nation’s future.
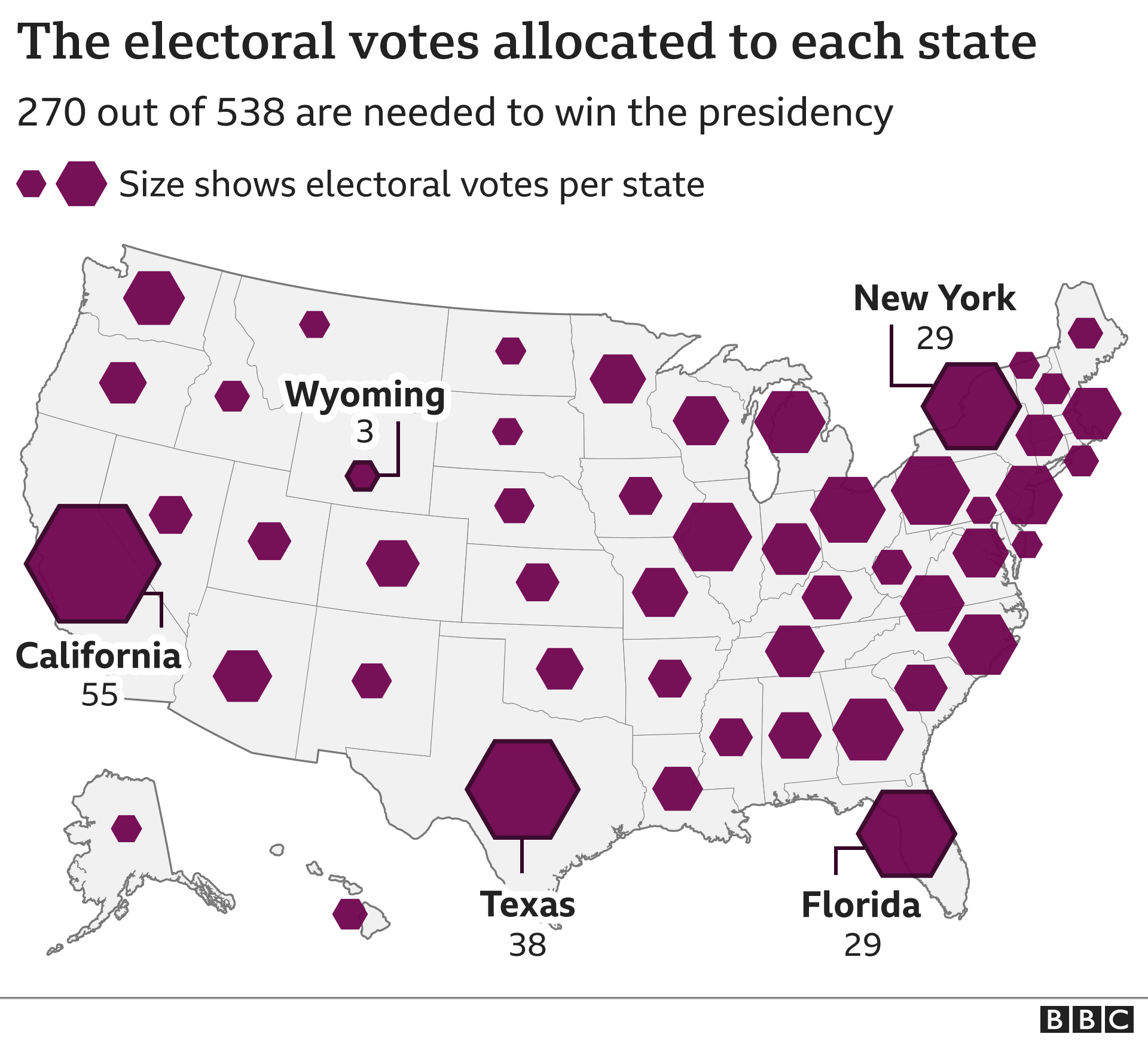
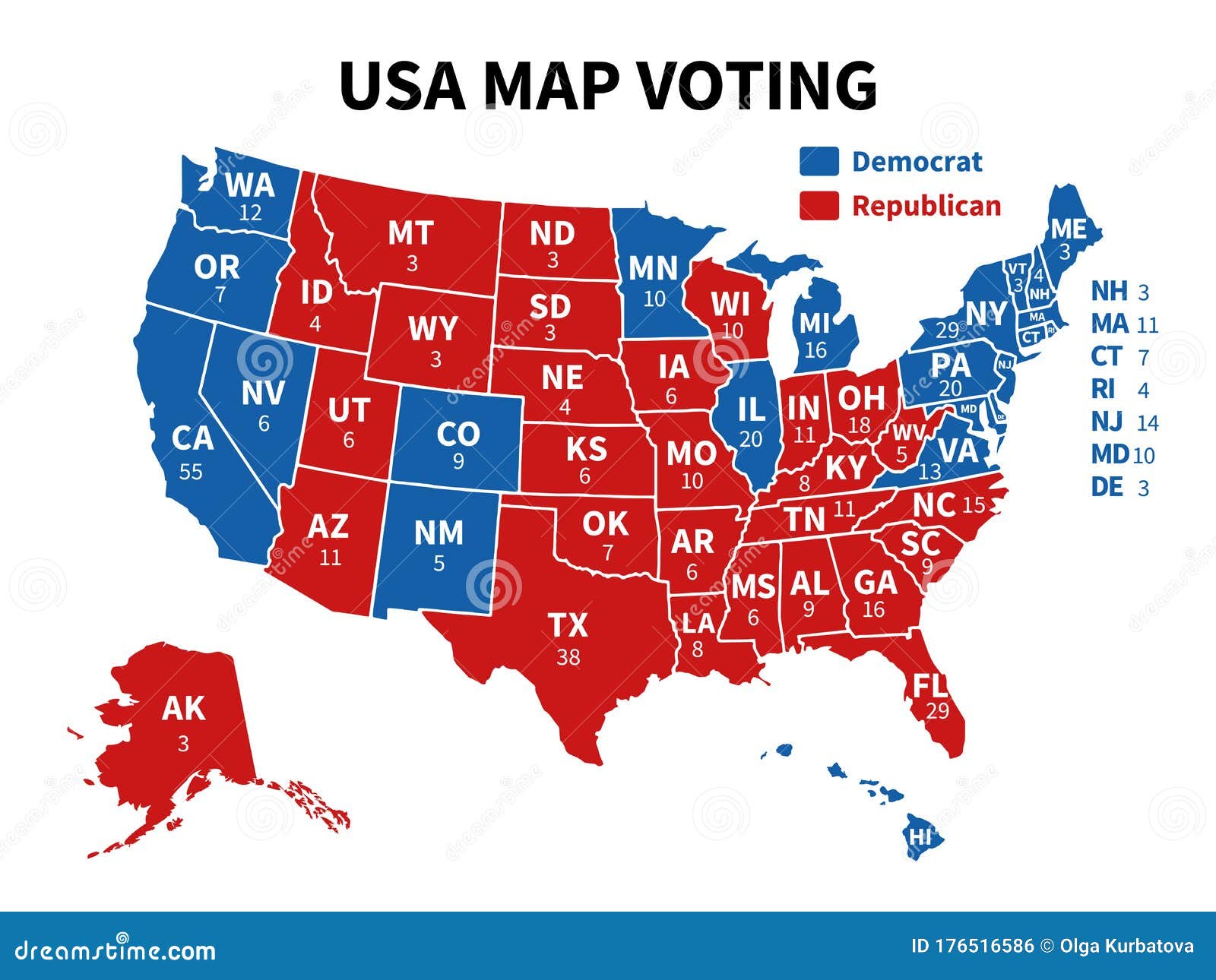
