Demystifying the RD Eligibility Map: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Research and Development Tax Credits
Related Articles: Demystifying the RD Eligibility Map: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Research and Development Tax Credits
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Demystifying the RD Eligibility Map: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Research and Development Tax Credits. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Demystifying the RD Eligibility Map: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Research and Development Tax Credits

The Research and Development (R&D) tax credit, a powerful tool for businesses engaged in innovative activities, is often shrouded in complexity. One of the most crucial aspects of navigating this credit is understanding the RD eligibility map, which outlines the specific activities that qualify for tax benefits. This guide aims to demystify this map, providing a comprehensive understanding of its intricacies and highlighting its significance for businesses across various industries.
Defining the Scope of Qualifying Activities
The RD eligibility map serves as a roadmap, guiding businesses through the maze of activities that can potentially qualify for tax credits. It defines the boundaries of what constitutes "qualified research" for the purpose of claiming these benefits. While the specific details may vary slightly depending on the jurisdiction, the core principles remain consistent.
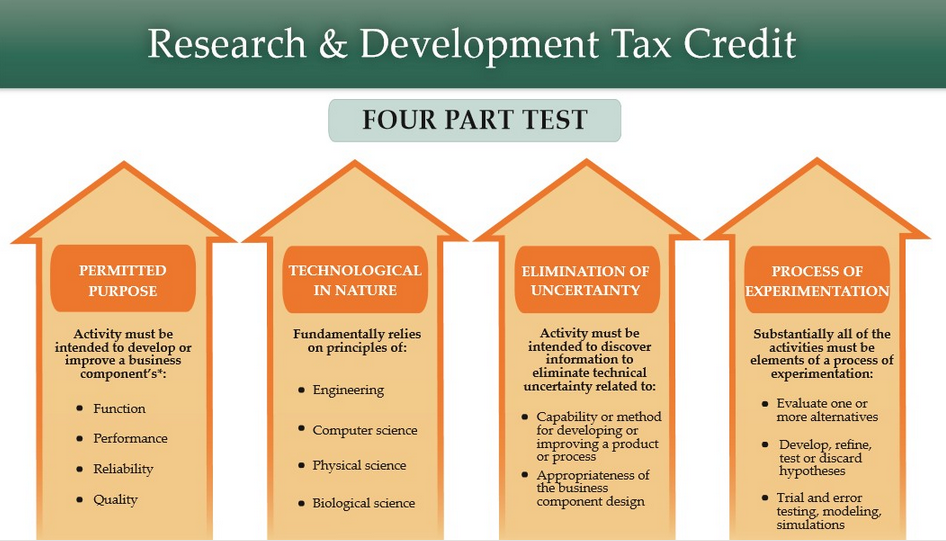
The Four-Part Test for Qualifying Research:
At its core, the RD eligibility map hinges on a four-part test, designed to ensure that the activities undertaken by a business genuinely contribute to the advancement of knowledge and technology. These four parts are:
- New or Improved Products or Processes: The research must be undertaken to develop a new product or process, or to significantly improve an existing one. This improvement must be substantial, not merely incremental.
- Technological Uncertainty: The research must involve overcoming technological uncertainty. This means that the outcome of the research is not readily known or predictable.
- Process of Experimentation: The research must be conducted through a systematic process of experimentation, analysis, and evaluation. This implies a structured approach to testing and refining ideas.
- Development of a Useful Product or Process: The research must ultimately lead to the development of a product or process that is useful in the business’s field. This signifies that the research has practical applications and contributes to the business’s core operations.
Key Considerations for Applying the Four-Part Test:
- The "New or Improved" Criterion: This criterion emphasizes the need for innovation and advancement. Simple modifications or routine improvements generally do not qualify.
- Technological Uncertainty: The research must address a genuine technological challenge, not merely a business or marketing problem.
- Process of Experimentation: This criterion emphasizes the scientific method and the systematic approach to research.
- Useful Product or Process: The research must ultimately result in a tangible output that contributes to the business’s objectives.
Beyond the Four-Part Test: Additional Considerations
While the four-part test forms the foundation of the RD eligibility map, certain additional considerations play a crucial role in determining the applicability of the tax credit. These include:
- The Business’s Primary Trade or Business: The research must be conducted in connection with the business’s primary trade or business. This ensures that the research is directly relevant to the company’s core operations.
- The Business’s Internal Research: The research can be conducted by the business’s own employees or by third-party contractors. However, the business must retain control over the research and its outcomes.
- The Business’s Internal Documentation: Maintaining detailed records of the research activities, including the methodologies, results, and expenses, is crucial for substantiating the claim for tax credits.
Navigating the Complexities: A Detailed Look at Specific Activities
Understanding the broad principles of the RD eligibility map is essential, but it’s equally important to delve into the specific activities that commonly qualify for tax credits. These activities can be categorized broadly as follows:
1. Research and Development in Manufacturing:
- New Product Development: Developing entirely new products, such as innovative consumer goods, medical devices, or advanced materials.
