Powerpoint Process Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing and Optimizing Workflows
Related Articles: Powerpoint Process Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing and Optimizing Workflows
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Powerpoint Process Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing and Optimizing Workflows. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Powerpoint Process Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing and Optimizing Workflows
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Powerpoint Process Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing and Optimizing Workflows
- 3.1 Understanding Process Maps: A Foundation for Efficiency
- 3.2 Powerpoint: A Versatile Tool for Process Mapping
- 3.3 Types of Process Maps for Diverse Applications
- 3.4 Powerpoint Process Map Templates: A Time-Saving Solution
- 3.5 Best Practices for Creating Effective Powerpoint Process Maps
- 3.6 FAQs: Addressing Common Queries on Powerpoint Process Mapping
- 3.7 Tips for Effective Process Mapping with Powerpoint
- 3.8 Conclusion: Harnessing the Power of Visual Representation
- 4 Closure
Powerpoint Process Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing and Optimizing Workflows

In the realm of business and project management, clarity and efficiency are paramount. Effective communication and understanding of processes are essential for seamless operations, optimal resource allocation, and the achievement of desired outcomes. Powerpoint, a ubiquitous presentation software, offers a versatile tool for visually representing and analyzing workflows through process mapping. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of Powerpoint process map templates, exploring their benefits, applications, and best practices for creating impactful visualizations.
Understanding Process Maps: A Foundation for Efficiency
Process maps, also known as flowcharts or process diagrams, are visual representations of a sequence of events or steps involved in a specific task, function, or workflow. They provide a structured and readily understandable overview of how a process unfolds, highlighting key activities, decision points, and potential areas for improvement.
Benefits of Process Mapping:
- Enhanced Clarity and Communication: Process maps translate complex procedures into easily digestible visual narratives, fostering clear understanding among team members, stakeholders, and clients.
- Improved Efficiency and Streamlining: By identifying redundancies, bottlenecks, and inefficiencies, process maps facilitate optimization, leading to smoother workflow execution and reduced time and resource consumption.
- Facilitated Problem Solving: Process maps pinpoint areas of weakness and potential failure points, enabling proactive identification and resolution of issues before they escalate.
- Enhanced Collaboration and Teamwork: Visualizing processes encourages open discussion, collaboration, and shared understanding, promoting a more cohesive and efficient working environment.
- Effective Documentation and Training: Process maps serve as valuable documentation tools, simplifying onboarding and training processes for new team members.
- Increased Accountability and Responsibility: By clearly outlining roles and responsibilities within a process, process maps promote accountability and encourage individual ownership of tasks.
Powerpoint: A Versatile Tool for Process Mapping
Powerpoint, with its user-friendly interface and extensive feature set, provides an accessible and powerful platform for creating professional-looking process maps. Its built-in shapes, connectors, and templates offer a range of options for visualizing different types of processes, from simple linear workflows to intricate, multi-branching diagrams.
Key Advantages of Using Powerpoint for Process Mapping:
- Accessibility and Familiarity: Powerpoint is widely available, familiar to most users, and requires minimal learning curve, making it an easy-to-use tool for process mapping.
- Visual Flexibility and Customization: Powerpoint offers a diverse selection of shapes, connectors, colors, and fonts, allowing for visually appealing and highly customizable process maps.
- Collaboration and Sharing: Powerpoint enables seamless collaboration on process maps through shared documents, enabling team members to contribute and refine the visualizations together.
- Presentation and Communication: Powerpoint’s presentation capabilities make it ideal for showcasing process maps to stakeholders, facilitating discussion and gaining buy-in for improvements.