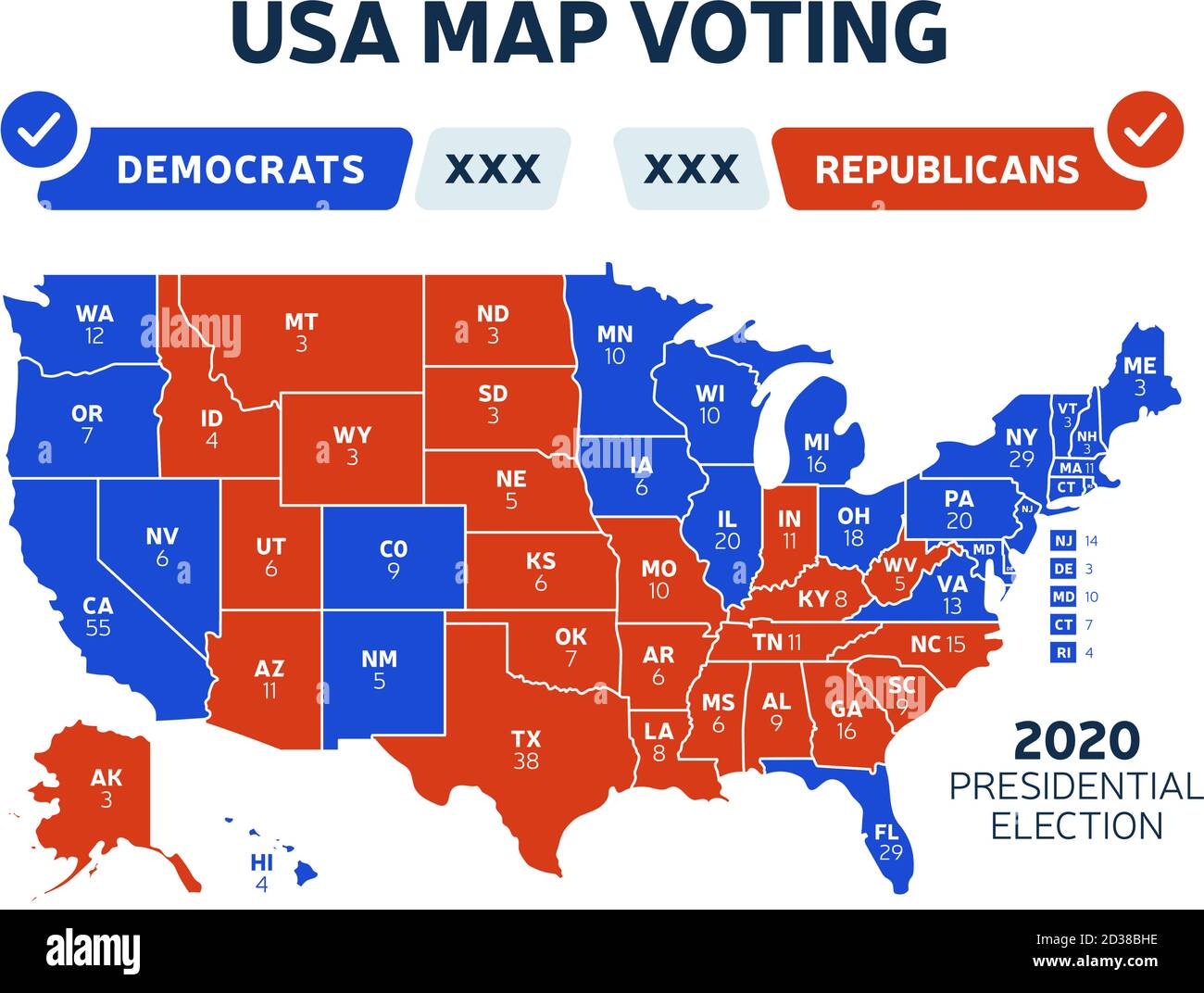


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The American Electoral Landscape: Understanding the State Voting Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!