- Process Improvement: Enhancing existing manufacturing processes to increase efficiency, reduce costs, or improve product quality.
- Materials Science: Exploring new materials with improved properties, such as durability, strength, or conductivity.
- Engineering Design: Optimizing product designs for performance, functionality, and cost-effectiveness.
2. Research and Development in Software and Technology:
- Software Development: Creating new software applications, algorithms, or platforms.
- Data Analytics: Developing innovative data analysis techniques and algorithms to extract valuable insights.
- Artificial Intelligence: Researching and developing AI-powered solutions for various applications.
- Cybersecurity: Enhancing cybersecurity systems and protocols to protect sensitive information.
3. Research and Development in Healthcare:
- Pharmaceutical Research: Developing new drugs and treatments for various diseases.
- Medical Device Development: Creating innovative medical devices for diagnosis, treatment, or rehabilitation.
- Biotechnology Research: Exploring new biological processes and applications in medicine and healthcare.
- Clinical Trials: Conducting clinical trials to evaluate the safety and efficacy of new drugs and treatments.
4. Research and Development in Agriculture:
- Crop Improvement: Developing new crop varieties with increased yield, disease resistance, or improved nutritional value.
- Animal Breeding: Improving animal breeds for productivity, disease resistance, or enhanced product quality.
- Sustainable Agriculture: Exploring environmentally friendly agricultural practices to reduce environmental impact and enhance resource efficiency.
5. Research and Development in Energy and Environmental Technology:
- Renewable Energy: Developing new technologies for harnessing renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, or geothermal.
- Energy Efficiency: Enhancing energy efficiency in buildings, transportation, and industrial processes.
- Environmental Remediation: Developing technologies for cleaning up pollution and restoring contaminated sites.
6. Research and Development in Aerospace and Defense:
- Aircraft Design: Developing new aircraft designs with improved performance, efficiency, and safety.
- Space Exploration: Researching and developing technologies for space exploration, such as spacecraft design and propulsion systems.
- Defense Technology: Developing new weapons systems, defense technologies, and military equipment.
The RD Eligibility Map: A Powerful Tool for Business Growth
Understanding the RD eligibility map is crucial for businesses seeking to leverage the benefits of the R&D tax credit. It provides a clear framework for identifying qualifying activities and maximizing the potential for tax savings. By carefully analyzing their research and development efforts, businesses can effectively claim the tax credits they deserve, thereby fostering innovation and driving growth.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about the RD Eligibility Map:
1. What is the difference between "basic research" and "applied research" for the purpose of the RD eligibility map?
- Basic Research: Focuses on fundamental scientific principles and knowledge without immediate commercial applications. It often involves exploring new theories and understanding natural phenomena.
- Applied Research: Aims to solve specific practical problems or develop new technologies with direct commercial applications. It builds upon basic research findings to create tangible solutions.
2. Does the RD eligibility map apply to all industries?
- The RD eligibility map applies to a wide range of industries, including manufacturing, technology, healthcare, agriculture, energy, and defense. However, the specific activities that qualify for tax credits may vary depending on the industry.
3. Can a small business claim the R&D tax credit?
- Yes, small businesses are eligible for the R&D tax credit. The credit is available to businesses of all sizes that meet the eligibility criteria.
4. How do I document my research and development activities for the purpose of claiming the R&D tax credit?
- Maintain detailed records of your research activities, including:
- The objectives of the research
- The methodologies used
- The results obtained
- The expenses incurred
- The personnel involved
- The dates of the research activities
5. What are the potential benefits of claiming the R&D tax credit?
- Tax Savings: The R&D tax credit can significantly reduce a business’s tax liability, providing valuable financial relief.
- Increased Investment: The tax savings can be reinvested into further research and development, fostering innovation and growth.
- Competitive Advantage: By investing in R&D, businesses can gain a competitive edge by developing new products, processes, or technologies.
Tips for Maximizing the Benefits of the RD Eligibility Map:
- Consult with a Tax Professional: Engage with a tax professional specializing in R&D tax credits to ensure accurate application of the eligibility criteria.
- Document Thoroughly: Maintain comprehensive records of your research activities to provide strong evidence for your claim.
- Stay Updated on Regulations: Keep abreast of any changes or updates to the R&D tax credit regulations.
- Explore All Qualifying Activities: Carefully assess your research and development activities to identify all potential areas for claiming tax credits.
- Consider Third-Party Assistance: If necessary, consider engaging with third-party consultants or experts to assist with your R&D tax credit claim.
Conclusion:
The RD eligibility map is a critical tool for businesses seeking to unlock the benefits of the R&D tax credit. By understanding the criteria for qualifying activities and meticulously documenting their research and development efforts, businesses can maximize their tax savings and fuel innovation. The R&D tax credit provides a valuable incentive for businesses to invest in research and development, driving economic growth and technological advancement.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Demystifying the RD Eligibility Map: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Research and Development Tax Credits. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!