Types of Process Maps for Diverse Applications
Process maps can be tailored to represent a wide range of processes, each with its unique characteristics and applications. Here are some common types of process maps used in various business contexts:
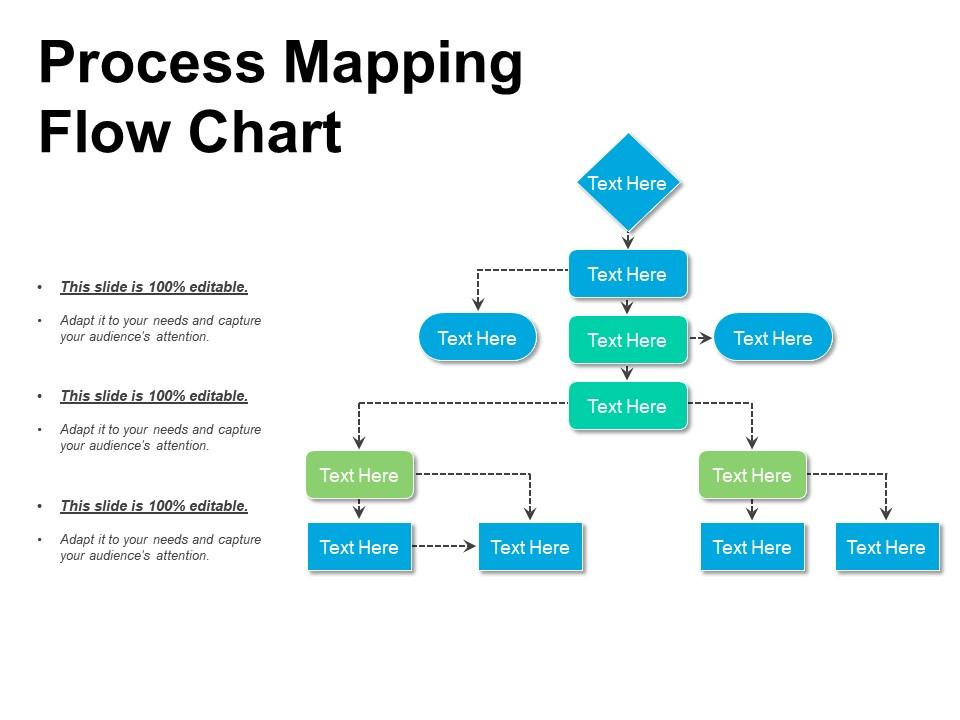
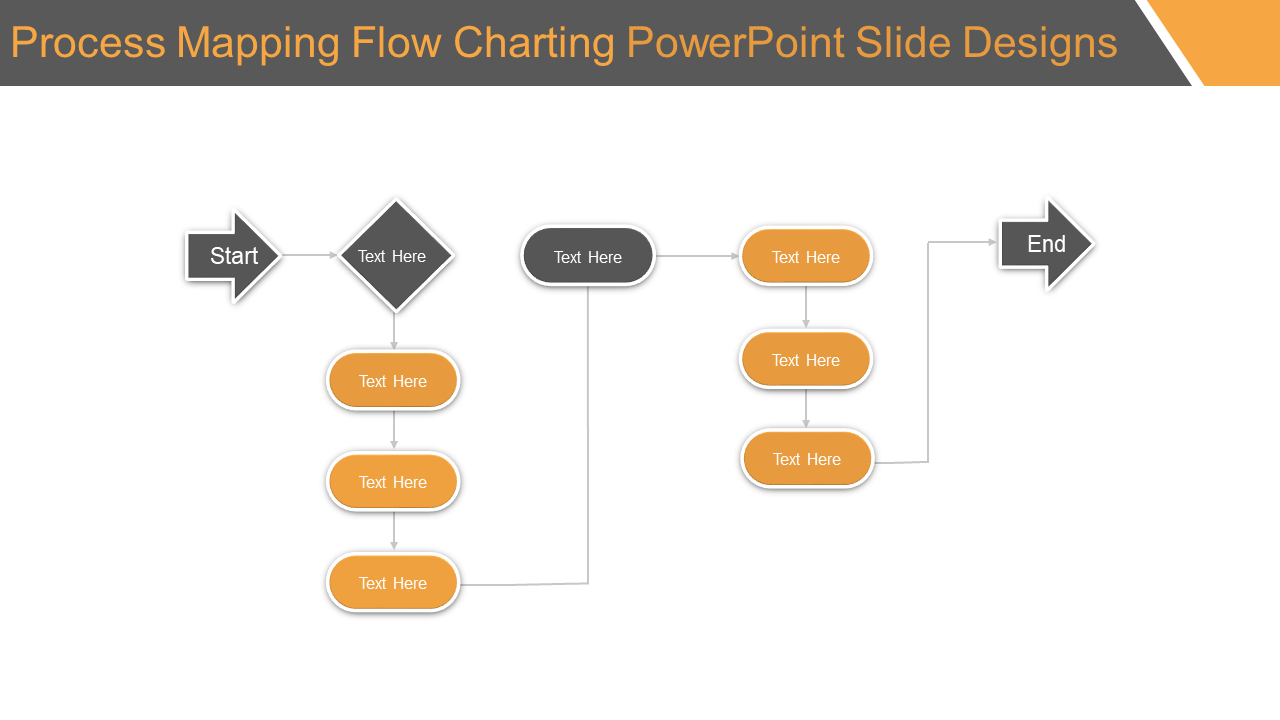
1. Flowchart: A basic type of process map that depicts a sequence of steps in a linear fashion, using arrows to indicate the flow of activities. Flowcharts are well-suited for illustrating simple, sequential processes, such as order fulfillment or customer service procedures.
