Navigating the Landscapes of Denmark and Germany: A Geographic Exploration
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscapes of Denmark and Germany: A Geographic Exploration
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscapes of Denmark and Germany: A Geographic Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Landscapes of Denmark and Germany: A Geographic Exploration
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Landscapes of Denmark and Germany: A Geographic Exploration
- 3.1 Denmark: A Kingdom of Islands and Peninsula
- 3.2 Germany: A Land of Diversity and Contrast
- 3.3 The Border Between Denmark and Germany: A Historical and Cultural Divide
- 3.4 The Importance of Understanding the Map of Denmark and Germany
- 3.5 FAQs about the Map of Denmark and Germany:
- 3.6 Tips for Navigating the Map of Denmark and Germany:
- 3.7 Conclusion:
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Landscapes of Denmark and Germany: A Geographic Exploration

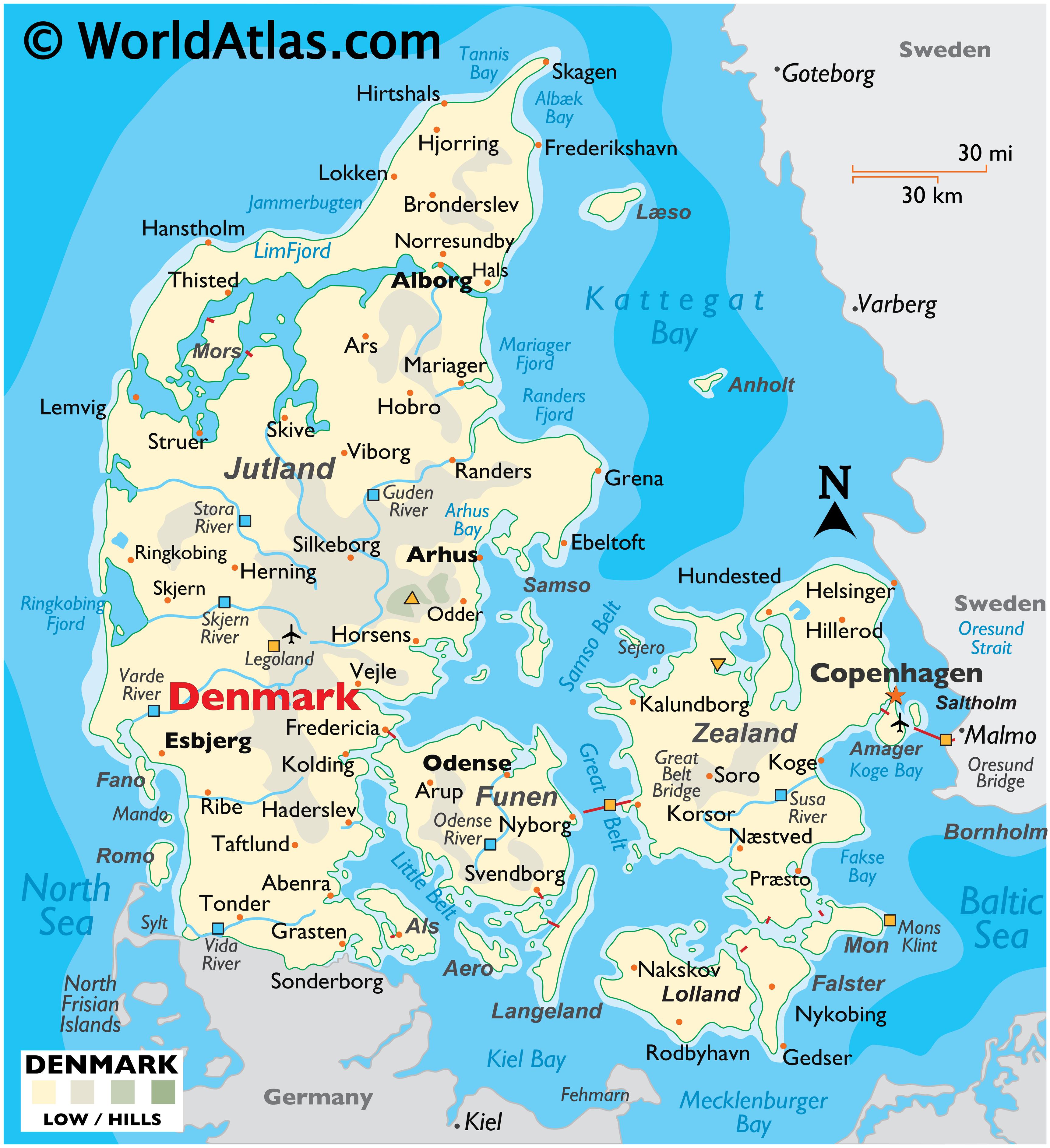
Denmark and Germany, two neighboring nations in Northern Europe, share a rich history, cultural exchange, and a fascinating geographical landscape. Understanding their physical features, from the rolling hills of Jutland to the rugged coastline of the Baltic Sea, provides valuable insight into their unique identities and the forces that have shaped their development. This exploration delves into the complexities of the map of Denmark and Germany, revealing its significance in understanding the region’s history, culture, and present-day challenges.
Denmark: A Kingdom of Islands and Peninsula
Denmark’s geography is characterized by its distinctive peninsular and island structure. The Jutland Peninsula, the largest landmass, forms the western portion of the country, connected to the European mainland. This region is dominated by rolling hills, fertile plains, and a coastline marked by inlets, fjords, and beaches. The eastern portion of Denmark comprises numerous islands, the largest being Zealand, where Copenhagen, the capital, resides. The islands are characterized by varied landscapes, including forests, meadows, and coastal areas.
