A Global Parched Landscape: Understanding the World Map of Drought
Related Articles: A Global Parched Landscape: Understanding the World Map of Drought
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Global Parched Landscape: Understanding the World Map of Drought. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: A Global Parched Landscape: Understanding the World Map of Drought
- 2 Introduction
- 3 A Global Parched Landscape: Understanding the World Map of Drought
- 3.1 Mapping the Global Drought Crisis: A Visual Representation
- 3.2 The Multifaceted Drivers of Drought: A Complex Interplay of Factors
- 3.3 The Ripple Effects of Drought: A Multifaceted Impact on Life
- 3.4 Mitigating Drought: A Collaborative Approach to Resilience
- 3.5 FAQs on Drought and its Impact:
- 3.6 Tips for Drought Preparedness and Mitigation:
- 3.7 Conclusion: A Global Call for Action
- 4 Closure
A Global Parched Landscape: Understanding the World Map of Drought
Drought, a silent and insidious threat, casts a long shadow across the globe. It is not a singular event but a complex phenomenon, characterized by prolonged periods of below-average precipitation, leading to a depletion of water resources and impacting ecosystems, agriculture, and human lives. This article aims to shed light on the global extent of drought, exploring its causes, consequences, and potential solutions.
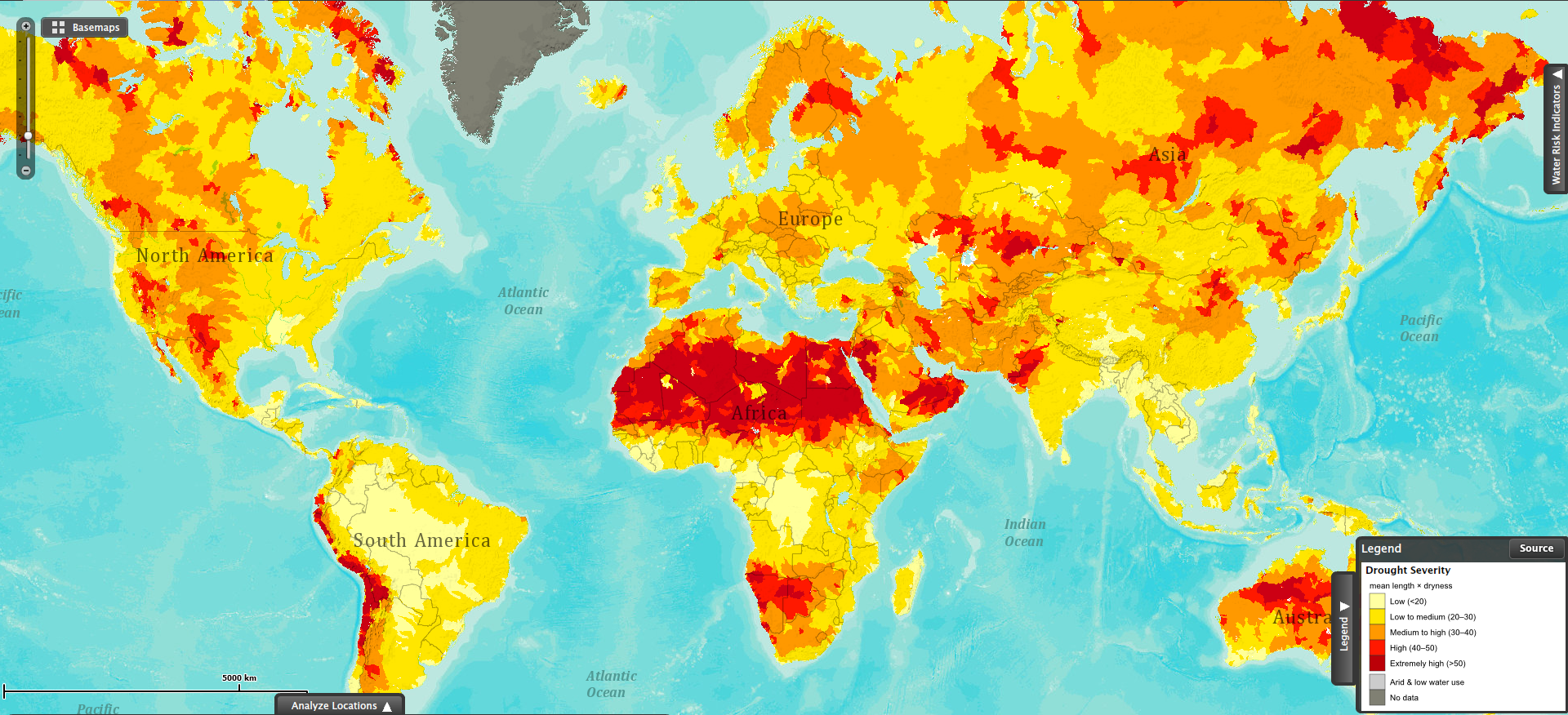
Mapping the Global Drought Crisis: A Visual Representation
A world map depicting drought severity provides a stark visual representation of the crisis. Regions painted in shades of red and orange highlight areas experiencing severe to extreme drought conditions, while those in yellow and green indicate moderate to minimal drought. This map serves as a critical tool for understanding the global distribution of drought and its potential impact on various regions.