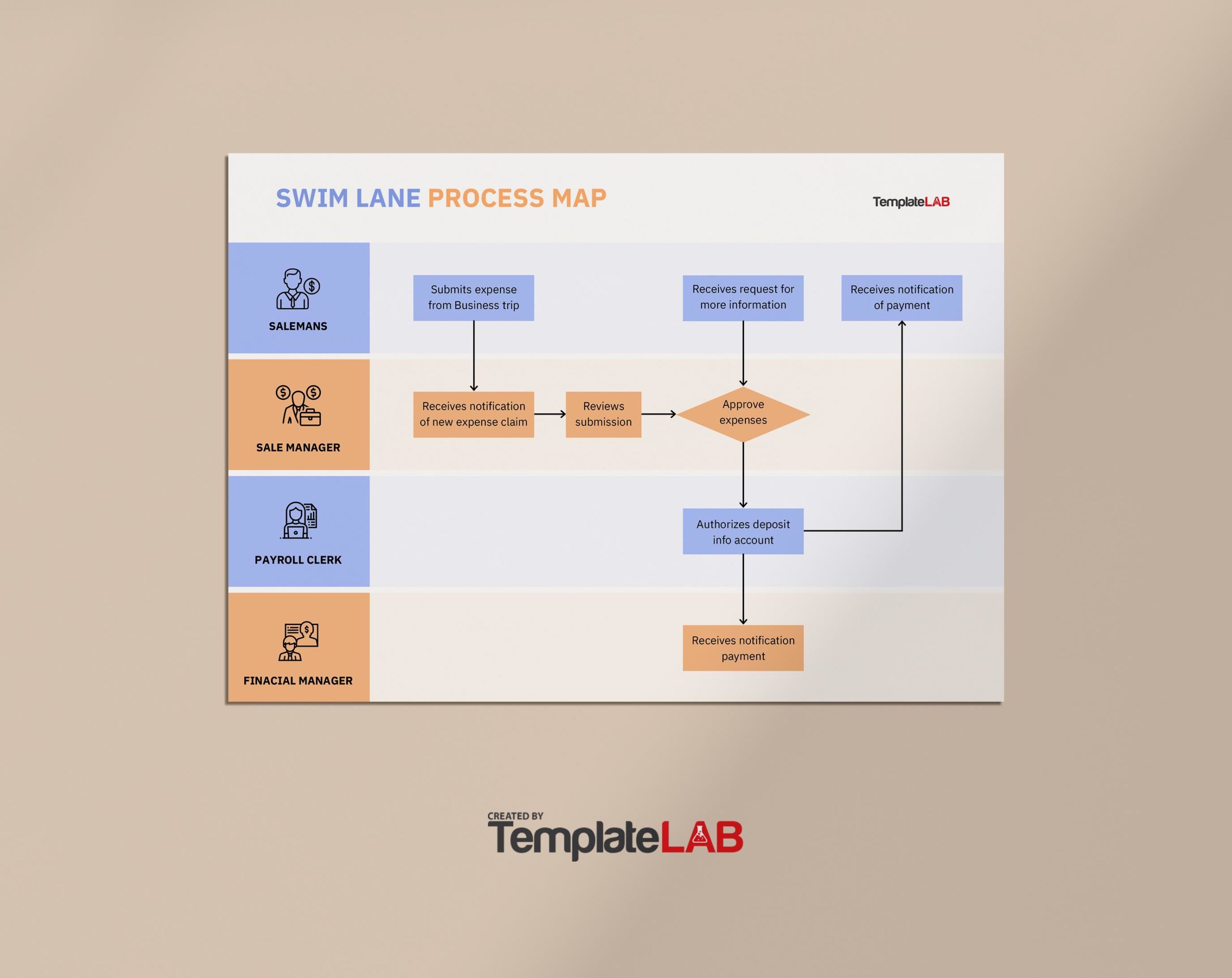
2. Swimlane Diagram: A process map that divides a workflow into distinct lanes, each representing a specific department, team, or individual responsible for different tasks. Swimlane diagrams are particularly useful for visualizing processes involving multiple stakeholders or departments, showcasing responsibilities and handoffs.
