Navigating Arizona’s Tracks: A Comprehensive Guide to the State’s Rail Network
Related Articles: Navigating Arizona’s Tracks: A Comprehensive Guide to the State’s Rail Network
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating Arizona’s Tracks: A Comprehensive Guide to the State’s Rail Network. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Arizona’s Tracks: A Comprehensive Guide to the State’s Rail Network
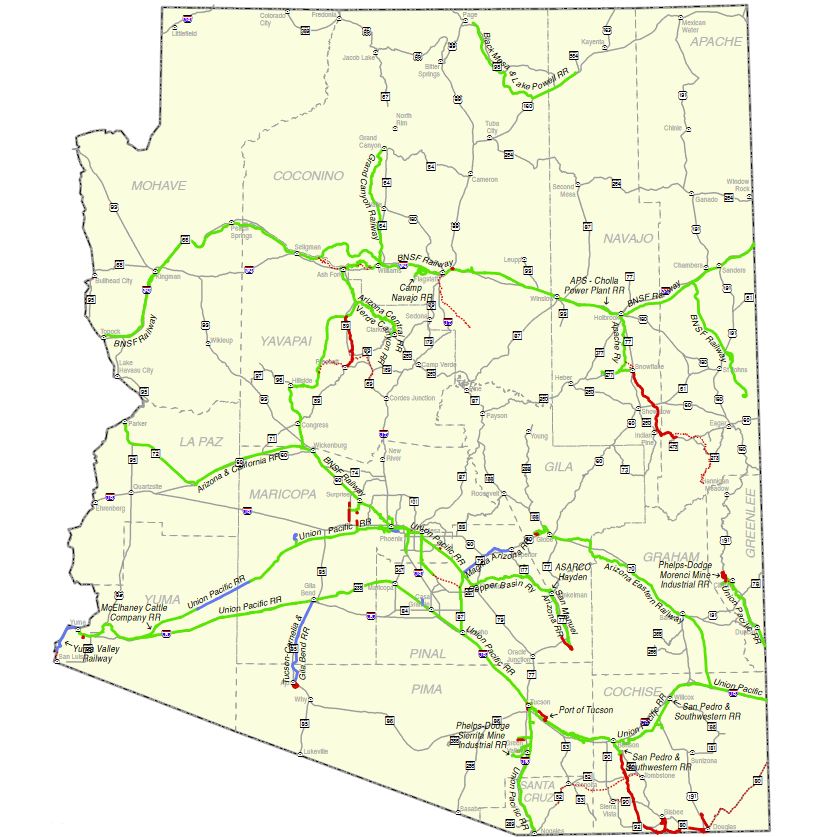
Arizona’s vast landscape, characterized by arid deserts, towering mountains, and sprawling cities, is crisscrossed by a network of rail lines that play a vital role in the state’s economy and transportation infrastructure. Understanding this intricate rail map is crucial for anyone seeking to navigate the state effectively, whether for business, leisure, or simply to gain a deeper understanding of Arizona’s history and development.
A History of Rail in Arizona
The story of Arizona’s rail network begins in the late 19th century, during the era of westward expansion and the development of the American Southwest. The arrival of the railroad transformed the state, opening up new possibilities for commerce, trade, and settlement.
The Southern Pacific Railroad, a major player in the transcontinental rail system, established its presence in Arizona in the 1870s. The arrival of the railroad facilitated the development of mining towns, agricultural centers, and bustling cities like Phoenix and Tucson.
As the 20th century progressed, the rail network in Arizona expanded and diversified. The Santa Fe Railway, another prominent railroad company, established its presence in the state, further strengthening its transportation infrastructure. The development of new lines, including the Prescott and Phoenix Railway, and the construction of the Roosevelt Dam, a monumental engineering feat that harnessed the power of the Salt River, solidified the importance of rail in Arizona’s growth.
The Modern Rail Network: A Vital Arterial System
Today, Arizona’s rail network is a complex tapestry woven from various lines and operators, serving a diverse range of purposes. The primary freight rail lines are operated by BNSF Railway, Union Pacific Railroad, and Arizona Rail Lines, connecting Arizona to major markets across the United States and Mexico.
These lines carry a vast array of goods, including agricultural products, manufactured goods, minerals, and energy resources. The movement of these commodities through Arizona’s rail network is critical to the state’s economy, contributing significantly to its industrial and agricultural sectors.
