Demystifying Guyana’s Regions: A Comprehensive Guide to the Administrative Divisions
Related Articles: Demystifying Guyana’s Regions: A Comprehensive Guide to the Administrative Divisions
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Demystifying Guyana’s Regions: A Comprehensive Guide to the Administrative Divisions. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Demystifying Guyana’s Regions: A Comprehensive Guide to the Administrative Divisions
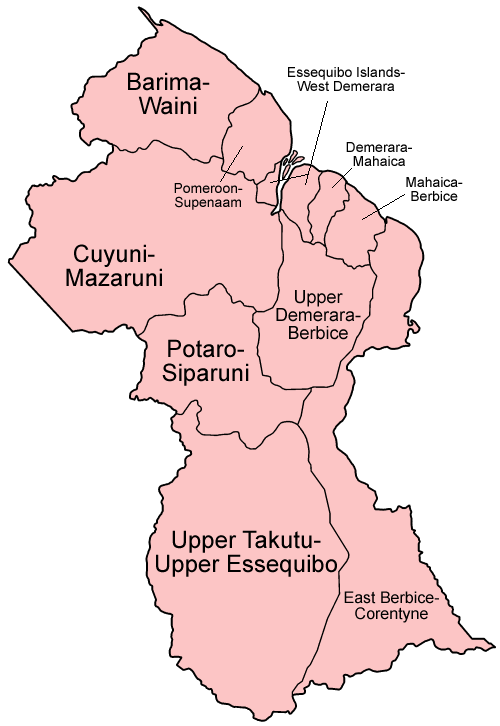
Guyana, a vibrant nation nestled on the northeastern coast of South America, is renowned for its lush rainforests, diverse wildlife, and rich cultural heritage. Understanding the country’s administrative divisions, known as regions, is crucial for appreciating its unique geography, economic activities, and cultural tapestry. This article provides a detailed exploration of Guyana’s ten regions, highlighting their distinct characteristics, key industries, and cultural nuances.
A Glimpse into Guyana’s Administrative Structure
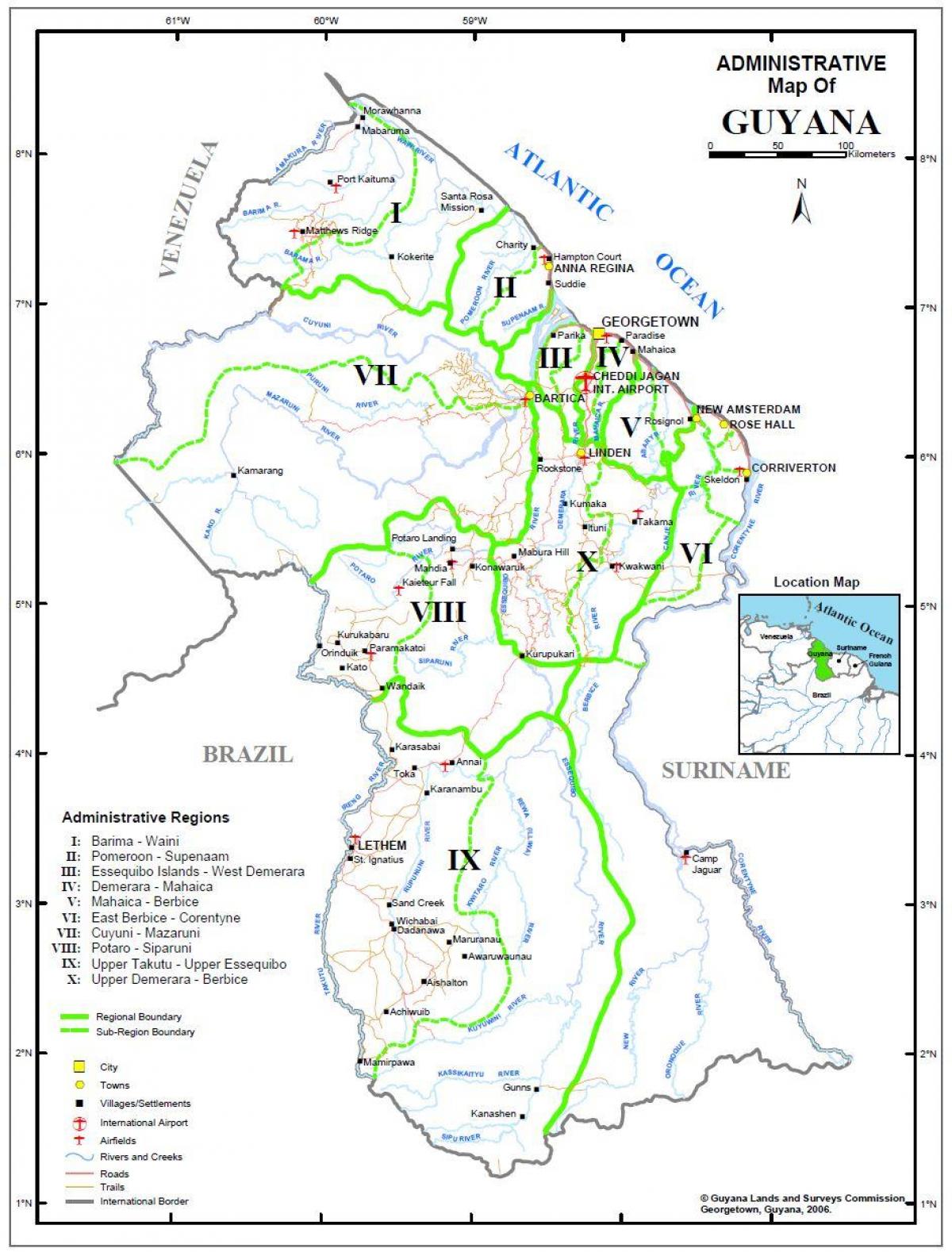