3. Value Stream Map: A process map that focuses on identifying and visualizing the flow of value from the customer’s perspective. Value stream maps highlight all activities involved in delivering a product or service, identifying areas of waste and opportunities for improvement.
4. SIPOC Diagram: A process map that defines the key elements of a process, including suppliers, inputs, process, outputs, and customers. SIPOC diagrams are valuable for providing a high-level overview of a process, identifying key stakeholders and their roles.
5. BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation): A standardized notation system for modeling and documenting business processes. BPMN diagrams are complex but offer a comprehensive and detailed representation of processes, suitable for sophisticated modeling and analysis.
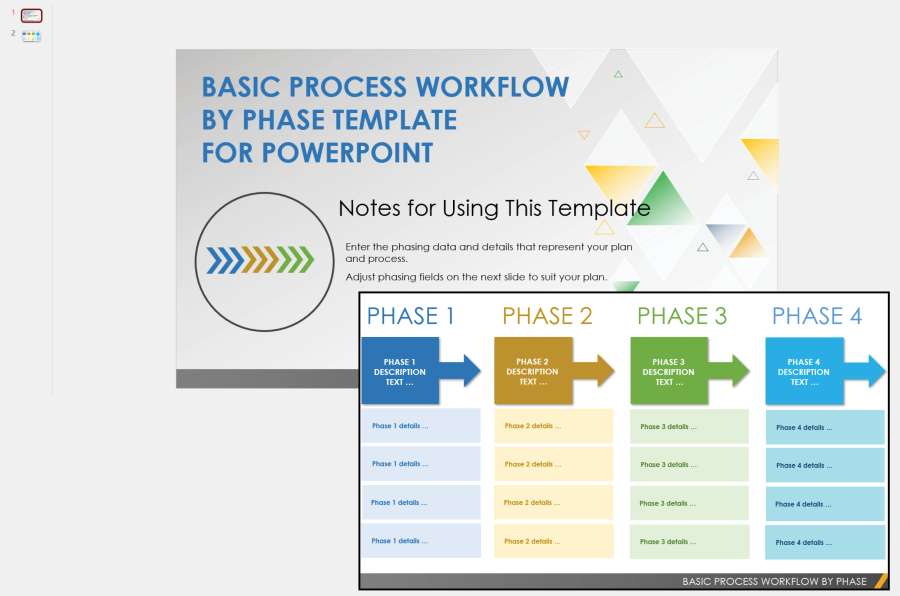
Powerpoint Process Map Templates: A Time-Saving Solution
Powerpoint offers a collection of pre-designed process map templates, providing a starting point for creating professional and informative visualizations. These templates offer a range of layouts, shapes, and connectors, saving time and effort in the initial setup.
Key Features of Powerpoint Process Map Templates:
- Pre-designed Layouts: Templates provide a structured framework for organizing process steps, ensuring consistency and visual appeal.