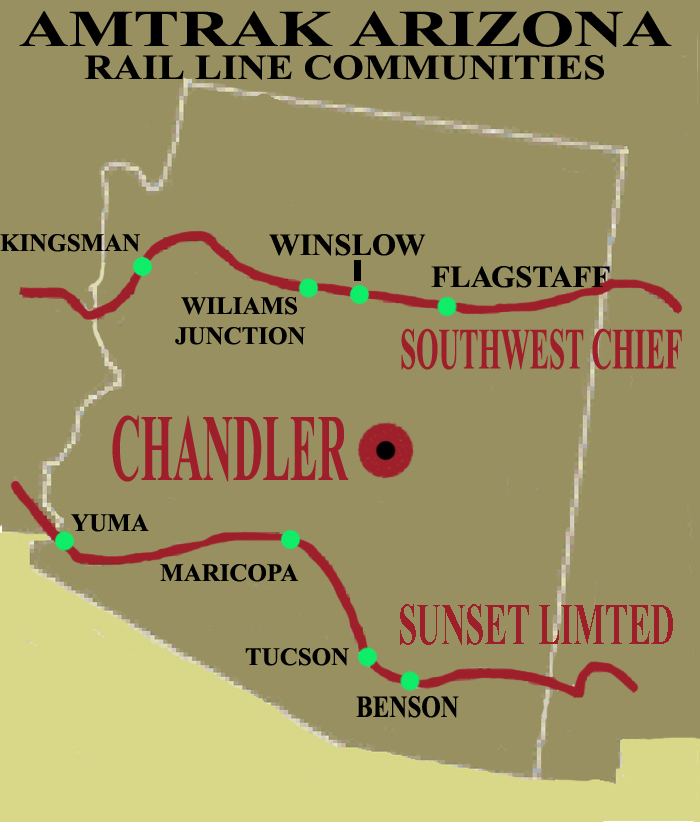
Beyond freight, the rail network also plays a vital role in passenger transportation. The Amtrak Southwest Chief, a long-distance passenger rail line, connects Chicago to Los Angeles with a stop in Flagstaff, Arizona. This line provides a scenic and convenient option for travelers seeking to experience the beauty of the American Southwest.
Additionally, the state is home to several commuter rail lines, including the Valley Metro Rail in the Phoenix metropolitan area, which provides efficient and reliable transportation for commuters and visitors alike.
Navigating the Rail Map: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the intricate layout of Arizona’s rail network can be daunting, but with a little guidance, it becomes a fascinating journey of discovery. The following sections provide a comprehensive overview of the key rail lines, their routes, and their significance in shaping Arizona’s landscape and economy.
1. Freight Rail Lines:
- BNSF Railway: One of the largest freight railroads in North America, BNSF operates a vast network of lines across Arizona, connecting major cities like Phoenix, Tucson, and Yuma to key transportation hubs throughout the country. Its lines primarily serve industrial centers and agricultural regions, facilitating the movement of goods like minerals, agricultural products, and manufactured goods.
- Union Pacific Railroad: Another major player in the freight rail industry, Union Pacific operates a network of lines that traverse Arizona from north to south, connecting the state to major markets in California, Texas, and beyond. The line carries a wide range of commodities, including manufactured goods, agricultural products, and energy resources.
- Arizona Rail Lines: This regional railroad operates a network of lines primarily serving the state’s industrial and agricultural sectors. Its lines connect major cities like Phoenix, Tucson, and Yuma, facilitating the movement of goods within Arizona and to neighboring states.
2. Passenger Rail Lines:
- Amtrak Southwest Chief: This long-distance passenger rail line connects Chicago to Los Angeles, traversing the heart of the American Southwest. The line offers a scenic and comfortable journey, passing through picturesque landscapes and historic towns. Passengers can enjoy stunning views of the Arizona desert, towering mountains, and vibrant cities.
- Valley Metro Rail: This commuter rail line operates in the Phoenix metropolitan area, providing efficient and reliable transportation for commuters and visitors alike. The line connects major destinations in the city, including downtown Phoenix, Tempe, and Mesa, offering a convenient alternative to driving.
3. Historic Rail Lines:
- Prescott and Phoenix Railway: This historic line, established in the late 19th century, connected the bustling mining town of Prescott to the growing city of Phoenix. The line played a crucial role in the development of both cities, facilitating the transportation of goods and people. Today, the line is no longer operational, but its legacy lives on in the form of preserved historic buildings and landmarks.
4. The Importance of Rail in Arizona’s Economy:
Arizona’s rail network is a vital component of the state’s economy, contributing significantly to its industrial, agricultural, and tourism sectors.