The Multifaceted Drivers of Drought: A Complex Interplay of Factors
Drought is not solely a result of insufficient rainfall. It arises from a complex interplay of factors, including:
1. Climate Change: The changing climate, characterized by rising global temperatures and altered precipitation patterns, is a significant driver of drought. Increased evaporation rates due to higher temperatures exacerbate water scarcity, further intensifying drought conditions.
2. Natural Climate Variability: The Earth’s climate is inherently variable, with natural cycles like El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) influencing rainfall patterns. These cycles can lead to prolonged periods of dryness, contributing to drought development.
3. Human Activities: Human activities, particularly unsustainable land use practices and water management strategies, can exacerbate drought conditions. Deforestation, for instance, reduces evapotranspiration, leading to drier soils and increased runoff. Over-extraction of groundwater for irrigation can deplete aquifers, further intensifying water scarcity.
The Ripple Effects of Drought: A Multifaceted Impact on Life
The consequences of drought are far-reaching and multifaceted, impacting:
1. Agriculture: Drought severely impacts agricultural productivity, leading to crop failures, reduced livestock yields, and food insecurity. This can trigger economic hardship, social unrest, and even mass migration.
2. Water Resources: Drought depletes water resources, leading to water shortages, reduced hydropower generation, and conflicts over access to water. It can strain existing infrastructure, impacting drinking water supply and sanitation.
3. Ecosystems: Drought disrupts ecosystems, leading to loss of biodiversity, increased wildfire risk, and soil degradation. It can alter the delicate balance of natural habitats, impacting wildlife populations and ecological stability.
4. Human Health: Drought can lead to malnutrition, dehydration, and the spread of waterborne diseases. It can also exacerbate existing health problems and lead to increased mortality rates, particularly among vulnerable populations.
Mitigating Drought: A Collaborative Approach to Resilience
Addressing drought requires a multifaceted approach, involving:
1. Climate Change Mitigation: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions is crucial for mitigating the impacts of climate change on drought. This involves transitioning to renewable energy sources, promoting energy efficiency, and adopting sustainable land management practices.
2. Water Conservation: Implementing water conservation measures is essential for managing drought. This includes improving irrigation efficiency, reducing water waste in households and industries, and promoting rainwater harvesting.
3. Early Warning Systems: Developing and implementing effective early warning systems can help anticipate and prepare for drought. These systems can provide timely information on drought conditions, allowing for proactive measures to mitigate its impacts.
4. Drought-Resistant Crops: Research and development of drought-resistant crops are crucial for ensuring food security in drought-prone regions. This involves breeding crops with enhanced water use efficiency and tolerance to arid conditions.
5. Water Management Strategies: Effective water management strategies are essential for allocating water resources efficiently and equitably. This includes implementing water pricing mechanisms, promoting water-sharing agreements, and managing water infrastructure for optimal utilization.
6. Community Engagement: Engaging communities in drought preparedness and mitigation efforts is crucial. This involves raising awareness about drought risks, promoting best practices for water conservation, and empowering communities to participate in decision-making processes.
FAQs on Drought and its Impact:
1. What is the difference between a drought and a dry spell?
A dry spell is a short-term period of low precipitation, typically lasting a few weeks or months. A drought, however, is a prolonged period of below-average precipitation, extending for months or even years, leading to significant water scarcity.
2. How is drought measured?
Drought is measured using various indices that consider factors like rainfall, soil moisture, streamflow, and groundwater levels. The Palmer Drought Severity Index (PDSI) and the Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) are commonly used indices for drought monitoring.
3. What are the most drought-prone regions in the world?
Regions like the Sahel in Africa, the Middle East, and parts of Australia and the United States are particularly prone to drought. These regions are characterized by arid or semi-arid climates and are often affected by recurrent droughts.
4. How does drought affect the economy?
Drought can have significant economic impacts, leading to crop failures, reduced livestock yields, and increased food prices. It can also disrupt industries reliant on water resources, such as agriculture, tourism, and hydropower generation.
5. What are the long-term consequences of drought?
Long-term drought can have devastating consequences, leading to land degradation, desertification, and irreversible loss of biodiversity. It can also trigger social unrest, mass migration, and conflict over scarce resources.
6. What are the potential solutions to drought?
Addressing drought requires a multi-pronged approach, including climate change mitigation, water conservation, early warning systems, drought-resistant crops, and effective water management strategies.
Tips for Drought Preparedness and Mitigation:
1. Conserve Water: Implement water-saving measures in your household and garden, such as using low-flow showerheads, fixing leaks, and watering lawns efficiently.
2. Support Sustainable Agriculture: Choose food products from farms that practice sustainable water management and promote responsible land use.
3. Educate Yourself and Others: Learn about drought risks and mitigation strategies, and share this knowledge with your community.
4. Advocate for Policy Changes: Support policies that promote water conservation, climate change mitigation, and sustainable resource management.
