Navigating the Sun’s Potential: Understanding Solar Maps of the United States
Related Articles: Navigating the Sun’s Potential: Understanding Solar Maps of the United States
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Sun’s Potential: Understanding Solar Maps of the United States. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Sun’s Potential: Understanding Solar Maps of the United States

The United States, with its vast expanse and diverse climates, offers a unique landscape for harnessing solar energy. Understanding the potential of solar power across the country requires a comprehensive and readily accessible resource – a solar map.
What is a Solar Map?
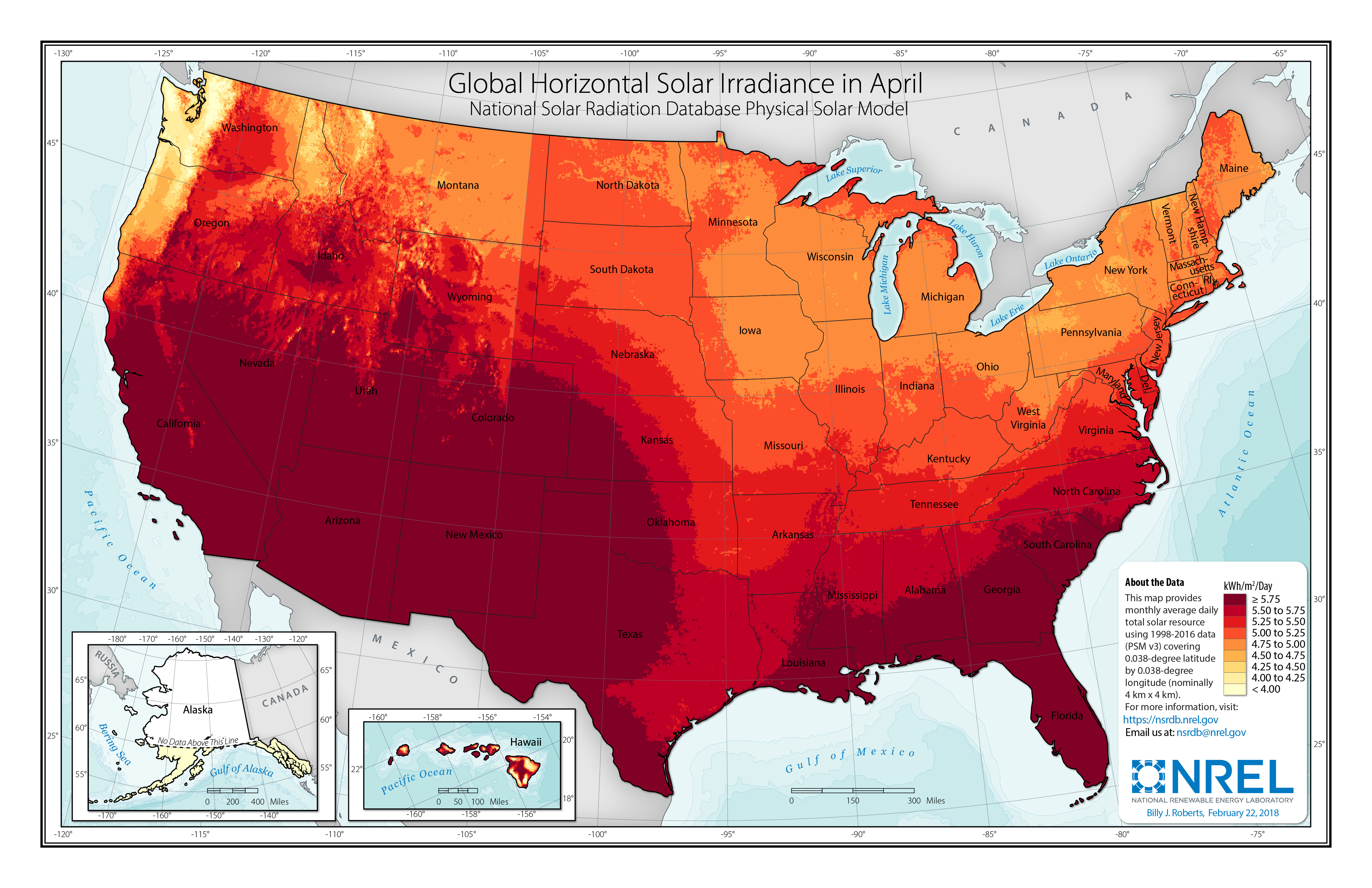
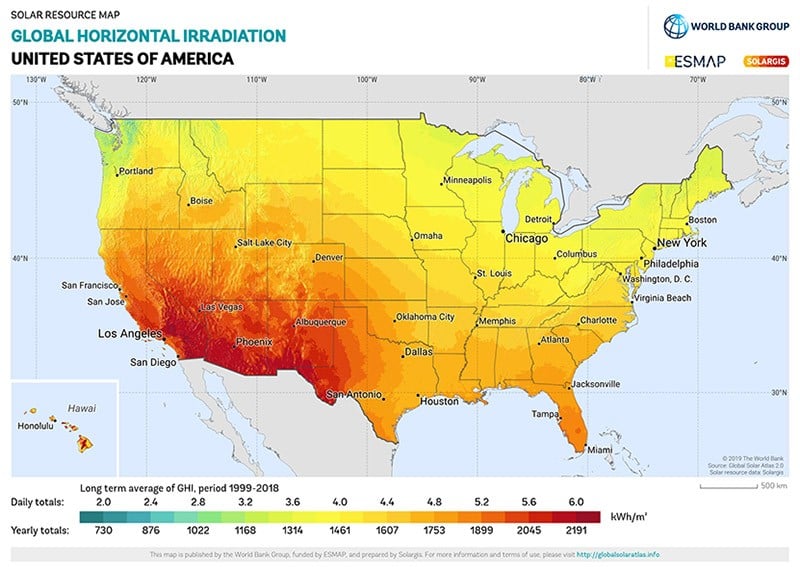
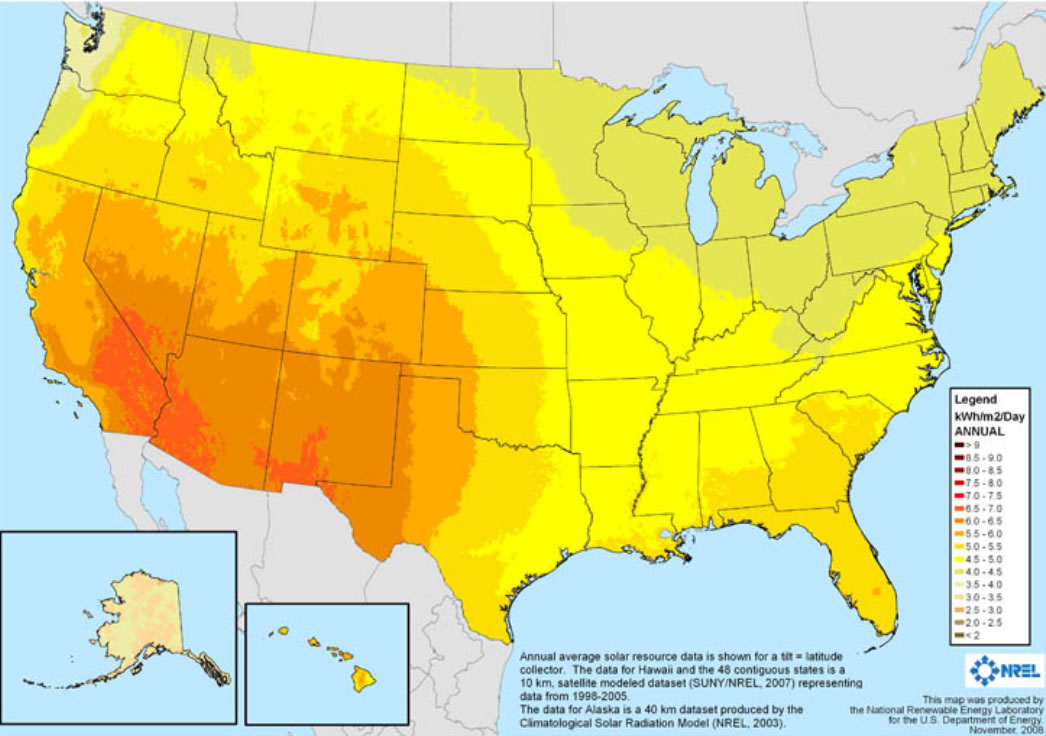
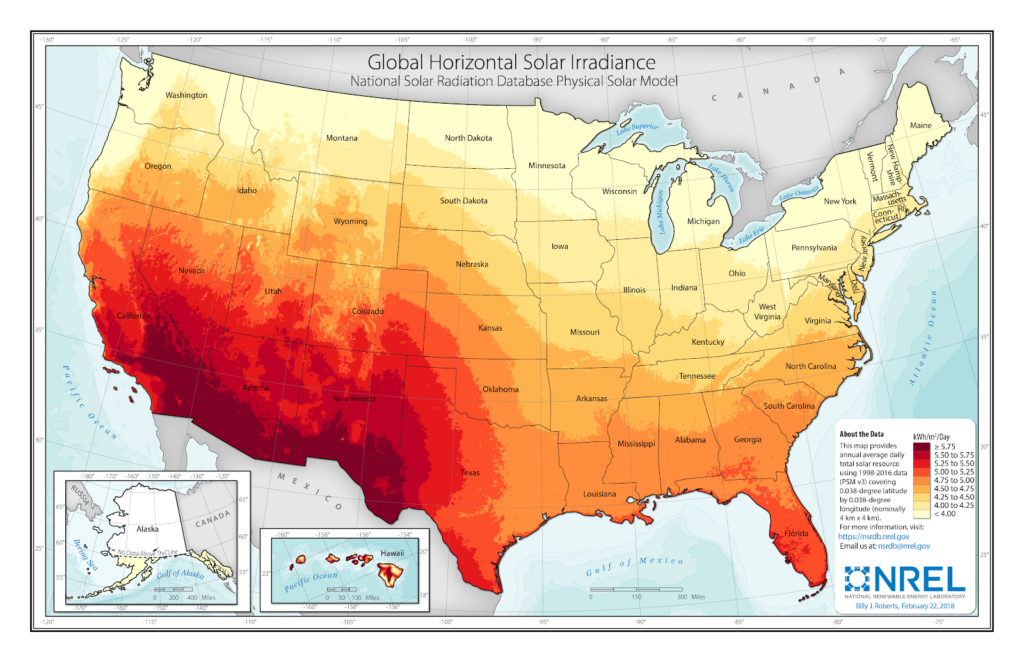
A solar map is a visual representation of solar energy potential across a geographic area. It typically uses color gradients or other visual cues to depict the amount of solar irradiance – the amount of sunlight received – at different locations. These maps provide valuable information for individuals, businesses, and policymakers interested in exploring solar energy options.