- Industrial Sector: The efficient movement of goods through the state’s rail network is crucial for Arizona’s manufacturing and industrial sectors. Factories, manufacturing plants, and distribution centers rely on rail for the transportation of raw materials, finished goods, and components. The rail network’s ability to transport heavy and bulky goods efficiently makes it a vital asset for these industries.
- Agricultural Sector: Arizona is a major agricultural producer, with crops like cotton, citrus fruits, and vegetables being grown in vast fields across the state. The rail network plays a crucial role in transporting these agricultural products to markets across the country and beyond. The efficiency and reliability of rail transportation ensure that farmers can transport their produce to consumers quickly and efficiently.
- Tourism Sector: The Amtrak Southwest Chief, with its scenic route through the Arizona desert, attracts tourists seeking to experience the beauty of the American Southwest. The line connects major tourist destinations like Flagstaff, known for its proximity to the Grand Canyon National Park, to major cities like Chicago and Los Angeles, making it a convenient and enjoyable way to explore the state.
FAQs: Delving Deeper into Arizona’s Rail Network
1. What are the major freight rail lines in Arizona?
The major freight rail lines in Arizona are BNSF Railway, Union Pacific Railroad, and Arizona Rail Lines. These lines connect the state to major markets across the United States and Mexico, carrying a vast array of goods, including agricultural products, manufactured goods, minerals, and energy resources.
2. How does the rail network contribute to Arizona’s economy?
Arizona’s rail network plays a vital role in the state’s economy, contributing significantly to its industrial, agricultural, and tourism sectors. The efficient movement of goods through the rail network is crucial for the state’s manufacturing and industrial sectors, while the transportation of agricultural products is essential for Arizona’s farmers. The Amtrak Southwest Chief, with its scenic route through the Arizona desert, attracts tourists seeking to experience the beauty of the American Southwest.
3. Are there any passenger rail lines in Arizona?
Yes, Arizona is served by the Amtrak Southwest Chief, a long-distance passenger rail line connecting Chicago to Los Angeles with a stop in Flagstaff, Arizona. Additionally, the state is home to several commuter rail lines, including the Valley Metro Rail in the Phoenix metropolitan area.
4. What is the history of rail in Arizona?
The story of Arizona’s rail network begins in the late 19th century, during the era of westward expansion and the development of the American Southwest. The arrival of the railroad transformed the state, opening up new possibilities for commerce, trade, and settlement. The Southern Pacific Railroad established its presence in Arizona in the 1870s, followed by the Santa Fe Railway. The development of new lines, including the Prescott and Phoenix Railway, and the construction of the Roosevelt Dam solidified the importance of rail in Arizona’s growth.
5. What are the future plans for rail in Arizona?
The future of rail in Arizona is promising, with ongoing efforts to expand and improve the state’s rail network. There are plans to extend the Valley Metro Rail, expand freight capacity, and explore the potential for high-speed rail lines. These initiatives aim to further enhance the role of rail in Arizona’s economy and transportation infrastructure.
Tips for Utilizing Arizona’s Rail Network:
- Plan your route: Before embarking on a rail journey, it’s crucial to plan your route carefully. Consider your destination, the available rail lines, and the schedule of train services.
- Check for updates: Rail schedules and routes can change, so it’s essential to check for updates before your journey. You can find this information on the websites of the relevant rail operators, such as Amtrak and Valley Metro.
- Book your tickets in advance: To secure your seat on a train, especially during peak seasons, it’s advisable to book your tickets in advance. This will also help you avoid potential delays and ensure a smooth journey.
- Explore the scenic routes: Arizona’s rail network offers breathtaking views of the state’s diverse landscapes. Take advantage of the journey to admire the desert scenery, towering mountains, and vibrant cities.
- Consider the environmental benefits: Rail travel is a more environmentally friendly mode of transportation compared to air travel. Opting for rail reduces your carbon footprint and promotes sustainable travel.
Conclusion: A Vital Network for Arizona’s Future
Arizona’s rail network is a testament to the state’s rich history, its economic vitality, and its commitment to sustainable transportation. From the historic lines that shaped the state’s development to the modern freight and passenger lines that connect Arizona to the world, the rail network plays a vital role in shaping the state’s future. As Arizona continues to grow and evolve, the rail network will remain a crucial component of its transportation infrastructure, facilitating the movement of goods and people, and contributing to the state’s economic prosperity.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Arizona’s Tracks: A Comprehensive Guide to the State’s Rail Network. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!