Navigating the Federal Court System: A Comprehensive Guide to the Federal Court Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Federal Court System: A Comprehensive Guide to the Federal Court Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Federal Court System: A Comprehensive Guide to the Federal Court Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Federal Court System: A Comprehensive Guide to the Federal Court Map
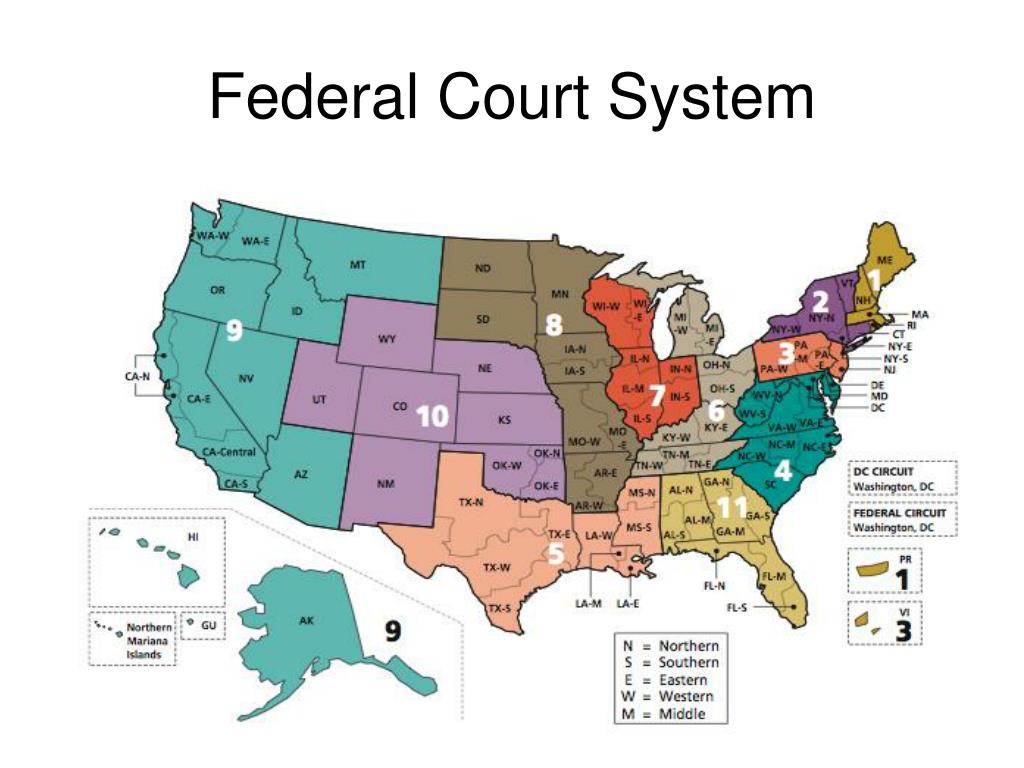
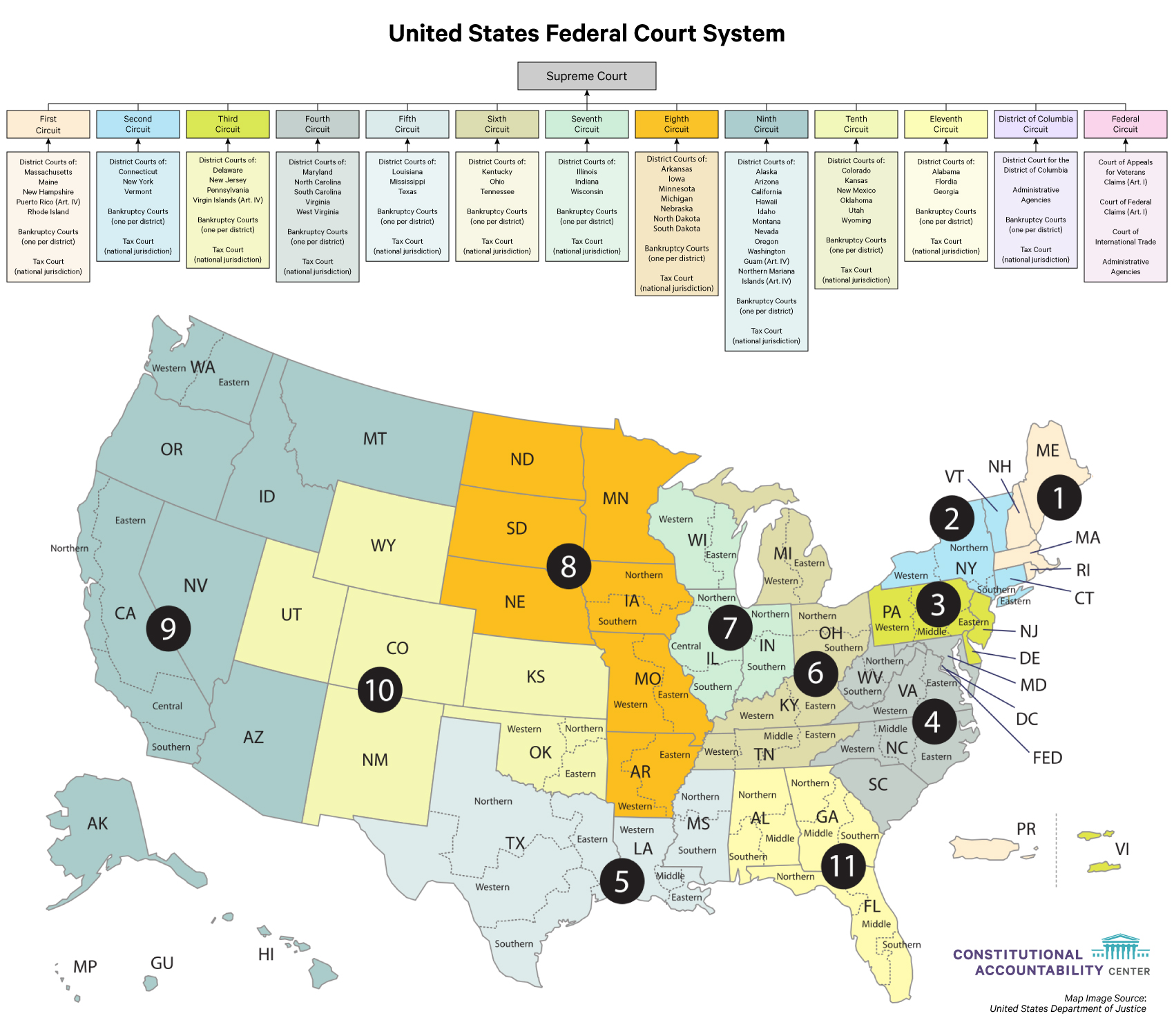
The United States federal court system is a complex and intricate network of courts responsible for adjudicating disputes arising under