Key Geographical Features of Denmark:
- Jutland Peninsula: This peninsula stretches from the North Sea to the Baltic Sea, forming the largest landmass of Denmark. Its diverse landscape includes rolling hills, fertile plains, and a coastline marked by inlets, fjords, and beaches.
- Danish Islands: The eastern portion of Denmark is comprised of numerous islands, including Zealand, Funen, and Bornholm. These islands offer varied landscapes, including forests, meadows, and coastal areas.
- The Baltic Sea: Denmark borders the Baltic Sea, which plays a significant role in the country’s economy and culture. The sea provides access to trade routes and contributes to the nation’s fishing industry.
- The North Sea: Denmark also borders the North Sea, which is known for its harsh weather conditions and strong currents. The North Sea is important for Denmark’s offshore wind energy production.
Germany: A Land of Diversity and Contrast
Germany, a nation of significant size and diversity, boasts a varied landscape ranging from the mountainous Alps in the south to the fertile plains of the north. The country’s geography is characterized by its central location in Europe, its numerous rivers, and its significant coastal areas.
Key Geographical Features of Germany:
- The Alps: The southernmost region of Germany is dominated by the Alps, a mountain range known for its towering peaks, scenic valleys, and renowned ski resorts.
- The Bavarian Forest: Located in the south-east, the Bavarian Forest is a national park known for its dense forests, rolling hills, and clear lakes.
- The Central Uplands: This region comprises a series of plateaus and hills, offering a diverse landscape of forests, meadows, and agricultural areas.
- The North German Plain: This vast, flat region stretches across northern Germany, characterized by fertile soil and extensive agricultural lands.
- The Rhine and Danube Rivers: Germany is home to two of Europe’s most significant rivers, the Rhine and Danube, which play vital roles in transportation, commerce, and recreation.
- The Baltic Sea: The north-east of Germany borders the Baltic Sea, offering access to important trade routes and contributing to the region’s fishing industry.
- The North Sea: Germany also borders the North Sea, which is important for its offshore wind energy production and harbors along its coastline.
The Border Between Denmark and Germany: A Historical and Cultural Divide
The border between Denmark and Germany is a dynamic line that has shifted throughout history. The two countries have experienced periods of conflict and cooperation, with the border reflecting these changing dynamics. The current border, established in the late 19th century, runs along the Jutland Peninsula, separating Denmark from the German state of Schleswig-Holstein.
This border holds historical significance, representing the division of the once-unified region of Schleswig-Holstein. The area has been a source of tension and conflict between Denmark and Germany, with both nations claiming ownership throughout history. Today, the border is largely symbolic, representing a shared history and a complex relationship between the two countries.
The Importance of Understanding the Map of Denmark and Germany
The map of Denmark and Germany is crucial for understanding the region’s unique characteristics and the factors that have shaped its history, culture, and present-day challenges. Analyzing the geography of the region reveals the following:
- Historical Significance: The map provides context for understanding the historical development of the region, including the rise and fall of empires, the impact of wars, and the formation of modern nation-states.
- Cultural Diversity: The map highlights the diverse cultural landscapes of Denmark and Germany, revealing the influence of geography on language, traditions, and art.
- Economic Development: The map illustrates the region’s economic strengths and weaknesses, revealing the importance of trade routes, natural resources, and industrial centers.
- Environmental Challenges: The map sheds light on the environmental challenges facing the region, including climate change, pollution, and the need for sustainable development.
FAQs about the Map of Denmark and Germany:
Q: What is the highest point in Denmark?
A: The highest point in Denmark is Møllehøj, located in the Jutland Peninsula, with an elevation of 170.86 meters (560.7 feet) above sea level.
Q: What are the major cities in Denmark and Germany?
A: Major cities in Denmark include Copenhagen, Aarhus, Odense, and Aalborg. Major cities in Germany include Berlin, Hamburg, Munich, Cologne, and Frankfurt.
Q: What are the primary industries in Denmark and Germany?
A: Denmark’s economy is driven by industries such as pharmaceuticals, wind energy, food processing, and tourism. Germany’s economy is characterized by its strong manufacturing sector, particularly in automotive, engineering, and chemicals.
Q: What are the main languages spoken in Denmark and Germany?
A: The official language of Denmark is Danish. The official language of Germany is German.
Q: What are the major rivers in Denmark and Germany?
A: Denmark’s major rivers include the Gudenå, the Skjern Å, and the Varde Å. Germany’s major rivers include the Rhine, the Danube, the Elbe, and the Weser.
Tips for Navigating the Map of Denmark and Germany:
- Use online maps: Online mapping tools such as Google Maps and Bing Maps provide detailed information on geographical features, cities, and transportation routes.
- Explore atlases: Traditional atlases offer comprehensive maps and information on the history, culture, and demographics of Denmark and Germany.
- Travel guides: Travel guides often include maps and descriptions of key attractions, landscapes, and cultural experiences in the region.
- Engage with local communities: Interacting with locals can provide valuable insights into the region’s unique characteristics and hidden gems.
Conclusion:
The map of Denmark and Germany offers a window into the rich history, diverse culture, and captivating landscapes of these two neighboring nations. Understanding their geographical features, from the islands of Denmark to the mountainous Alps of Germany, provides a framework for comprehending their unique identities and the forces that have shaped their development. Whether exploring the vibrant cities, the serene countryside, or the rugged coastline, the map serves as a valuable guide for navigating the complexities and beauty of this fascinating region.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscapes of Denmark and Germany: A Geographic Exploration. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!