5. Be Prepared for Drought: Develop a household drought preparedness plan, including a plan for water rationing and alternative water sources.
Conclusion: A Global Call for Action
Drought is a global challenge that requires collective action. By understanding its causes, consequences, and potential solutions, we can work together to mitigate its impacts and build resilience in the face of this growing threat. Addressing drought is not just about protecting our environment and resources but also about ensuring the well-being and prosperity of future generations.
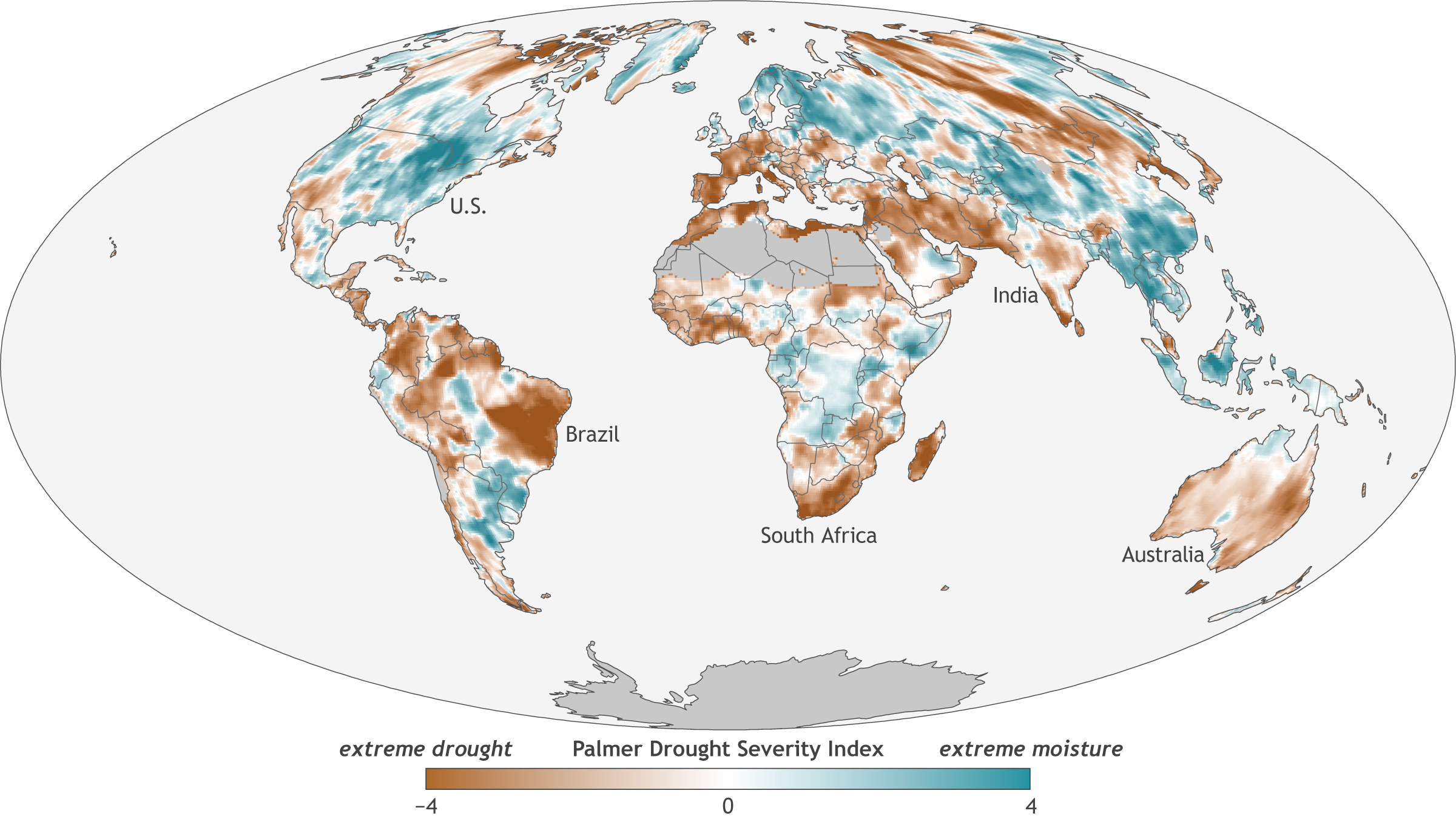



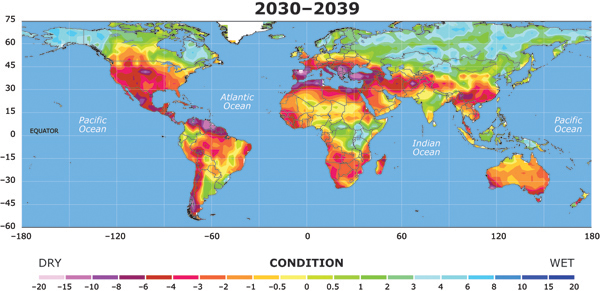



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Global Parched Landscape: Understanding the World Map of Drought. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!