federal law. Understanding the structure and organization of this system is crucial for anyone seeking to navigate the legal landscape, whether as a litigant, legal professional, or simply an informed citizen. This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth exploration of the federal court map, outlining its key components and highlighting its significance in the American legal framework.
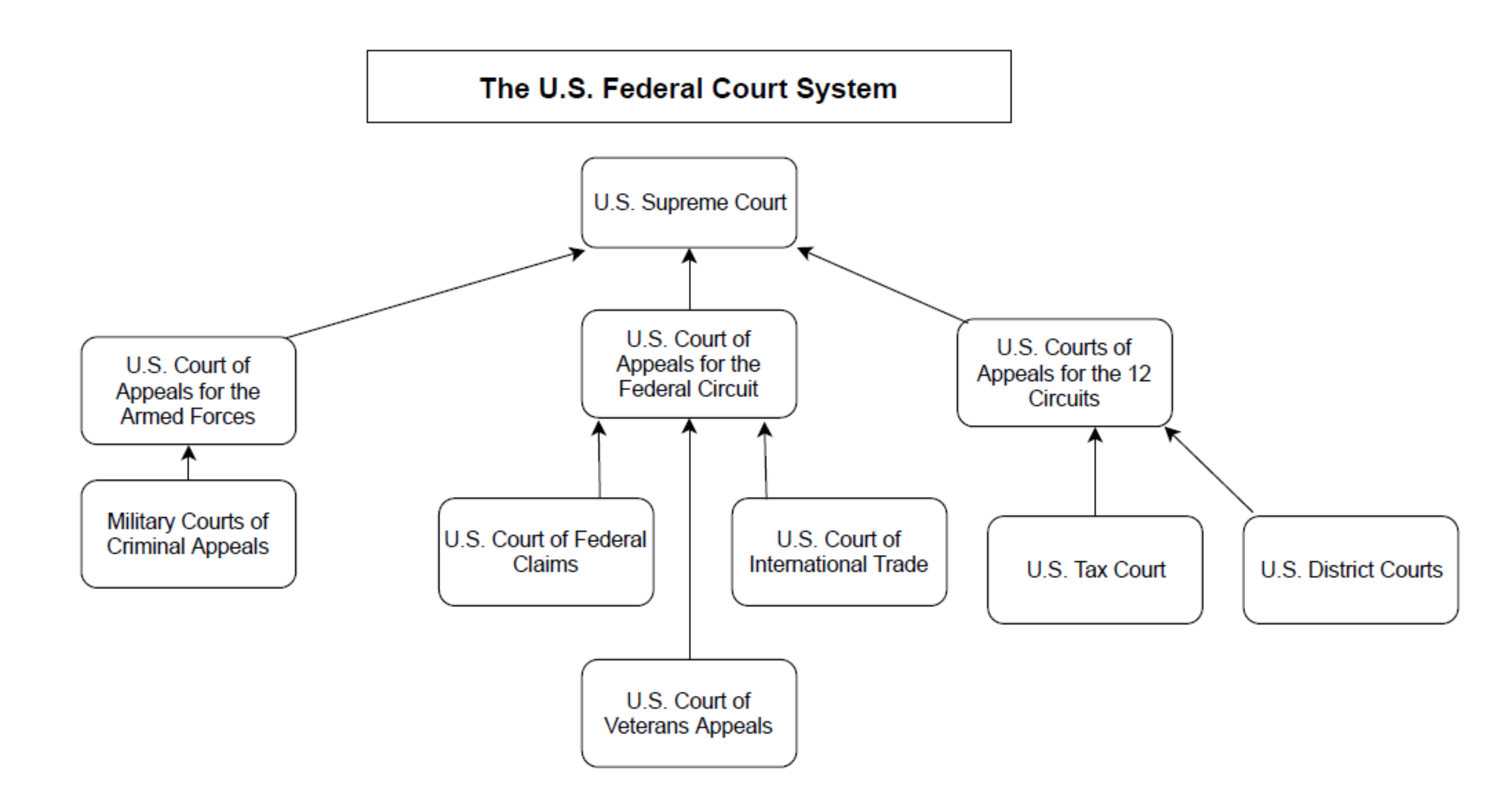
The Foundation: Understanding the Three Tiers
The federal court system operates on a hierarchical structure, encompassing three distinct tiers:
-
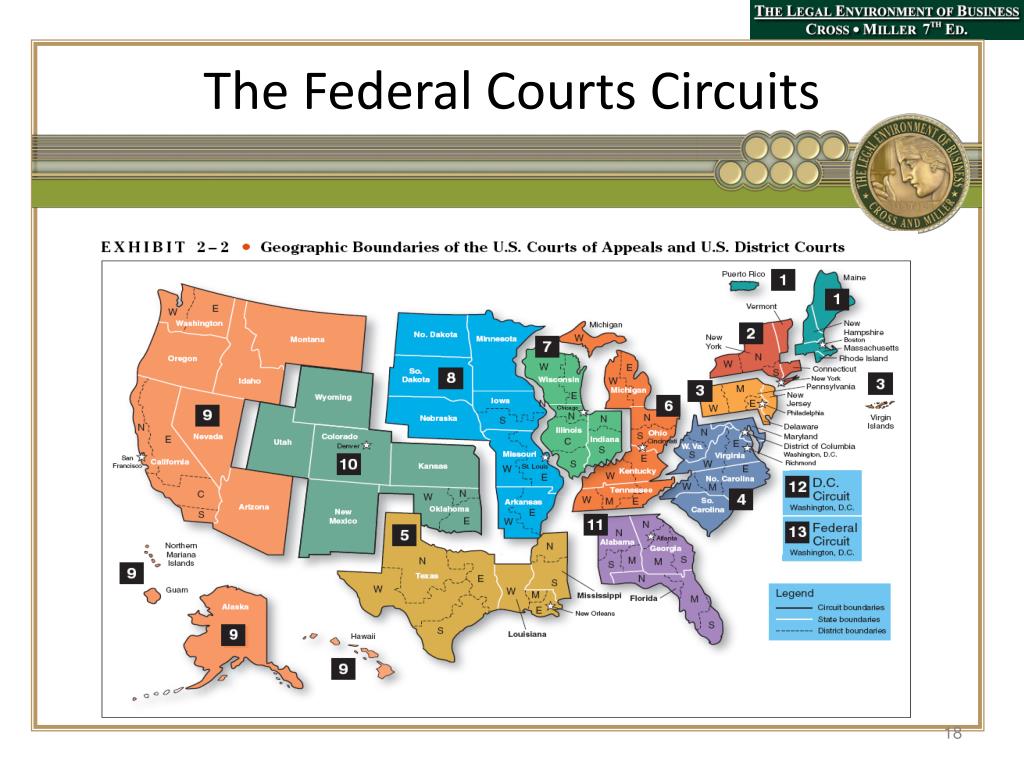
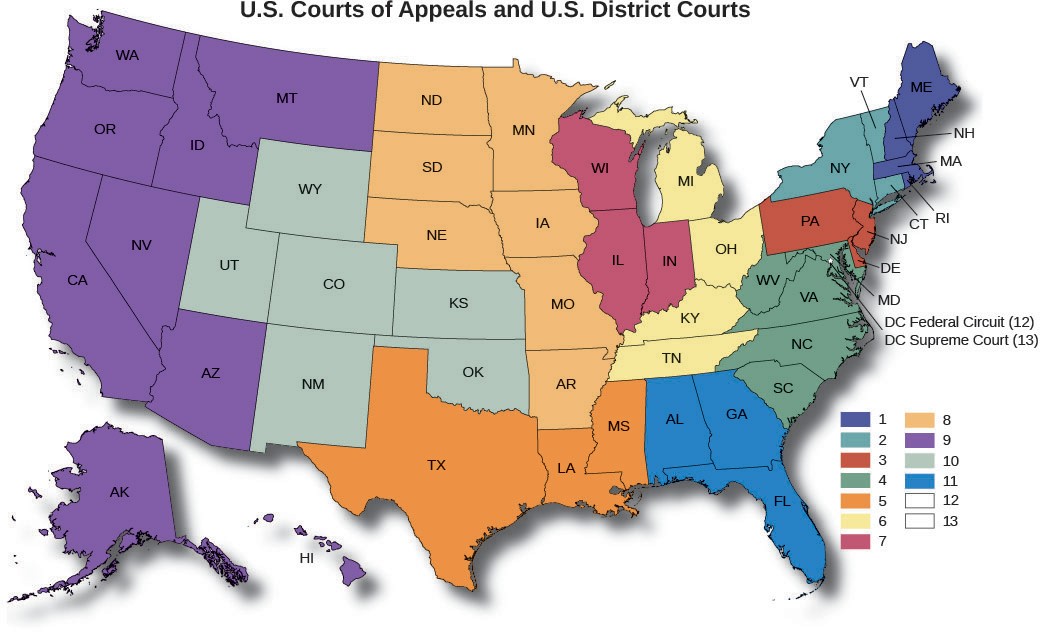
District Courts: The foundation of the federal court system, district courts are the trial courts of original jurisdiction. They handle a vast array of cases, including civil disputes, criminal prosecutions, and bankruptcy proceedings. The United States is divided into 94 judicial districts, each with at least one district court. These courts are responsible for hearing evidence, determining facts, and applying the law to specific cases.
-
Courts of Appeals: Sitting above the district courts are the thirteen United States Courts of Appeals, also known as circuit courts. These courts review decisions made by district courts within their respective geographic jurisdictions. They do not hold trials but rather examine legal issues and determine whether the lower court applied the law correctly. Appeals courts play a vital role in ensuring consistency and uniformity in the application of federal law across the country.
-
Supreme Court: The apex of the federal court system, the Supreme Court is the highest court in the land. It has the final say on all legal matters arising under federal law. The Supreme Court primarily acts as an appellate court, reviewing decisions from lower courts, but it also has original jurisdiction in certain limited cases, such as disputes between states.