Key Features of Solar Maps of the United States:
Solar maps of the United States typically incorporate several key features to provide a comprehensive understanding of solar potential:
- Solar Irradiance: This is the primary data displayed on solar maps. It represents the amount of solar energy received per square meter per year, usually measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh).
- Geographic Coverage: Solar maps cover the entire United States, providing a national overview of solar potential.
- Data Resolution: The level of detail on solar maps varies depending on the source. Some maps provide data for specific locations, while others offer broader regional information.
- Interactive Features: Many solar maps are interactive, allowing users to zoom in on specific areas, explore different data layers, and generate reports.
- Additional Information: Some solar maps may include additional data, such as average annual sunshine hours, cloud cover, and even cost estimates for solar panel installations.
Benefits of Utilizing Solar Maps:
- Informed Decision-Making: Solar maps provide valuable data that can guide decision-making regarding solar energy investments. They help individuals, businesses, and policymakers assess the feasibility and profitability of solar projects.
- Site Selection: Solar maps assist in identifying locations with optimal solar irradiance, facilitating the selection of suitable sites for solar panel installations.
- Project Planning: The data from solar maps helps in planning the size, orientation, and tilt of solar panels to maximize energy output.
- Economic Analysis: Solar maps can be used to estimate the potential energy savings and financial returns from solar projects, enabling cost-benefit analysis.
- Policy Development: Policymakers can leverage solar map data to develop informed policies that promote solar energy adoption and sustainable energy practices.
Exploring Available Solar Maps:
Several resources offer solar maps of the United States, each with its unique features and data sources:
- National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL): NREL provides a comprehensive solar resource map, including data on solar irradiance, sunshine hours, and cloud cover. It also offers tools for calculating solar energy production and assessing economic feasibility.
- Google Project Sunroof: Google Project Sunroof uses satellite imagery and machine learning to estimate solar potential for individual homes and businesses. It provides personalized reports, including cost estimates and potential energy savings.
- Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA): SEIA offers a solar map that highlights the growth of the solar industry across the United States. It provides information on installed solar capacity, jobs created, and economic benefits.
- State and Local Government Resources: Many state and local governments provide solar maps specific to their regions. These maps often include information on local incentives, permitting requirements, and solar installation contractors.
FAQs: Demystifying Solar Maps of the United States
Q: What is the difference between solar irradiance and sunshine hours?
A: Solar irradiance refers to the amount of solar energy received per square meter per year, while sunshine hours represent the total number of hours of sunlight received in a year. Solar irradiance is a more accurate measure of solar energy potential, as it accounts for the intensity of sunlight.
Q: How accurate are solar maps?
A: The accuracy of solar maps depends on the data sources and methodology used. Maps based on satellite data are generally more accurate than those based on ground-based measurements. However, all solar maps provide valuable estimates that can guide decision-making.
Q: Can I use a solar map to determine the exact energy output of my solar panel system?
A: While solar maps provide estimates of solar irradiance, they cannot predict the exact energy output of a specific solar panel system. Factors such as panel efficiency, shading, and system losses can influence actual energy production.
Q: How can I find a solar installer in my area?
A: Many solar maps provide links to local solar installers. Alternatively, you can search for solar installers on the websites of organizations like SEIA or the National Solar Jobs Census.
Tips for Utilizing Solar Maps Effectively:
- Consider the Data Resolution: Ensure the data resolution of the solar map aligns with your needs. For individual homes, you may require high-resolution data, while for large-scale projects, regional data may suffice.
- Explore Additional Data Layers: Look for solar maps that offer additional data layers, such as cloud cover, shading, and local incentives.
- Verify Data Sources: Before relying on solar map data, verify the source and methodology used. Check for reputable organizations and government agencies.
- Consult with Solar Experts: For complex projects, consider consulting with solar professionals to interpret solar map data and develop a comprehensive plan.
Conclusion: Embracing Solar Potential with the Power of Maps
Solar maps serve as powerful tools for understanding and harnessing the vast solar energy potential of the United States. By providing comprehensive data on solar irradiance and other factors, these maps empower individuals, businesses, and policymakers to make informed decisions regarding solar energy investments, site selection, project planning, and policy development. As the United States continues to embrace renewable energy solutions, solar maps will play an increasingly crucial role in navigating the transition to a sustainable future.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Sun’s Potential: Understanding Solar Maps of the United States. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!