- Ready-to-use Shapes and Connectors: Templates include a selection of shapes representing various process elements, as well as connectors for linking steps and decisions.
- Customizable Elements: Templates allow for customization of colors, fonts, and other design elements to align with brand guidelines or project requirements.
- Time Efficiency: Templates streamline the process map creation process, reducing the time required to design and layout the diagram.
Best Practices for Creating Effective Powerpoint Process Maps
While Powerpoint provides a robust platform for process mapping, effective visualization requires adherence to certain best practices to ensure clarity, accuracy, and impact:
1. Define the Scope and Objectives: Clearly define the process being mapped, its purpose, and the desired outcomes. This will guide the selection of relevant steps and ensure a focused representation.
2. Identify Key Stakeholders: Involve relevant stakeholders in the process mapping exercise to gather input, ensure buy-in, and promote shared understanding.
3. Collect Data and Information: Gather accurate data about the process, including steps, decision points, inputs, outputs, and potential bottlenecks.
4. Choose the Right Template: Select a template that aligns with the type of process being mapped and the level of detail required.
5. Use Clear and Concise Language: Employ simple, straightforward language to label steps, decision points, and other elements. Avoid jargon or technical terms that may not be universally understood.
6. Employ Visual Cues Effectively: Utilize different shapes, colors, and connectors to differentiate between steps, decision points, and other elements. Ensure consistency in visual elements throughout the map.
7. Simplify Complexity: Avoid overcrowding the map with unnecessary detail. Focus on presenting the core elements and relationships within the process.
8. Seek Feedback and Iterate: Share the process map with stakeholders for feedback and iterate on the design to ensure clarity and accuracy.
FAQs: Addressing Common Queries on Powerpoint Process Mapping
1. What are the limitations of using Powerpoint for process mapping?
While Powerpoint is a versatile tool, it may not be suitable for highly complex or dynamic processes that require specialized modeling capabilities. In such cases, dedicated process mapping software or BPMN tools might be more appropriate.
2. Can I use Powerpoint templates for different types of process maps?
Powerpoint templates are generally flexible and can be adapted for different process map types. However, some templates might be better suited for specific types of diagrams. It’s advisable to select a template that aligns with the desired structure and visual style.
3. How can I ensure my Powerpoint process maps are visually appealing and effective?
Follow best practices for visual design, such as using consistent colors and fonts, employing clear and concise labels, and avoiding overcrowding the map. Seek feedback from stakeholders to ensure the map is easily understood and impactful.
4. Can I collaborate on process maps in Powerpoint?
Yes, Powerpoint allows for collaboration on shared documents, enabling team members to contribute and refine process maps together.
5. Can I export Powerpoint process maps to other formats?
Yes, Powerpoint allows you to export process maps in various formats, including PDF, JPEG, and PNG, making them easily shareable and printable.
Tips for Effective Process Mapping with Powerpoint
1. Start Simple: Begin with a basic flowchart or swimlane diagram to capture the core elements of the process. Gradually add complexity as needed.
2. Use a Consistent Style: Maintain consistency in the use of shapes, colors, fonts, and connectors throughout the map. This promotes visual clarity and professionalism.
3. Focus on the Audience: Tailor the level of detail and complexity of the map to the intended audience. A simple map might suffice for internal communication, while a more detailed map might be needed for external stakeholders.
4. Test and Refine: Share the process map with stakeholders for feedback and make necessary adjustments to ensure accuracy and clarity.
5. Use a Legend: Include a legend to explain the meaning of different shapes, colors, and connectors used in the map.
Conclusion: Harnessing the Power of Visual Representation
Powerpoint process map templates provide a valuable tool for visualizing and analyzing workflows, fostering efficiency, clarity, and collaboration. By understanding the benefits, types, and best practices of process mapping, individuals and teams can leverage the power of visual representation to optimize processes, drive improvements, and achieve organizational goals. Remember to choose the right template, employ clear and concise language, and prioritize visual clarity to create impactful process maps that effectively communicate and facilitate progress.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Powerpoint Process Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing and Optimizing Workflows. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!