The Geographic Landscape: Navigating the Judicial Districts
The federal court map is a visual representation of the geographical distribution of federal courts across the United States. It helps visualize the intricate network of courts and the jurisdictional boundaries that define their authority. Each state is assigned to at least one federal judicial district, and larger states may have multiple districts.
Understanding Jurisdiction: The Key to Navigating the Map
Jurisdiction, the authority of a court to hear and decide a particular case, is a crucial aspect of the federal court map. Federal courts have jurisdiction over cases that involve:
- Federal Law: Cases involving federal statutes, treaties, or the Constitution fall under federal jurisdiction.
- Diversity of Citizenship: Cases involving citizens from different states or a citizen and a foreign citizen, where the amount in controversy exceeds a certain threshold, may also be brought in federal court.
- United States as a Party: Cases where the United States government is a party are typically heard in federal court.
The Importance of the Federal Court Map: Ensuring Justice and Consistency
The federal court map plays a crucial role in ensuring the efficient and fair administration of justice in the United States. It helps:
- Guarantee Access to Justice: By establishing a clear geographic framework, the map ensures that every citizen has access to a federal court within a reasonable distance.
- Maintain Consistency in Law: The map promotes uniformity in the application of federal law by defining clear jurisdictional boundaries and ensuring that appeals are heard by courts with expertise in specific areas of law.
- Facilitate the Administration of Justice: The map provides a clear and organized structure for the federal court system, facilitating the efficient handling of cases and the smooth flow of legal proceedings.
Beyond the Map: Understanding Specialized Courts
The federal court system also includes specialized courts with specific jurisdictions:
- United States Court of Federal Claims: This court handles claims against the United States government.
- United States Court of International Trade: This court adjudicates disputes related to international trade.
- United States Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit: This court has nationwide jurisdiction over certain types of appeals, including patent cases and claims against the United States government.
Navigating the System: A Guide for Legal Professionals and Litigants
For legal professionals and litigants, the federal court map is an indispensable tool for navigating the complex legal system. It provides:
- Clear Identification of the Appropriate Court: The map helps identify the correct court for a particular case based on its subject matter and the location of the parties involved.
- Understanding the Appellate Process: The map outlines the chain of appeals, allowing legal professionals to anticipate potential avenues for challenging lower court decisions.
- Access to Case Information: The federal court map can be used to access information about specific cases, including court filings, dockets, and case decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about the Federal Court Map
Q: What is the difference between a federal court and a state court?
A: Federal courts have jurisdiction over cases involving federal law, while state courts handle cases involving state law. Some cases may be heard in both federal and state court, but jurisdiction ultimately depends on the specific facts of the case.
Q: How do I determine which federal court has jurisdiction over my case?
A: Jurisdiction is determined by factors such as the subject matter of the case, the location of the parties involved, and the amount in controversy. You can consult with a legal professional or use online resources to determine the appropriate court for your case.
Q: What are the different types of federal courts?
A: The federal court system includes district courts, courts of appeals, the Supreme Court, and specialized courts such as the Court of Federal Claims and the Court of International Trade.
Q: Can a case be appealed from a federal district court to the Supreme Court?
A: No, cases must first be appealed to the appropriate Court of Appeals. The Supreme Court only hears a limited number of cases each year, typically those involving significant legal issues or conflicts between lower courts.
Tips for Navigating the Federal Court System
- Consult with a legal professional: Seek legal advice from an attorney experienced in federal court proceedings to ensure you understand your legal rights and obligations.
- Familiarize yourself with the federal court map: Understand the jurisdictional boundaries of each court and the appropriate court for your case.
- Research case law and precedent: Review relevant case decisions from federal courts to gain insight into how similar cases have been handled in the past.
- File your case in the correct court: Ensure you file your case in the appropriate federal court to avoid delays or dismissals.
Conclusion: The Federal Court Map: A Vital Component of American Justice
The federal court map serves as a crucial framework for the American legal system, ensuring access to justice, promoting uniformity in the application of federal law, and facilitating the efficient administration of justice. By understanding the structure and organization of the federal court system, individuals and legal professionals can navigate the complexities of the legal landscape with greater confidence and clarity. The federal court map is not merely a geographic representation but a vital tool for safeguarding the principles of justice and ensuring the smooth functioning of the American legal system.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Federal Court System: A Comprehensive Guide to the Federal Court Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!