Guyana’s administrative structure is based on a decentralized system, with ten regions encompassing the entire country. Each region is governed by a Regional Democratic Council (RDC), responsible for managing local affairs and ensuring efficient delivery of public services. This regional framework empowers communities, fosters local development, and promotes a sense of regional identity.
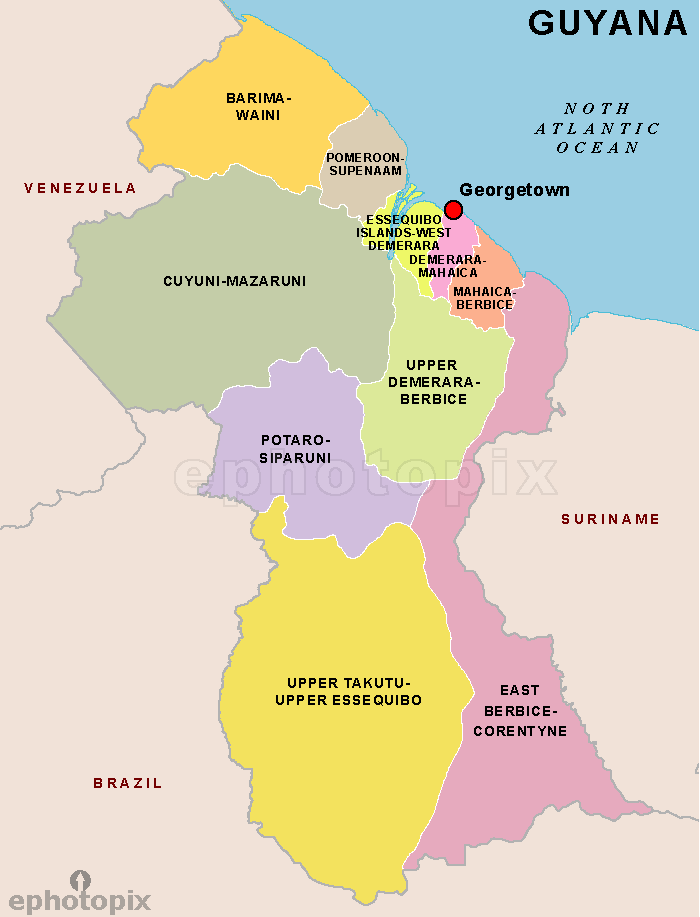
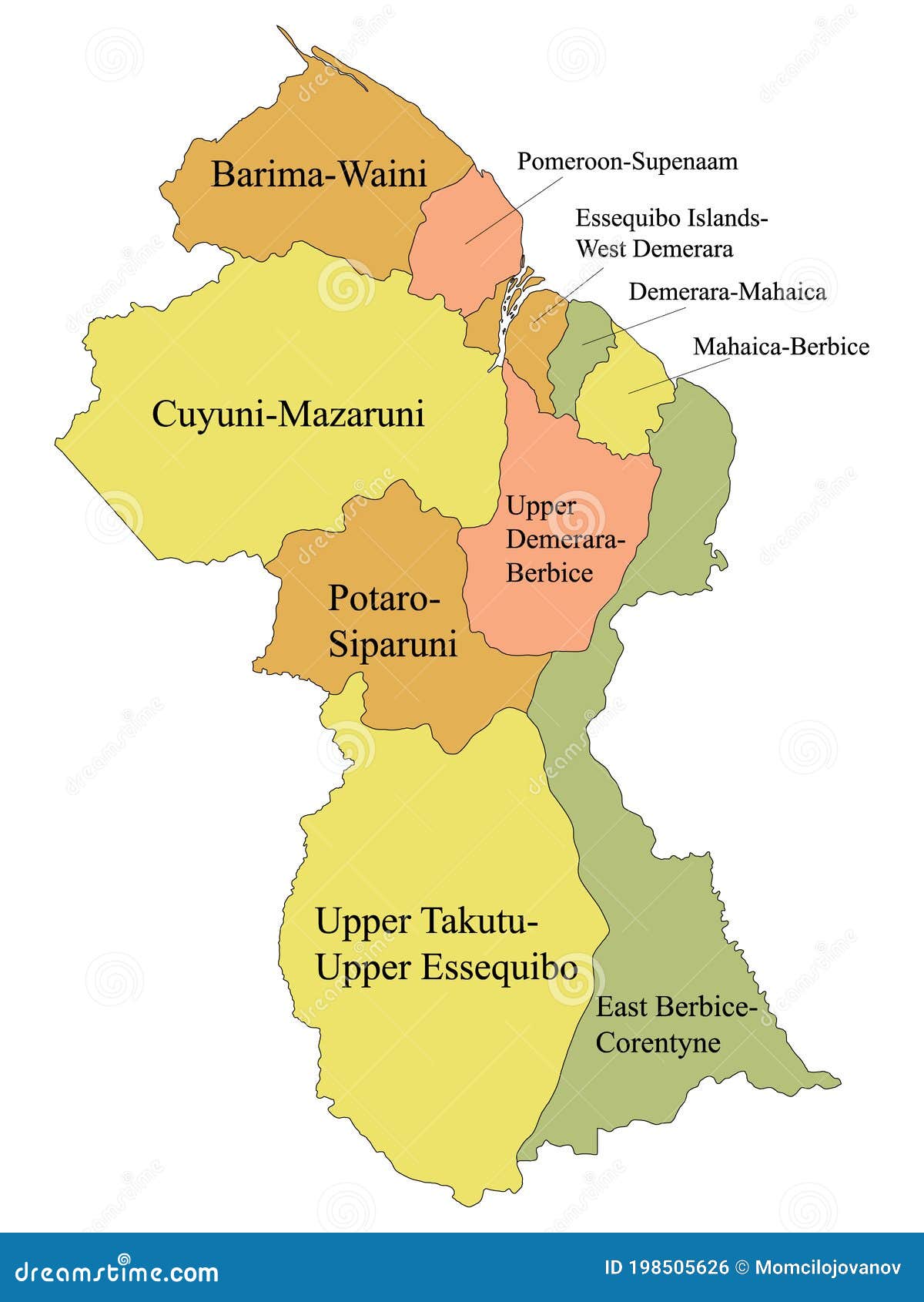
Region 1: Barima-Waini
Located in the northwest, Barima-Waini is Guyana’s largest region by land area. Characterized by dense rainforests and vast savannahs, it is sparsely populated and home to indigenous communities like the Arawaks and Caribs. The region’s economy relies heavily on mining, particularly gold and diamonds. The majestic Kaieteur Falls, one of the world’s tallest waterfalls, lies within Region 1, attracting tourists and nature enthusiasts alike.
Region 2: Pomeroon-Supenaam
Nestled along the Essequibo River, Region 2 is known for its fertile agricultural lands and vibrant fishing industry. Rice cultivation is a major economic activity, while fishing communities thrive along the coast. The region also boasts beautiful beaches, including the popular Anna Regina Beach, attracting domestic and international visitors.
Region 3: Essequibo Islands-West Demerara
Region 3 encompasses the bustling city of Georgetown, Guyana’s capital and largest city. It is the country’s economic hub, housing key government institutions, businesses, and industries. The region also includes the historic Leguan and Wakenaam Islands, known for their agricultural produce and idyllic landscapes.
Region 4: Demerara-Mahaica
Region 4, situated on the Demerara River, is home to a diverse population and a thriving agricultural sector. It is renowned for its sugarcane plantations, rice fields, and fruit farms. The region also boasts the scenic Mahaica River, offering opportunities for fishing and eco-tourism.
Region 5: Mahaica-Berbice
Region 5, located on the eastern coast, is known for its fertile lands and significant sugar cane production. It also boasts a vibrant fishing industry and a growing tourism sector, with attractions like the historic Fort Wellington and the picturesque Mahaica Creek.
Region 6: East Berbice-Corentyne
Region 6, Guyana’s second-largest region by population, is situated on the Corentyne River and is known for its diverse agricultural activities, including rice, sugarcane, and livestock farming. The region also boasts a rich cultural heritage, with a significant Indian population and vibrant festivals.
Region 7: Cuyuni-Mazaruni
Region 7, located in the heart of Guyana, is a vast region characterized by dense rainforests, rugged mountains, and vast savannahs. It is a major gold-mining region and home to indigenous communities like the Wapishana and Patamona. The region also boasts the majestic Mount Roraima, a table-top mountain revered by indigenous peoples.
Region 8: Potaro-Siparuni
Region 8, situated in the south-central part of Guyana, is a sparsely populated region dominated by the Potaro River and the Kaieteur National Park. The region is home to indigenous communities like the Makushi and the Wai Wai and is renowned for its pristine rainforest landscapes and exceptional biodiversity.
Region 9: Upper Takutu-Upper Essequibo
Region 9, located in the southwest of Guyana, is Guyana’s largest region and is home to the country’s highest peak, Mount Ayanganna. It is a sparsely populated region characterized by vast savannahs, dense rainforests, and the majestic Rupununi River. The region is home to diverse indigenous communities, including the Wai Wai, Macushi, and Wapishana.
Region 10: Upper Demerara-Berbice
Region 10, located in the south-central part of Guyana, is known for its bauxite mining industry and the scenic Linden Town, a historic mining center. The region also boasts the beautiful Essequibo River, offering opportunities for fishing and eco-tourism.
The Importance of Guyana’s Regions
Understanding the distinct characteristics of Guyana’s regions is crucial for various reasons:
- Economic Development: Each region possesses unique resources and industries, contributing significantly to Guyana’s overall economic growth. By understanding regional strengths, policymakers can implement targeted development strategies to maximize economic potential.
- Infrastructure Development: Regional mapping provides valuable insights into infrastructure needs, enabling the government to prioritize projects and allocate resources effectively. This ensures equitable distribution of services and promotes sustainable development across the country.
- Cultural Preservation: Guyana’s regions are home to diverse indigenous communities, each with unique cultural traditions and languages. Recognizing the importance of regional identities fosters cultural preservation and promotes a sense of national unity.
- Tourism Development: Guyana’s diverse regions offer a plethora of tourist attractions, from pristine rainforests and waterfalls to vibrant cultural experiences. Regional mapping helps promote tourism development, attracting visitors and generating economic benefits for local communities.
- Disaster Preparedness: Understanding regional vulnerabilities to natural disasters like floods and droughts is crucial for effective disaster preparedness. Regional mapping helps identify areas at risk, facilitating timely interventions and minimizing the impact of disasters.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the largest region in Guyana by land area?
A: Barima-Waini (Region 1) is the largest region by land area.
Q: Which region is home to Guyana’s capital city, Georgetown?
A: Essequibo Islands-West Demerara (Region 3) encompasses Georgetown, Guyana’s capital and largest city.
Q: Which region is known for its significant gold mining activities?
A: Cuyuni-Mazaruni (Region 7) is a major gold-mining region, contributing significantly to Guyana’s economy.
Q: Which region boasts the majestic Kaieteur Falls?
A: Barima-Waini (Region 1) is home to the breathtaking Kaieteur Falls, one of the world’s tallest waterfalls.
Q: Which region is known for its diverse indigenous communities and pristine rainforest landscapes?
A: Potaro-Siparuni (Region 8) is renowned for its exceptional biodiversity and indigenous communities, offering a unique glimpse into Guyana’s cultural heritage.
Tips for Exploring Guyana’s Regions
- Research Thoroughly: Before embarking on a journey to Guyana, research the specific region you plan to visit. Understand its unique features, attractions, and cultural nuances to enhance your experience.
- Engage with Locals: Interact with local communities to gain a deeper understanding of their culture, traditions, and way of life. This fosters cultural exchange and provides valuable insights into the region.
- Respect Local Customs: Be mindful of local customs and traditions, showing respect for the indigenous communities and their cultural heritage.
- Support Local Businesses: Patronize local businesses and vendors, contributing to the local economy and supporting sustainable development.
- Protect the Environment: Be mindful of the environment and practice responsible tourism, minimizing your impact on natural ecosystems and preserving the beauty of Guyana’s regions.
Conclusion
Guyana’s ten regions are a testament to the country’s diverse geography, rich cultural heritage, and dynamic economy. Understanding the distinct characteristics of each region provides a deeper appreciation for the country’s unique attributes and fosters a sense of national unity. By embracing regional diversity and promoting sustainable development, Guyana can unlock its full potential and create a brighter future for all its citizens.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Demystifying Guyana’s Regions: A Comprehensive Guide to the Administrative Divisions. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!